From time immemorial, people have been faced with the burning of wood. And since then, wood has been used as the main type of fuel, which is used to heat various rooms and prepare food. Despite the variety of combustible substances, wood remains a common fuel in the 21st century, due to its low cost, availability and ease of handling. For its effective and safe use in stoves and fireplaces, it is necessary to possess some information about its physical and chemical characteristics.
Factors affecting combustion temperature
The maximum combustion temperature of wood depends on the species and can be achieved under the following conditions:
- the amount of moisture content is not more than 20%;
- a closed space is used for combustion;
- availability of oxygen in the required volume.
It is also possible to burn fresh firewood with a moisture content of 40 to 60%, while:
- raw firewood ignites only in a well-melted stove;
- heat transfer will decrease by 20-40%;
- there will be an increase in firewood consumption, approximately two times;
- soot will settle on the walls of the stove and chimney.

The efficiency of combustion will be significantly reduced due to the need for an increased temperature, which is used to evaporate water and burn tar in conifers. Under ideal conditions, beech and ash have the highest burning temperatures and poplar have the lowest. Beech, larch, oak and hornbeam are valuable wood species and are not used as fuel. In domestic conditions, birch and coniferous trees are used for burning wood in stoves, considering that they give the highest temperature during combustion.
Coal or wood?
Thoughtful choice of fuel will help maintain combustion over time. Coal is significantly ahead of wood here.
However, for the theory to work in practice, remember: your boiler must have a large firebox. Otherwise, the system may simply not have enough resources. And with good fuel, you will not be able to achieve the desired effect.
Calculation method
- Find out the power of the boiler (take the manufacturer's data from the equipment passport, taking into account the efficiency).
- Take into account the volume of the chamber and the actual volume of fuel loading. Here you need to take into account both the passport data and the real volume of fuel. When using firewood, it can, for example, be significantly reduced due to the nature of the installation. Due to the gaps between the wood, the value of the stacking factor reaches 0.35-0.5.
- Now you can proceed to the calculations.
Let's say you have a boiler with a capacity of 12 kW and efficiency = 70%. Its chamber volume is 33 liters. The firebox will be produced with wood with a density of 650 kg per 1 cubic meter.
With a volume of 0.033 cubic meters, the theoretical capacity of the furnace is 21 wood logs (650x0.033), practical - 8 (21 x 0.4)
It remains to calculate the calorific value of the bookmark. To do this, the amount of firewood should be multiplied by the calorie content (8x4200 kcal = 33600 kcal). This corresponds to 39 kW. This number must be multiplied by the efficiency of the equipment (39x0.7 = 27 kW), and the result obtained is divided by the power A simple calculation shows: real burning time your boiler long burning time is 2.25 hours.

Which wood burns hotter?
As already mentioned, wood is one of the most used fuels for heating homes outside the city. Considering that all firewood burns at different temperatures, you need to choose the ones that are better.The main condition for burning wood is the presence of oxygen, and this largely depends on the design of the stove. In addition, each wood has its own chemical composition and density. The denser the wood, the greater the heat transfer from it. Especially important for the greater heat transfer of wood during combustion? in addition to the density and the presence of oxygen, wood has moisture.


Dry wood burns better and generates more heat than raw wood. Therefore, after cutting, they are folded into woodpiles and dried under a canopy for a year. Everyone who has had a chance to heat the stove with wood has noticed that some of them burn brightly, giving off a lot of heat, while others smolder and heat the stove a little. Everything, it turns out, depends on the heat output of the firewood. According to this indicator, the most suitable species for burning in furnaces are birch, pine and aspen.
How to squeeze the maximum out of wood: 9 ways to prolong burning, increase heat transfer and reduce consumption
The same amount of wood can burn at different speeds and produce different amounts of heat.
Further in the article, there are ways to extend the burning time of firewood, increase their heat transfer and reduce consumption without significant costs.
Change the way you stack your firewood
Usually firewood is set on fire like this: they build a pyramid of logs, put paper, chips in the center and set it on fire. First, the chips flare up, and over time, the firewood itself. The disadvantage of this method is that you do not control the combustion. Firewood lights up all at once and completely, burns unevenly and quickly. When some of the logs burn out, you will throw in new ones, which will also quickly flare up and burn.
The burning time of firewood can be increased by changing the way they are placed in the firebox. For example:
- Lay the first bottom row of firewood.
- On top, lay the second row with an offset to the right or left by 5-10 cm to form a ledge. Lay the third and next rows on top.
- Place paper or wood chips at the edge with the tab and set them on fire.
Laying on the example of fuel briquettes. The briquettes do not ignite entirely, but burn evenly: the flame gradually moves from left to right. The firewood burns for a long time and generates a sufficient amount of heat.
Subtleties:
- Do not put firewood close to each other. Leave a small gap between them for air movement.
- The denser and drier the wood, the more evenly it burns and the easier it is to ignite.
Close the valve in time
The stronger the draft, the faster the wood burns. But when there is a lack of air, they burn poorly and form a lot of soot. The balance is important so that the minimum air necessary for combustion gets to the wood.
- Before lighting, open the heater damper to the maximum to ensure good draft for firewood.
- When the wood is on fire, start closing the valve gradually. If the wood starts to go out, open the latch slightly and increase the draft. Over time, you will find the optimal valve position.
The drier and denser the wood, the less air is required to burn it.
Use dense hardwood
At the cellular level, wood is made up of many empty cells with walls of woody matter. The density of the woody substance (walls) itself is the same for all types of wood, but the size of the cells is different.
The smaller the size of the cells, the higher the density of the wood and each of its square centimeters contains a lot of combustible woody substance. And vice versa: the larger the size of the cells, the lower the density of the tree. It contains a lot of air and little flammable woody substance.
Imagine a circle is 1 square centimeter of wood. In the first case, the cells are small and there are many walls between them. In the second case, the number of cells and walls is less, and the voids that are filled with air are more. The density of such wood is low.
What conclusions can be drawn:
- Less dense wood burns quickly. When wood burns, air is released, which fuels the combustion.The more air there is, the faster and less evenly the wood burns.
- Dense firewood generates more heat, since it contains more combustible wood matter per unit volume.
- Dense firewood leaves more coals that smolder for a long time. Soft woods hold their shape worse, crumble into small coals and quickly go out.
All wood is divided into three categories of density: small, medium, high.
| Density | Tree species |
| Low density 0.15 - 0.55 g / cm3 | Spruce, Willow, Aspen, Pine, Linden, Alder, Siberian Fir, Poplar |
| Average density 0.56 - 0.70 g / cm3 | Maple, Walnut, Birch, Cherry, Larch, Beech, Oak, Sycamore, Pear, Apple tree |
| High density 0.75 - 1.08 g / cm3 | Ash, Plum, Boxwood, Ebony persimmon, Acacia |
Prepare firewood in advance
Bring the wood to a warm room 2-3 days before lighting to increase its starting temperature.
The warmer the wood is initially, the:
- They spend less heat on their own heating and more on heating the room. You use heat better.
- The firewood achieves optimal combustion faster, which further increases its calorific value and reduces the amount of soot emitted. This is because the resin, creosote, tar, essential oils and other substances that are part of the wood do not burn at low temperatures and settle on the walls in the form of soot. And under optimal conditions, the combustion temperature is sufficient so that they burn out entirely and generate additional heat.
The difference between the combustion of "warm" and "cold" wood is immediately noticeable: cold wood emits a lot of smoke, which characterizes incomplete combustion. And warm dry firewood burns practically without smoke.
When the wood starts to burn in a cold firebox, then:
- part of the heat is spent on heating the firebox, and not heating the room (as in the previous paragraph).
- it is more difficult for them to flare up, since the warm air overcomes the resistance of the cold air in the chimney.
It is best to light the main firewood in a preheated firebox so that they do not waste extra energy on heating the firebox and chimney.
You can use the heat from the previous laying of firewood or pre-burn the prepared splinters and paper in the firebox.
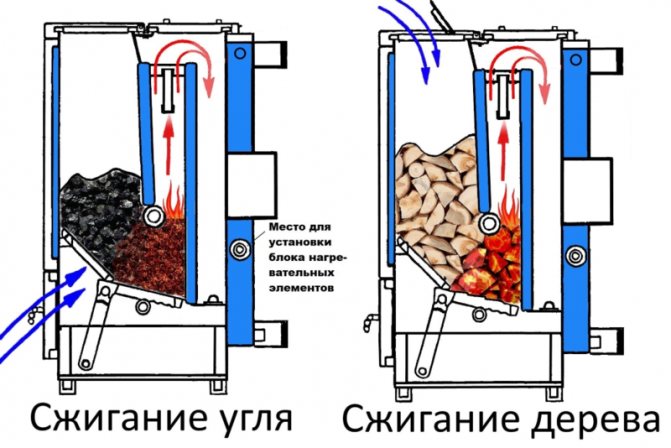
Use bottom combustion
There are two ways to burn wood: grate (bottom) and bottom (top).
Bottom burning is traditional, when air enters the wood from below and the flame gradually moves upward. With upper burning, air is supplied to the wood from above, the fire also burns at the top and gradually descends.
With hearth burning, the largest logs are stacked below, and smaller paper and firewood are placed on top.
Benefits:
- The completeness of wood combustion increases, due to which they generate more heat.
- You reduce the emission of volatiles that pollute the chimney with soot.
- This is a more environmentally friendly way of burning.
How to do it
For hearth burning, firewood is stacked in a pyramid: the most logs are put down, and the smaller ones up. At the very top, chips and paper are set on fire.
While wood chips and paper are burning, the firebox is warming up. Then the flame begins to descend and ignite the main firewood. At this point, the combustion temperature and the strength of the flame are sufficient for the volatile substances that make up the wood to start burning. Due to the completeness of combustion, firewood emit more heat, and due to uniform combustion, it burns for a long time and economically.
Do not allow an increased mode of burning firewood
There are three modes of wood burning: low, high and optimal.
In the reduced mode, the wood does not burn completely and form a lot of soot. With an increased amount, you waste firewood: some of the heat escapes through the chimney, since the heat exchanger and the room do not have time to take it off completely. This happens in two cases: you use too much wood or you supply a lot of air. It is necessary to reduce the volume of the bookmark or cravings.
The best option is when the wood burns in the optimal mode: not weak and not strong. The easiest way to determine the burning mode is to use the burning indicator, which shows the current mode in real time. If the temperature of the flue gases is more than 320 degrees, then the wood burns in an increased mode.
The combustion indicator in real time determines the temperature of the flue gases and the combustion mode
Change the volume of the bookmark of firewood from the temperature outside
The warmer it is outside, the less heat the building loses. Accordingly, he needs less firewood for heating. If you put the same amount of wood at 0˚C or -10˚C, then in the first case, you consume more wood than you need.
The combustion indicator allows you to monitor the combustion mode in real time and, over time, experimentally set the required amount of firewood, depending on the outside temperature.
Remove soot in a timely manner
Soot needs to be removed not only when the chimney is clogged and the draft has disappeared, but regularly. Soot not only impairs chimney draft, but also serves as thermal insulation. It covers the inner walls of the heater and the heat exchanger, which reduces their heat transfer. If soot is removed in a timely manner, the volume of firewood burned can be reduced without loss of heating power.
Obviously, but it's worth remembering: the wood must be dry. Wet wood ignites poorly, goes out quickly and emits 2-2.5 times less heat than dry wood.
Remember
- Stack the wood carefully so that it burns evenly and for a long time.
- Close the air damper in time. The minimum amount of air required for combustion should get to the wood.
- Heavy wood burns longer and leaves more long-emitting coals.
Use hard hardwoods: maple, walnut, birch, cherry, larch, beech, oak, sycamore, pear, apple - Bring the wood into the house 2-3 days before lighting it up and put it in the firebox an hour before lighting it up.
- Preheat the firebox with a small amount of torches.
- If you have a fireplace or stove, use hearth combustion.
- Maintain optimal combustion. If the wood burns too much, then some of the heat escapes into the chimney, and does not remain in the room.
- Change the volume of the firewood bookmark depending on the outside temperature.
- Remove soot in a timely manner. Soot acts as thermal insulation and reduces the heat output of the heater and heat exchanger.
- Firewood must be dry. Published by econet.ru
Subscribe to our VIBER channel!
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consumption - together we are changing the world! © econet
What is emitted when burning wood?
When wood burns, smoke is formed, consisting of solid particles (soot) and gaseous combustion products. They contain substances found in wood. The products released during the combustion of wood consist of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapor, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide, which is capable of burning further.


It is estimated that each kilogram of wood releases about 800 g of gaseous products and 200 g of coal during combustion. The composition of wood combustion products also depends on the conditions under which this process takes place. He can be:
- Incomplete - occurs when there is insufficient oxygen access. As a result of combustion, substances are released that are capable of burning again. These include: soot, carbon monoxide and various hydrocarbons.
- Full - occurs when there is sufficient oxygen supply. As a result of combustion, products are formed - carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, water vapor - which are no longer able to burn.
Can the burning time be extended?
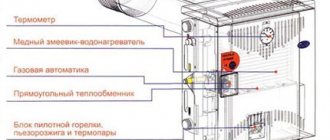
A number of users are interested in whether it is possible to influence the burning time without changing the fuel. Can! To do this, you need to reduce the flow of air into the system. The best way to solve the problem is automation, which, when the desired temperature is reached, allows the fan to work at a moderate speed, and the fuel does not burn intensively, but smolders.
Why is it necessary to automate, and experiments on turning the fan on and off, but not suitable? The fact is that when artificially regulating one press, it is important to be able to take control of all the others. And it is important that control was established both over the operating modes of the pumps and over the temperatures. And it is easiest to provide it precisely by means of equipment with automation.
Description of the combustion process
In the process of wood burning, several stages are noted:
- Warming up - occurs at a temperature of at least 150 degrees Celsius and in the presence of an external source of fire.
- Ignition - the required temperature is from 450 to 620 degrees Celsius, depending on the moisture content and density of the wood, as well as the shape and amount of firewood.
- Combustion consists of two phases: fiery and smoldering. For some time, both types occur simultaneously. After the cessation of the formation of gases, only coal burns (smolders).
- Attenuation - occurs when the oxygen supply is cut off or when the fuel runs out.


Dense wood burns more slowly than less dense wood due to the fact that it has a higher thermal conductivity. When burning raw wood, a lot of heat is spent on evaporation of moisture, so they burn more slowly than dry wood. Is wood burning a physical or chemical phenomenon? This question is of practical importance, and the conditions for maximum heat transfer and combustion duration will depend on its correct interpretation. On the one hand, this is a chemical phenomenon: when burning wood, a chemical reaction occurs and new substances are formed - oxides, heat and light are released. On the other hand, it is physical: during the process, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases. As a result, it turns out that the process of wood burning is a complex physicochemical phenomenon. Getting to know him will help you choose the right wood species to provide yourself with a long and stable source of heat.
Warming up process
Heating is called heating a piece of wood surface from a separate heat source to a temperature sufficient for ignition. 120-150 ° C is enough for the wood to start charring very slowly.
Later, the process continues with the appearance of coal. At a temperature of 250-350 ° C, wood, under the influence of high degrees, actively begins to decompose into components.
Further, it smolders, but there is no flame yet, and white or brown smoke begins to appear. With further heating, the percentage of pyrolysis gases increases and a flash occurs, after which the wood ignites.
Features of the smoke that occurs when burning a fire
Throwing wood into the fire leads to increased emission of smoke and carbon monoxide - carbon monoxide. Moreover, the smoke appears in different colors:
- White is an aerosol consisting of small droplets of water and tar vapors coming out of cold wood. The smoke has a specific soot smell. As the log heats up, it evaporates, bursts into flame and disappears.
- Gray - comes from red-hot, but not burning logs and embers. It is formed at high temperatures from boiling oils and resins and condenses into a mist. Its particles are much finer than that of white smoke, and it itself is lighter and drier than it.
- Black is a burnt tar called soot. It is formed during the decomposition of hydrocarbons in a flame with insufficient oxidation.


Smoke from a fire lingers in the body for a long time and contains a large amount of harmful substances. This must be remembered by everyone who likes to sit by the fire.
Prepare firewood in advance
Bring the wood to a warm room 2-3 days before lighting to increase its starting temperature.


The warmer the wood is initially, the:
- They spend less heat on their own heating and more on heating the room. You use heat better.
- The firewood achieves optimal combustion faster, which further increases its calorific value and reduces the amount of soot emitted. This is because the resin, creosote, tar, essential oils and other substances that are part of the wood do not burn at low temperatures and settle on the walls in the form of soot. And under optimal conditions, the combustion temperature is sufficient so that they burn out entirely and generate additional heat.
The difference between the combustion of "warm" and "cold" wood is immediately noticeable: cold wood emits a lot of smoke, which characterizes incomplete combustion. And warm dry firewood burns practically without smoke.
Wood properties
Different tree species have the following physical properties:
- Color - it is influenced by climate and wood species.
- Shine - depends on how the heart-shaped rays are developed.
- Texture - related to the structure of the wood.
- Moisture is the ratio of moisture removed to the dry weight of wood.
- Shrinkage and swelling - the first is obtained as a result of the evaporation of hygroscopic moisture, swelling is the absorption of water and an increase in volume.
- Density is approximately the same for all tree species.
- Thermal conductivity - the ability to conduct heat through the surface thickness, depends on the density.
- Sound conductivity - characterized by the speed of sound propagation, depends on the location of the fibers.
- Electrical conductivity is the resistance to the passage of electric current. It is influenced by the breed, temperature, humidity, fiber direction.


Before using wood raw materials for certain purposes, first of all, they get acquainted with the properties of wood, and only then it goes into production.
Types of materials that can be used to heat a fireplace in the house
Better suited for burning dry wood in the fireplace. A fifth of the moisture remains in the raw material after 2 years of drying the wood outside. It is recommended to dry it in woodpiles folded under the shelter, in which the chopped chocks are well blown by the wind:
- the length of the logs should not exceed 40 cm. The best option is 3/4 of the width of the firebox;
- the diameter of firewood, ensuring good combustion, is 6-8 cm;
- in the woodpile, it is desirable to alternate the longitudinal and transverse arrangement of the chocks in 1 row.
Free blowing of wood with air masses promotes drying of raw materials. Oak firewood is dried for 2 years before use.
Kindling the hearth
Before starting to light up the fireplace, you need to check the draft by holding a lighted match to the opening of the pipe in the place of the valve for the forward passage of the smoke. If the room is colder than outside, there may be no draft, and then the smoke from burning wood will go directly into the house. To avoid smoke, you can warm up the air in the pipe with burning paper rolled into a roll.
How to light a fireplace depends on the laying of firewood (hut, well, taiga). But the general rule: there should be a gap between the dry chocks so that the resulting traction fan the fire. In this case, paper is used, thin splinters that flare up faster.
To avoid heat loss, you should make an approximate estimate of how to properly heat the fireplace by the brightness of the flame:
- the normal color of the reeds of fire is bright yellow;
- a white flame says the thrust is too strong. It is necessary to cover the blower and slightly reduce the gap in the pipe with a fireplace valve;
- a dark color indicates a lack of oxygen for combustion. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the air flow;
- it is recommended to fill the firebox with wood with a volume of slightly less than half. Otherwise, the high temperature in the firebox will lead to cracks in the fireplace body, which are almost impossible to repair.
When choosing how to heat an open-design fireplace, you need to take into account that the smell of burning material enters the room. Therefore, tree species with a high resin content in the composition are not suitable. But you can add a little pine needles for a pleasant aroma.
Alder firewood is considered to be of good quality.It is easy to identify the belonging by the orange color of the wood. In tsarist times, alder was used to quickly warm up the bathhouse. High heat transfer, pleasant smell and almost no smoke characterize alder wood.
Birch wood is more common and less expensive. If you peel off the bark, then the emission of smoke during combustion will be negligible. And birch bark can be excellent for kindling a fireplace. If the house is constantly heated with birch, then it is advisable to clean the chimney every month. The exercise provides good traction when firing up.


Provide beautiful combustion with low heat emission for aspen wood. It is recommended to heat the fireplace with aspen raw materials several times a season in order to clear the chimney from excess soot.
Charcoal fireplace insert
For more heat, it is good to heat the fireplace with coal. Only the material should be purchased special, adapted for kindling the fireplace. First, you need to create heat with the help of firewood, on which the coal is placed on top in small pieces, gradually increasing its size.
It is more difficult to light a hearth with coal than with wood. Specialty tablets or kindling liquid are often used. Heating systems of modern times are equipped with gas or electric igniters, which significantly speed up the process.
A fireplace with a closed firebox is distinguished by a special door made of heat-resistant glass, therefore, when choosing which wood to heat the fireplace, it is better to take into account the formation of fumes and soot.
For example, coniferous wood contains a lot of resins, which, when burned, emit an increased content of soot that settles on the glass.
Important
Continuous cleaning will scratch the surface and the soot accumulated in the chimney can catch fire.
When choosing which firewood is best for the firebox, it is recommended to take into account the purpose of the fireplace. If high heat transfer is not required, firewood is used from poplar, willow, which burn brightly, but practically do not emit heat.


An alternative to the use of wood is considered to be eurowood, made by pressing from the remains of raw materials in the manufacture of furniture. Wood shavings, sawdust, dust are pressed into logs or briquettes. They are characterized by slow burning with increased heat transfer, ideal for closed-type fireplaces.
To light the briquettes, you must first heat the fireplace with wood, and it is recommended to throw the pressed logs into the heat. What is the best firewood to use, they decide based on the cost of the product and the possibilities of its delivery.
Fulfilling simple requirements on how to properly heat a fireplace, a person gets aesthetic pleasure, watching the play of the flame, inhaling the pleasant aroma of burning wood.
The height of the flame, burning time and heat transfer depend on the correct choice of how to heat the fireplace. Also, fuel affects how the firebox will look after several operations. The wrong choice of fuel can ruin the fireplace and contribute to the formation of soot in the room.
There are many types of fuel that can be used to light a fireplace in your home. Suitable as a combustible material:
- eurowood (briquettes);
- wood;
- coal;
- gas;
- biofuels.
When wondering how to properly heat a fireplace, it is worth considering the properties of the stove. After all, the type of fireplace depends on what kind of fuel should be used.
Choosing which wood is better to heat the fireplace, you should give preference to briquettes. Eurodrova is a fuel specially developed for furnace heating. It has many advantages over regular logs:
- When using briquettes, the flame flares up faster than when using wood.
- Eurowood is made of pressed wood, the moisture content of the material does not exceed 11%. As a result, the flame is uniform and non-sparking.
- One full load of briquettes will burn for 2 hours.
- In the process of burning Euro wood, heat transfer is 30-50% higher than after using ordinary wood.
Eurowood can be made of wood or peat. Peat briquettes take longer to ignite, but the flame will last twice as long as compared to the wood counterpart.
Nothing beats a real wood fire. The characteristic crackling and lively flames are only possible if real logs are used.
There are several nuances of how to heat a fireplace with wood correctly:
- You must follow the rules for storing firewood. You can heat the room only with dry wood, which contains as little moisture as possible. The firewood of freshly felled trees is not suitable. You need to use logs that have dried for at least a year. Such wood is easy to distinguish - it has a darker shade compared to other wood, there are several cracks on its surface. The burning process of dry wood is characterized by a distinctly audible crackle.
- Choose the same size logs. The thickness of the tree should be no more than 6-10 cm, otherwise the log will burn out badly. The length should be ¾ part of the combustion hole.
- A horizontal way of laying firewood is used for the fireplace insert. Logs are placed in the furnace hole next to each other with an interval of 1 cm.The height of the bookmark should not exceed the mark of 30 cm.
Another important criterion for how to heat the stove is the choice of wood species for kindling the fireplace.
How warm it will be in the room after starting the fireplace, how much soot and smoke there will be - it all depends on the type of wood for kindling. You need to know exactly what kind of wood is better to heat the fireplace. The following types of wood are used for kindling:
- Hardwood. These include birch, hawthorn, pear and apple trees. It is a malleable wood that ignites easily. The combustion process produces a minimum amount of tar and soot.
- Hard rocks. For long burning, it is better to choose logs of oak, yew and beech. Such wood is difficult to chop, it takes a long time to ignite. But logs will also burn much longer than other types of wood.
- Softwood. Elm, cherry, cedar and fir generate much less heat than other types of wood. In addition, the logs smoke heavily, and a large amount of soot and ash is formed. It is worth refraining from choosing such logs if the chimney of the fireplace has a rectangular shape and a small hole. If the draft of the duct is weak, smoke can fill up rooms.
- Conifers. Pine and spruce logs are used to create a pleasant aroma in the room. Conifers burn quickly, but the flame turns out to be uneven, many sparks are formed. A large amount of smoke and soot is also emitted. Due to the high resin content of conifers, coals can fall out of the fireplace, which is quite unsafe.
- Cleansing rocks. These include alder and aspen. Wood does not emit smoke during combustion. From the use of firewood from alder and aspen, not only soot is not released, but also the chimney is cleared of soot. It is advisable to heat the fireplace with frequent use with clearing logs at least once every two weeks.
- Fragrant branches. You can add fragrant tree branches to the fireplace flame, which will fill the room with a pleasant smell. You can use the branches of fruit trees. The addition of juniper twigs to the fire will bring a healing and relaxing effect.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with Autumn DIY crafts for kindergarten


Whichever type of wood is used for the fireplace, only dry wood should be chosen. If there is a lot of moisture in the branches and logs of trees, the fireplace will be covered with soot and soot, which can weaken the draft in the chimney.
Coal fuel is rarely used for fireplaces. You need to clearly know how to properly heat the fireplace with coal so that the stove will last as long as possible.
It is possible to heat the fireplace with coal only if there is a grate in the stove. In the process of burning coal, a large amount of ash is formed, which must be removed in a timely manner. Also, the fireplace should have a special cover that will cover the furnace hole. The blower door must be kept open until the flame has ignited.
Advantages and disadvantages of wood
Wood has the following advantages:
- excellent workability;
- light nailing;
- well painted, polished, varnished;
- has the ability to absorb sounds;
- resistance to acids;
- high bending ability.
The disadvantages of wood include:
- change in shape and size due to shrinkage and swelling;
- low resistance to splitting;
- rotting;
- damage by insects;
- lighting up if safety rules are not followed.


Remove soot in a timely manner
Soot needs to be removed not only when the chimney is clogged and the draft has disappeared, but regularly. Soot not only impairs chimney draft, but also serves as thermal insulation. It covers the inner walls of the heater and the heat exchanger, which reduces their heat transfer. If soot is removed in a timely manner, the volume of firewood burned can be reduced without loss of heating power.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FM3DUUe9d9E
Obviously, but it's worth remembering: the wood must be dry. Wet wood ignites poorly, goes out quickly and emits 2-2.5 times less heat than dry wood.
The use of wood in various sectors of the national economy
Wood is widely used in the following industries:
- plywood - veneer, plywood;
- woodworking - wood boards, matches, joinery, furniture;
- logging - raw materials used in the wood-chemical industry, consumer goods, firewood of all kinds;
- sawmill - various lumber;
- wood chemical - tar, charcoal, acetic acid;
- pulp and paper - paper, cardboard, cellulose;
- hydrolysis - feed yeast, ethyl alcohol.
Heat transfer when burning wood in a stove
There is a direct relationship between the temperature of burning wood in the stove and heat transfer - the hotter the flame, the more heat it emits into the room. The amount of heat generated is influenced by various characteristics of the tree. The calculated values can be found in the reference literature.
It should be noted that all standard indicators were calculated under ideal conditions:
- the wood is well dried;
- the furnace is closed;
- oxygen is supplied in precisely metered portions to maintain the combustion process.
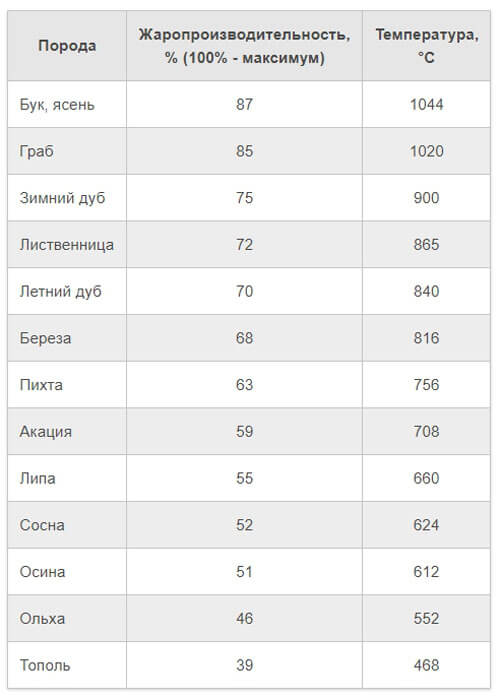

Naturally, it is impossible to create such conditions in a home stove, so less heat will be released than the calculations show. Therefore, the standards will be useful only for determining the overall dynamics and comparison of characteristics.
Heat output of wood
In addition to the calorific value, that is, the amount of heat energy released during fuel combustion, there is also the concept of heat output. This is the maximum temperature in a wood-burning stove that a flame can reach at the time of intense wood burning. This indicator also completely depends on the characteristics of the wood.


In particular, if the wood has a loose and porous structure, it burns at rather low temperatures, forming a bright high flame, and gives quite little heat. But dense wood, although it flares up much worse, even with a weak and low flame gives high temperature and a large amount of thermal energy.
How to determine the combustion temperature in a wood-fired oven
The measurement of the combustion temperature of wood in the fireplace can only be performed with a pyrometer - no other measuring devices are suitable for this.
If you do not have such a device, you can visually determine the approximate indicators based on the color of the flame. For example, a low temperature flame has a dark red color.A yellow light indicates too high a temperature obtained by increasing the draft, but in this case, more heat immediately evaporates through the chimney. For a stove or fireplace, the most suitable combustion temperature is at which the color of the flame will be yellow, as, for example, with dry birch wood.


Modern stoves and solid fuel boilers, as well as closed-type fireplaces, are equipped with an air supply control system to adjust heat transfer and combustion intensity.
How to know if you need to clean your chimney
If you do not clean the chimney, then the roughness of the walls becomes larger, the force of air friction against the side surfaces increases. The thrust force is spent on overcoming this resistance, and as a result, the rate of exit of combustion products decreases, the air consumption for heating decreases.
The temperature in the furnace is dropping the house is getting cold... Instead of unclogging the canal, the owners of the private house begin to add fuel. All of the above reasons lead to a violation of traction, which is manifested in the following performance indicators:
- The amount of heat in the house remains constant, but more fuel is required to achieve this.
- From hot gases, soot in the pipe can ignite and cause a fire.
- Burning soot emits black smoke visible from the chimney, and absolutely dry fuel can be loaded into the furnace.
- The color of the flame turns to a dark red hue, which indicates a lack of supply of fresh oxygen due to reduced thrust.
The chimney in the house should be cleaned only if it removes food. combustion of solid fuel... If gaseous fuels are burned in the chimney, other condensation problems arise.
It is considered the norm to clean the chimney from soot. once a year, this is done in any way at the beginning and end of the season, which prevents major cleaning or even disassembly of the chimney.