The most used heat sources for heating homes are electricity, gas, coal or wood. Despite the technical availability of each of them, the use of one or another is due to some factors, such as: economic feasibility, place and frequency of use, safety. Nowadays, the first two types of energy listed are the most popular. Consider the aspects of the use of electricity, as well as the types of electric heating devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Electricity for Heating Purposes
It should be noted right away that the use of electric heating devices for heating is not the cheapest option, since the cost of the equipment itself, as well as operating costs, are too high. Therefore, it is most often considered as an alternative, in case of gas supply interruptions or, if there is no gasification at all. At the same time, heating the house with electrical appliances has some obvious advantages:
- Almost ubiquitous availability.
- Very quick and easy installation.
- Convenient management.
- Compact device device.
- Complete absence of any combustion products.
Thus, with all its shortcomings, mainly associated with the economic component of the issue, electrical appliances have a lot of useful qualities that heating devices based on fuel combustion cannot boast.
Methodical furnaces
Methodical furnaces (two-zone, three-zone and multi-zone) operate with counter-zone movement of metal and combustion products using heat in recuperators. They operate according to the same principle: the movement of metal and furnace gases occurs in mutually opposite directions. With the help of a pusher, the metal moves from the landing window to the delivery window. As it moves forward, the metal takes heat from the furnace gases moving towards it, and gradually (methodically) heats up. Furnace gases, giving off heat to the metal at the end of the furnace, go through the appropriate channels to the regenerators or recuperators (if any) and to the bur, and through it into the chimney.
Methodical furnaces differ from each other in the shape of the vault, in the method of supplying fuel for its combustion, in the presence of devices for heating air and gas, in the method of delivering metal from the furnace and in a number of design features.
In addition to the corresponding heat engineering parameters, heating furnaces must meet modern requirements in terms of reliable remote maintenance. mechanization and automation of the entire complex of operations. The heating rate depends on the steel grades in the heat transfer efforts. At first, the heating rate should be low, then as the workpieces warm up, it increases.
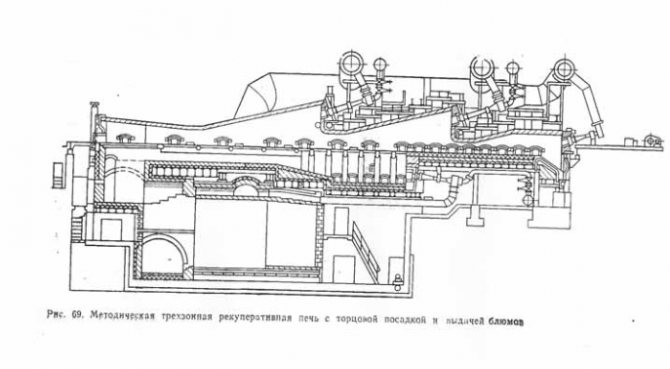
In recent years, at rail and beam mills, methodical three-zone recuperative furnaces with air heating have been used to heat metal (Fig. 69). A mixture of blast furnace and coke oven gases with a heat of combustion of 7560–8400 kJ / m3 is used as fuel. The productivity of one furnace at a hot injection reaches 80-90 t / h, the heating temperature of blooms in these furnaces reaches 1200 ° C.
Blooms are transported along a roller table from the blooming to an inclined conveyor equipped with chain sliders, and then along a loading roller table to furnaces, through which they are pushed by pushers.After weighing on a scale built into the section of the loading roller table in front of the first furnace, the bloom moves along the roller table and, with the help of a stop, stops on the section of the loading roller table of the corresponding furnace. The blooms are loaded into the oven with a pusher having two rods, from the bottom of which toothed racks are fixed; the latter are driven through gears and gearboxes from two electric motors.
After loading the next bloom into the furnace from the opposite end side, the heated bloom is dispensed over cast guide sheets (slimes) onto an unloading roller table. Thus, the pusher is also a pusher.
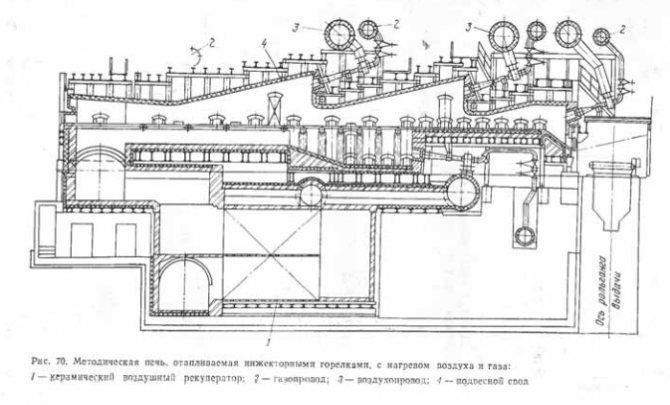

On medium-section and large-section mills, methodical furnaces are used (Fig. 70) with end fit and delivery, with ceramic air recuperators. In the furnaces of the latest designs, high-pressure injection flameless burners are used, which provides a higher air heating, significantly improves combustion and allows you to automatically adjust the ratio of gas and air of the burner itself, this greatly simplifies the automation scheme and facilitates the control of the furnace.
Furnaces of this type are equipped with ceramic recuperators for heating air to 500-600 ° C and metal tubular recuperators for heating gas up to 350 ° C. The furnace operates on a relatively low-calorie mixture of blast furnace and coke oven gases with a calorific value of 3760–6260 kJ / ml.
To heat workpieces with a cross section of less than 100 × 100 mm and a length of 9 m on small-section and wire mills, one wide furnace is installed with side loading and side delivery without bottom heating, with a monolithic hearth. Ceramic recuperators are used to heat the air to 300-350 ° C in these furnaces. The workpieces move along the inclined bottom, and in the methodical part - along the bottom beams. The workpieces are moved in the furnace with a lever pusher.
Side loading of blanks is carried out using a pushing carriage installed under the loading roller table, or using pulling rollers installed behind the loading window in the furnace. The billets are discharged from the furnace by a pusher. Furnaces of this type are heated with a mixture of blast furnace and coke oven gases with a calorific value of up to 10.5 MJ / m3. They achieve a productivity of 70-80 t / h in the presence of a hot injection.
Methodical furnaces of the latest designs have a useful length of up to 18 m; to ensure reliable pushing of workpieces with a cross section of 60 × 60 mm, the bottom along the longitudinal axis is made concave (curved).
Furnaces with injection burners installed in two upper zones and one lower one turned out to be successful in their design and thermal regime. Such furnaces with a capacity of up to 80 t / h can operate on one blast furnace gas. These furnaces are equipped with ceramic recuperators for heating the air up to 600 ° C. The active hearth length is 16.5 m with a workpiece length of 9 m.
In the latest designs of these furnaces, the length of the workpieces was increased to 12 m with the length of the active sub-curved shape equal to 18 m. Forcing the thermal power is achieved by using injection burners and heating gas and air. The air recuperator is ceramic, the gas recuperator is tubular metal. These furnaces without bottom heating have a capacity of up to 140 t / h.
What are the principles for the classification of electric heating devices
All modern electric heating devices are classified as follows.
By the way the device is mounted:
- Portable or mobile, which include oil coolers and various convectors.
- Installed in one place or stationary, including boilers, air conditioners, electric boilers and fireplaces, infrared heaters.
By the type of coolant that heats up in the device:
- Air - heating of the surrounding space is carried out by heating the air. These include convectors, radiators, electric fireplaces and many other devices.
- Liquid - the coolant in them is any liquid that has a good heat capacity: water, oil, antifreeze. The most famous devices with this principle of operation are electric boilers and boilers.
- Solid-state or radiative - heat in these devices is transferred from a source to some solid surface, which then heats the air in the surrounding room. These include radiant and infrared heaters.
By type of heating element (heating element):
- Standard tubular elements are successfully used in many types of heating devices that run on electricity. They can have a very wide range of technical characteristics, both in terms of performance and power. They are made from steel and titanium.
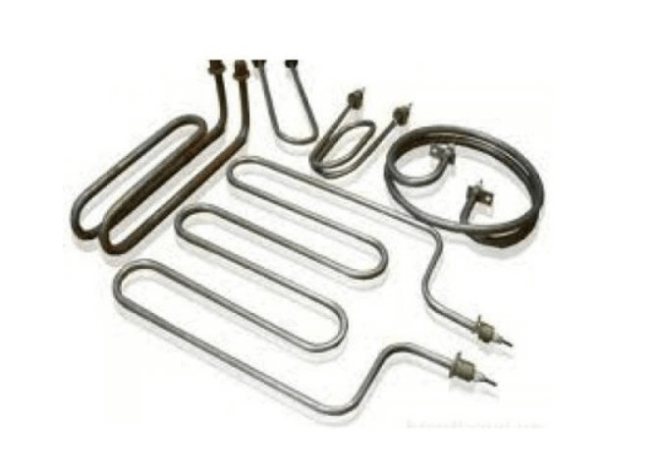


Standard tubular type heating elements
- Ribbed tubular - similar to the previous ones, but have a ribbed surface that increases heat transfer. They are used only in devices where the heating medium is a gaseous medium (air curtains and convectors). Such elements are made of stainless or structural steel.


This is how finned heating elements look
- Block electric heaters are several heating elements connected into one structural unit. Such devices are installed in devices where there is a possibility of power regulation. Heat carriers in them can be liquid or free-flowing solids.


Block of electric heaters, assembled in one unit
- Equipped with a thermostat - they are the most common type of household electric heaters for heating with a liquid heat carrier. They are made from copper, steel, or nickel-chromium alloy.


Equipped with a heating element thermostat
All considered heating elements are only the main details of the devices, about the features of which read below.
What is a heating element
What is a heating element Is a device used in solving engineering problems associated with the use of heating a physical substance. It can have various forms depending on the specific conditions and methods of application during thermal processes, as well as be made of a variety of conductive materials.
Its use in household appliances allows heating any medium that guarantees the necessary conditions for the functioning of technical procedures related to the use of heat. Heating a physical substance to the required temperature is a very costly process, requiring, as a rule, the use of large amounts of energy. Therefore, it is important to use a heating element with high performance and reliability during its operation. Thus, it is possible to achieve high rates of profitability of manufactured products associated with heat consumption.
Thermal heating elements
Thermal heating elements, as a rule (with some exceptions) create heat by converting electricity. The current passing through different converters is converted into thermal energy, which directly takes part in the work on heating a particular substance by spreading thermal energy in solid matter, liquids and gases through convection, thermal conductivity, or radiation. Thus, it becomes possible to produce heating in those places (volumes) of the equipment where it is necessary and to exclude unnecessary power consumption where it is not required. In the course of some thermal cycles, particular importance is attached to the uniformity of the generated heat, which ensures the high quality of the products.This result can be achieved with the help of flat-shaped heat-generating surfaces and better with small distances between the turns of the heating wire, which allows you to create the most constant heat flux in accordance with the entire area of the heater. However, as a rule, it is very problematic to create thermal heating elements with small intervals between the wires due to the possibility of electrical breakdown. It is necessary to increase the thickness of the insulator, which in turn leads to an increase in the turn-to-turn distance, and this can lead to an abrupt distribution of heating over the entire area. Some examples of the effective use of heating elements of a new type in solving technical problems with the introduction of thermal processes are presented below in the text.
Heating element materials
Heating element materials it is a set of chemical materials of the periodic table with pronounced metallic properties with good electrical and thermal conductivity used in the manufacture of heating elements. Heat-generating surfaces are the main sources of temperature rise during thermal processes in industrial production. Therefore, the choice of the applied thermoelement largely depends on the type and characteristics of the environment in which it will be used. The alloy composition is selected according to the environment. The performance and service life of heating elements depend on the nature of the material used in its manufacture, which must satisfy the following qualities: high melting point; protection against oxidation in an open atmosphere; high tensile strength; sufficient plasticity; high electrical resistance; low temperature coefficient. According to its design features, the heater material can be a wire spiral, tapes or strips of open or closed form, a flexible film with a resistive track applied to its plane, a rigid flat base emitting infrared radiation. The spiral is usually made from high resistance wire. Heating element materials are chrome-nickel precision alloys (80% nickel, 20% chromium) or fechral alloy. The combination of 80/20 nichrome is considered optimal for manufacturing, since it has high resistance and is capable of forming a sticky layer of chromium oxide during the first heating, which protects the surface from oxidation. Most flat thermal devices, such as those on metal or ceramics, are made from this alloy. In these cases, a spiral with a high resistance is placed in a ceramic or pressed into an electrical insulator and covered with a metal sheath. Thus, a heating surface is obtained that emits an uneven heat flux resulting from a non-optimal radiating surface. The technology of the new type of heating elements is significantly different. Therefore, the materials used for their production are taken from others. The material of the heating element includes: base (metal, ceramic or film); dielectric paste; contact paste; resistive film track; protective dielectric layer. In this case, the heat-generating surface is obtained in the form of a set of multilayer circuits laid in a certain order on a substrate (base). The heaters obtained using the new technology make it possible to obtain a continuous uniform thermal field on the heat-generating surface.
Manufacturing of heating elements
Manufacturing of heating elements it is a process for the production of high quality heating elements with good technical parameters and high operational reliability.Flexible film heaters can also be made from a wire spiral embedded in silicone, polyethylene or fiberglass. They have the same problems as for flat thermoelements. It is possible to solve the problem of unevenness of the released energy by etching the foil. The used method of foil etching in the production cycle of flexible heat-generating devices makes it possible to develop an electric heater taking into account all the conditions provided by the customer. In this case, there is a high probability that most of the requirement will be fulfilled in such a way that the electric heater will turn out with optimal electrical characteristics. Engraved electric foil heaters are typically made from the same alloys as the resistance of wire heaters, but are manufactured using a photozincographic operation that starts with a continuous sheet of metal foil and ends with a complex resistive pattern. This process is very costly, which is ultimately too expensive for the manufacturer. The same effect of uniform heat distribution is possessed by devices that are made according to energy-saving technology based on conductive pastes, at the same time, the production costs of heating elements with good technical parameters and high operational reliability are much lower.
Air convectors
These devices are made in the form of compact portable devices equipped with legs or wheels for installation on the floor or wall. The working element in them is ribbed heating elements, closed with a decorative metal case with slots for air circulation. They are used in apartments or private houses, mainly as additional sources of heat.


Electric convectors
The principle of operation of such devices is based on the fact that cold air freely or forcibly enters the device and passes through all heating elements (heating elements). Then, as it should be for heated gases, it rises up and passes through a special grate. Convectors can be equipped with built-in fans for forced air circulation. These devices do not have any restrictions for their use.
Oil-cooled radiators
The appearance and principle of operation of such devices is completely similar to ordinary heating batteries. Only they are filled with mineral oil, and electric heating elements installed directly inside the inner cavity of the device heat it. They are successfully used in offices and residential premises. There are oil coolers open and closed. The ribs of the latter are protected by a metal casing. The main advantage of these devices is that they do not burn out oxygen in the room and do not heat up to temperatures that are dangerous for small children. Especially the latter property applies to closed radiators.


Open and closed oil coolers
Which heater is better for giving
The specifics of a country house are small rooms and the need for quick warm-up. From this point of view, all options are suitable for giving, except for oil:
- fan heater;
- convector;
- infrared heater.
In addition, stationary heating is rarely installed at the dacha; the heater often comes and goes with the summer residents.
This means that it should be lightweight and mobile (this factor must be taken into account when buying, since there are bulky and compact models inside the species), again, an oil radiator is not suitable, because it is the heaviest and largest device.


Heater in the country
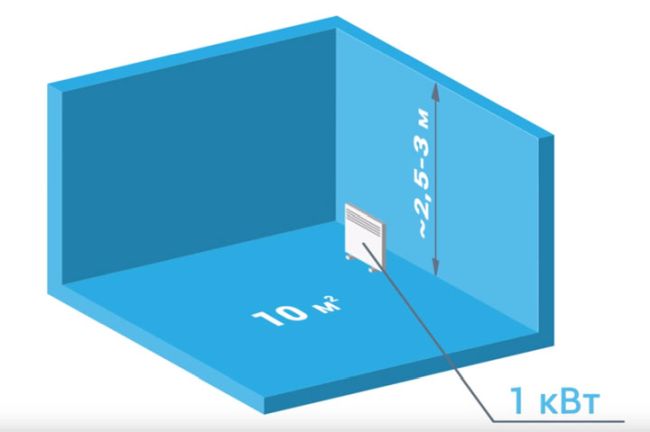
Any heater must be selected correctly: its power must correspond to the area of the heated room. For a well-insulated building, 1 kW of power is taken per 10 m2 of area.
Electric fireplaces
These electric heaters have a great design, so they can be used not only as heaters, but also as a decorative element. These devices can be found in luxury apartments or country houses due to their prohibitive cost.
Modern electric fireplaces are made floor-standing, imitating classic wood-burning options and wall-mounted, which look like thin panels hung on the wall. The principle of operation of fireplaces is similar to that of convectors.


Wall and floor electric fireplaces
High-speed heating furnaces
Reducing the duration of heating the metal in the furnace provides not only high productivity with good quality, but also solves a number of fundamental issues of the rational layout of technological equipment. The thermophysical properties of most steels provide a large reserve for accelerating the heating of workpieces, especially at temperatures above 700 ° C.
Rapid heating of the metal provides a rapid increase in surface temperature, uniform distribution of heat fluxes and the organization of fuel combustion with the correct direction of the flame and high thermal power of the heating devices. The high speed continuous furnace consists of a series of small sections (often removable). Heated workpieces, pipes or rods move longitudinally along rollers. In the sections, high temperatures are obtained due to preliminary mixing of gas with air, completeness of fuel combustion with a small excess of air, and also due to an increase in heat transfer by convection. The design of the burners and their placement ensure symmetrical heating. Other high-speed heating furnaces are also used - electric and induction.
Continuous sectional furnaces operate on tube-rolling and modern section mills in combination with walking hearth furnaces.
vKontakteFacebookTwitterWhatsAppEmail
Electric boilers
Unlike previous appliances, these devices are used to create a permanent heating system in the home. They are used in conjunction with a liquid heat carrier circulating in a closed loop that ties all rooms in the house.
By the type of the main heating element, electric boilers are divided into:
- Heating elements - work with any kind of liquid and have the simplest design. They allow you to smoothly change the power, stepwise change the heating intensity by switching on a different number of devices.
- Electrode, which are compact in size and are used exclusively for water systems. In this case, the coolant must strictly comply with the requirements of GOST 2874-82 "Drinking water". This circumstance greatly affects the cost of equipment. Thermal energy arises according to the principle of electrolytic dissociation, due to which a potential difference arises on the electrodes due to dissolved salts. This heats the water up nicely. Such a device is much more economical than the previous one.
- Induction boilers are the most innovative and expensive devices. They are very reliable and durable. Any coolant can heat such boilers due to the principle of electromagnetic induction. Such a device consumes the maximum amount of electricity, but it is easy to install, does not require a separate room and has maximum efficiency at the smallest size.
All electric boilers must be grounded very reliably.
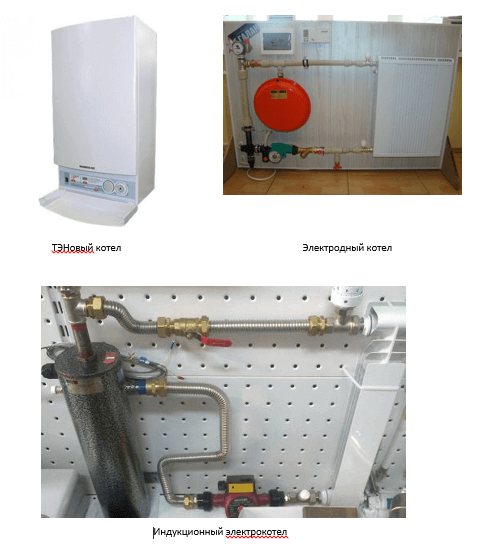


All types of electric boilers
Choosing a good home heater - 5 rules.


Central heating capacity is not always sufficient to heat an apartment or house. And there are also houses and premises where it is completely absent.
Installing an electric boiler for a one-room apartment or kopeck piece is a rather costly and troublesome business and requires constant monitoring and maintenance.
An old proven way out of this situation can be an ordinary heater.But what are they? What are their pros and cons, and what are the rules for choosing a heater for a bath, nursery, bedroom, office, etc.
Today, the following types of heaters are most popular:
- fan heaters


- convection models


- oil


- infrared


Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here's a pivot table for comparison:
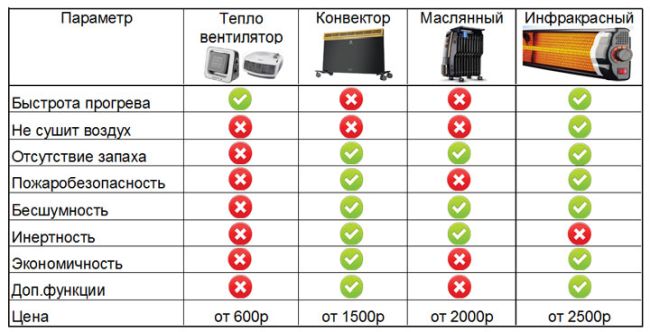

Although infrared received the most plus signs, there is no need to rush to make a choice. To find the right model for you, use the five rules.


First of all, you need to decide what area you want to heat. The device of what power you need depends on this. How to calculate this power?
There is a simple and reliable formula that is suitable for all types of heaters except infrared.

For an infrared heater, there is an unspoken rule that 100W per 1m2 of area, this is its maximum power, not minimum.
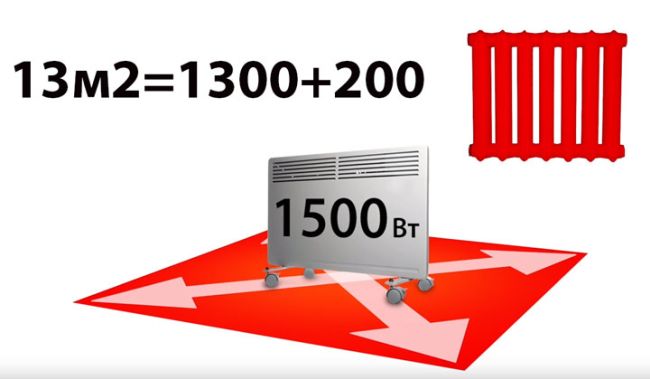
To the resulting value, add 200W for each window.
It follows from this that, for example, one room with an area of 13m2 will rather effectively heat a model of 1.3kW + 0.2kW = 1.5kW.

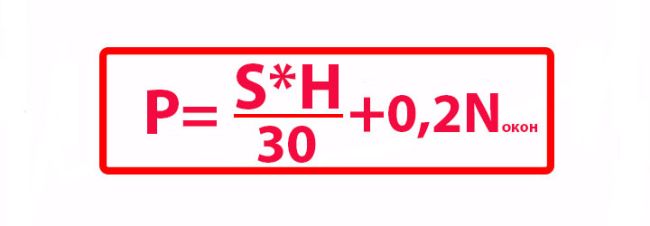
And if you have a ceiling height of 3m or more? Then use a slightly different calculation. The total area of the room is multiplied by the actual height of the ceiling and divide this value by the average coefficient equal to 30. Further, you also add 0.2 kW per window.

Of course, according to the calculation, you can choose a less powerful device, especially for apartments where there is already main heating (central or boiler).
But given the constant heat loss and the fact that it will warm up the room longer, it is better to insure yourself. Devices with several heating stages are ideal. The more, the better.


Moreover, when the set temperature is reached, the built-in thermostat must turn off the device, no matter what stage it is at. And when it is lowered, turn it on again. Thus, significantly saving energy.


It is quite logical to assume that the greater the power of the heater, the larger its overall dimensions will be.
Note, however, that in many models this only changes the width. But the height and thickness remain unchanged.
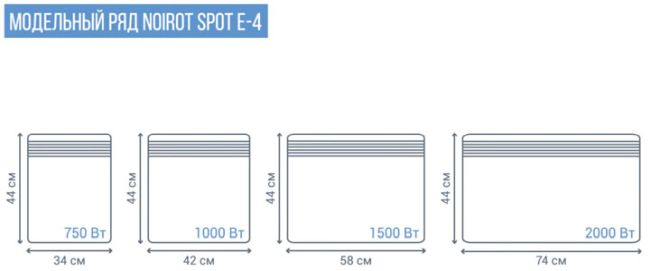

This is a very important point when placing heating on the wall and integrating it into other design elements.
At the same time, from leading manufacturers, even with the same power, you can always choose the following:
- low and very wide, for large windows or stained glass


- and vice versa - tall and narrow in small rooms


For example, two models of the same power 2kW, but what is the difference in the width of the case. Which one do you think will heat better?


In stores, you can buy heaters with two types of control:
- mechanical
- electronic
Mechanically operated models are the simplest and cheapest. However, they have a whole bunch of shortcomings, which not everyone knows about.
- firstly limited functionality


- in addition, they are more susceptible to wear during long-term use. This means they will fail earlier than electronic ones.


- the error in setting the set temperature can reach several degrees!


- when automatically turned on and off, they click quite loudly
And it happens all the time every 10-20 minutes. So you don't want to leave such a unit in the bedroom at night.
The temperature in expensive models can be set with an accuracy of up to a few tenths of a degree!
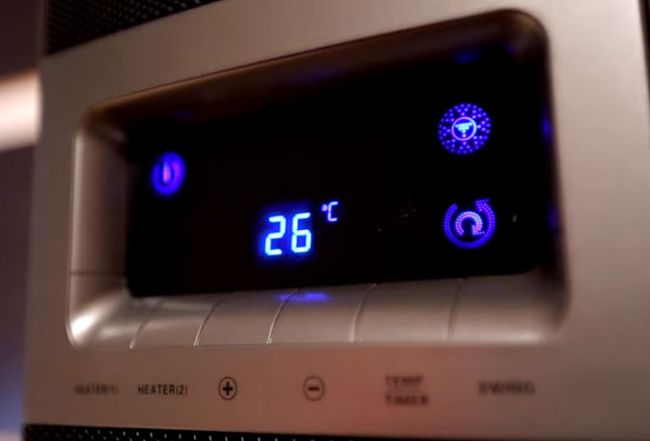


And this can be quite annoying, especially if you are used to falling asleep in complete darkness.
There is a natural desire to cover such a screen with something. And here the most important thing is not to forget the basic safety rules for heaters:
- do not dry anything on them and do not cover the radiator openings


- do not place next to curtains or furniture


Therefore, check the backlight, as they say, without leaving the checkout.


For an apartment, especially in which there are small children, it is not recommended to buy heaters, the bodies and elements of which themselves heat up to high temperatures.


It turns out that 2 kW are hidden in a small case, which can be fully obtained only by heating the heater to such temperatures.
At the same time, in order to comply with safety rules and not to overheat the surface above 60-70 degrees, temperature sensors are mounted. And they, in turn, turn off the heater, which in fact never reached its maximum parameters.
And what can we say about the open incandescent spiral of the fan heater!


Therefore, in this respect, convectors can be considered the safest. They have a ceramic design, the temperature of the cases does not exceed 60 degrees. No wonder many of them hang signs - "For kindergartens."


Among the infrared models for safety, micathermal ones stand out.


The heating element in them emits heat, but does not heat up itself.
But in quartz, carbon and halogen, the filaments warm up from 2000 degrees and above, after which infrared radiation actually begins to be generated.


When you have decided on the type of heater, all that remains for you is to choose a specific brand and manufacturer. And then the majority immediately open websites of online stores with reviews.
Oddly enough, but on the same models, on different sites, you can find absolutely opposite opinions. It is no secret that often the stores themselves or the moderators of the Internet portal can write certain paid comments, and supposedly the opinions of experts.


Whom to believe? The advice here can be simple.
Let's consider in more detail the principle of operation and each type of heaters separately. To view it, click on the corresponding tab with the name.


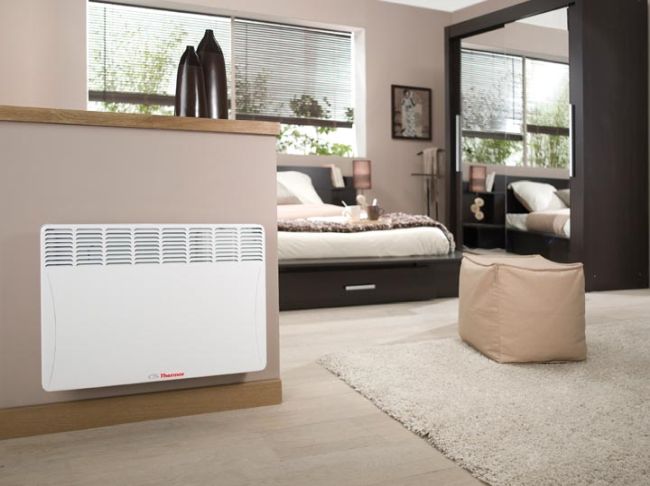
The convector's operating principle is based on a simple law of physics. Cold air enters the appliance naturally from below. After that, heating occurs inside the case and, already heated, it comes out through the upper grilles (at an angle) into the ceiling.
The case itself does not heat up here as much as in radiator models. It is the air that heats up.


The truth does not get warmer in the room right away. Unless an additional fan is built inside. If you come from work to a cold apartment and turn on the convector, then anyway your floor will be cold for a very long time.


Moreover, at a low height from the floor, there will also be a layer of cold air. The warmest place in this case is the ceiling. In the presence of even a small draft, it will be quite difficult to warm up the walls and furniture in the room.
Almost all convectors are wall-mounted, but some are also equipped with legs.


The wall-mounted version of the installation looks very aesthetically pleasing, but it will no longer work to transfer it from the bedroom to the hall or to the kitchen.
The main heating element of the convector is a spiral. Therefore, such devices also burn oxygen.


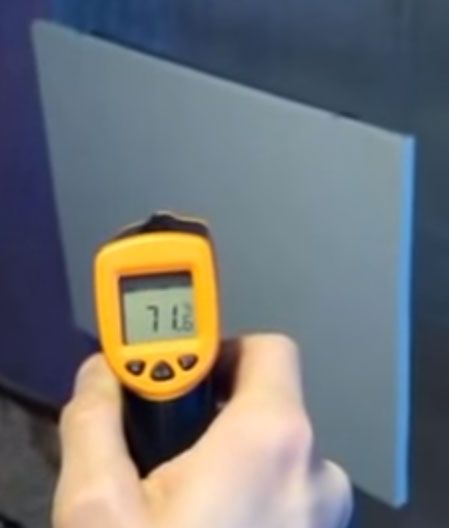
But in recent years, heaters with a tube consisting of a large number of fins have become increasingly used.


Due to this, even with prolonged operation, the case does not heat up more than 90 C. And for many models the temperature is even less than + 55-60 degrees.
Such options will be a good solution for families with small children.
The first number indicates that the device is protected from penetration of solid objects larger than 12mm into it. For example, the fingers of an adult's hand.
The second digit (4) indicates that the heater is protected against splashing water from any direction.


How much it will really cost you to heat your house with convectors as the main source of heat, you can find out from this video:
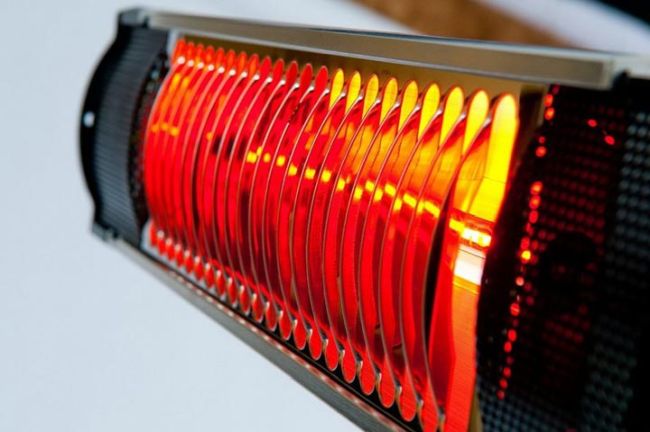
Most people are still wary of infrared models.Their principle of operation is somewhat similar to the sun.
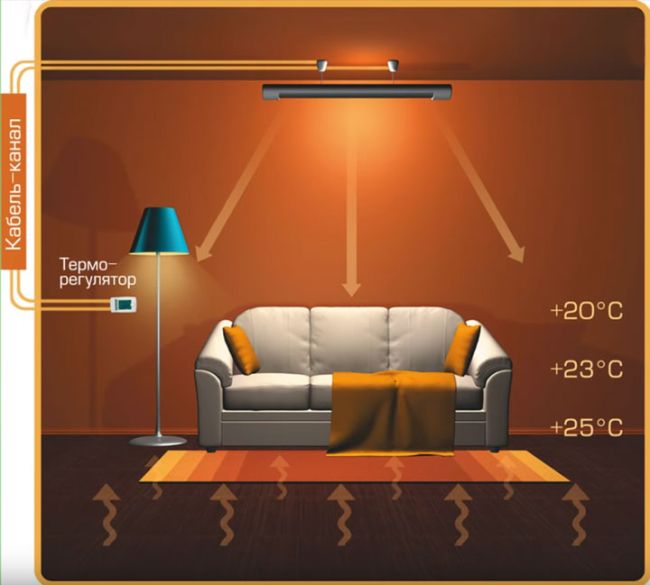

Infrared radiation of lamps heats not the air in the room, but the objects located in it, which then give off heat to the surrounding space. Heating occurs due to invisible rays in the infrared spectrum.
You need to get used to this. Feelings under the heater itself will be as if you are sitting near the stove. One side is fried and the other at room temperature.


To protect yourself from the effects of such equipment, follow the basic rules of use.
In addition, the infrared spectrum in excessive amounts can adversely affect the skin. Such a beam is able to penetrate to a depth of several centimeters under the skin and only then give off heat from the inside, heading towards the outer surface of the skin.
Everything here depends on the power of the source and the duration of being under it. If you follow the instructions, then you should not be afraid of such radiation. How can you protect yourself?
Most importantly, maintain a minimum distance from the infrared heater. It must be at least 2 meters.


The advantages of infrared technology include:
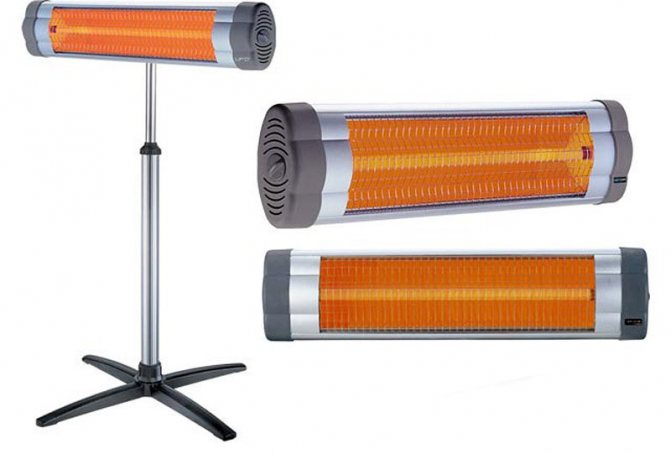
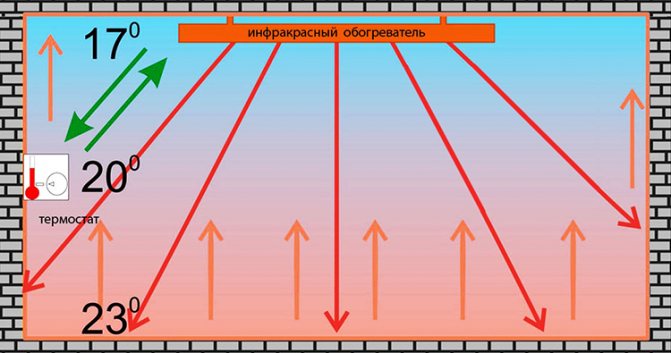
Infrared electric heaters
This is the most modern type of electrical devices for space heating. Its work is based on the emission of electromagnetic waves in the infrared spectrum. In this case, thermal energy is transferred from the device to those objects that are located nearby. The radiant energy reflected from them effectively heats the air in the room. This is probably the most economical type of electric heaters. In addition, such devices do not dry out the air. Some of them have a very nice decoration.

Ceiling infrared electric heater
Despite the high cost of electricity, the popularity of electric heaters is not decreasing. This is due to their convenience and, in many cases, to mobility, which is not available for gas equipment.