The greatest drawback of solid fuel boilers is their cyclicality: at maximum load and combustion, a peak (often excessive) thermal power is reached, which constantly decreases to 0 (complete attenuation) and is renewed by a new fuel load. This cycling does not allow for a stable, quickly and accurately controlled heating system.
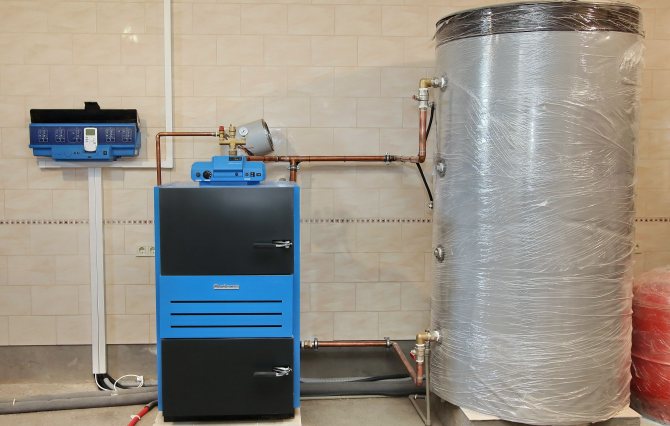
Smoothing the uneven heat transfer of the TT boilers allows the buffer tank (it is also a heat accumulator), which accumulates excess heat during peak operation of the boiler unit. However, there are many nuances in choosing and calculating the required volume of a heat accumulator.
What is a buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler
A buffer tank (also a heat accumulator) is a tank of a certain volume filled with a coolant, the purpose of which is to accumulate excess heat power and then distribute them more rationally in order to heat a house or provide hot water supply (DHW).
What is it for and how effective is it

Most often, the buffer tank is used with solid fuel boilers, which have a certain cyclicity, and this also applies to long-burning TT boilers. After ignition, the heat transfer of the fuel in the combustion chamber rapidly increases and reaches its peak values, after which the generation of thermal energy is extinguished, and when it dies out, when a new batch of fuel is not loaded, it stops altogether.
The only exceptions are bunker boilers with automatic feed, where, due to a regular uniform supply of fuel, combustion occurs with the same heat transfer.
With such a cyclicity, during the period of cooling or attenuation, thermal energy may not be enough to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house. At the same time, during the period of peak heat output, the temperature in the house is much higher than the comfortable one, and part of the excess heat from the combustion chamber simply flies out into the chimney, which is not the most efficient and economical use of fuel.

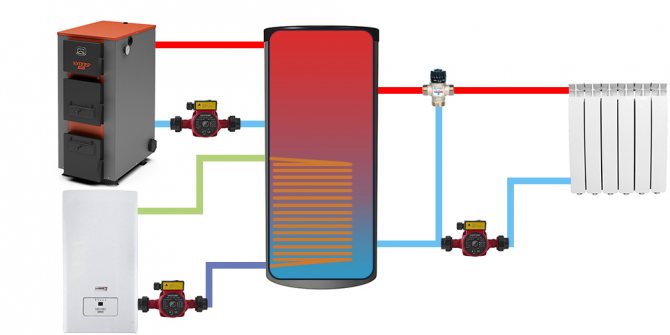
A visual diagram of the buffer tank connection, showing the principle of its operation.
The efficiency of the buffer tank is best understood on a specific example. One m3 of water (1000 l), when cooled by 1 ° C, releases 1-1.16 kW of heat. Let us take as an example an average house with a conventional masonry of 2 bricks with an area of 100 m2, the heat loss of which is approximately 10 kW. A 750 liter heat accumulator, heated by several tabs to 80 ° C and cooled to 40 ° C, will give the heating system about 30 kW of heat. For the aforementioned house, this is equal to 3 additional hours of battery heat.
Sometimes a buffer tank is also used in combination with an electric boiler, this is justified when heating at night: at reduced electricity tariffs. However, such a scheme is rarely justified, since in order to accumulate a sufficient amount of heat per night for daytime heating, a tank is needed not for 2 or even 3 thousand liters.
Device and principle of operation
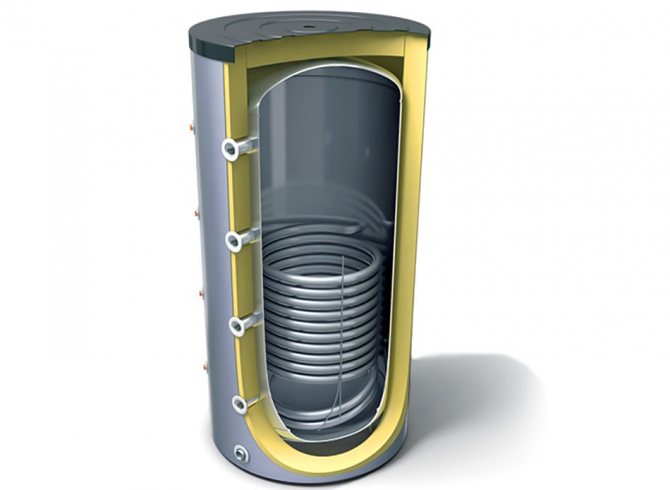


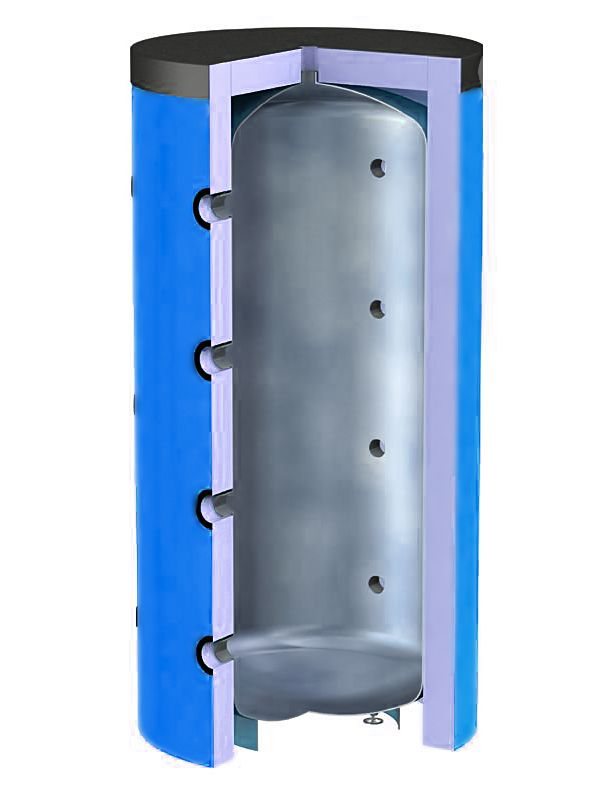
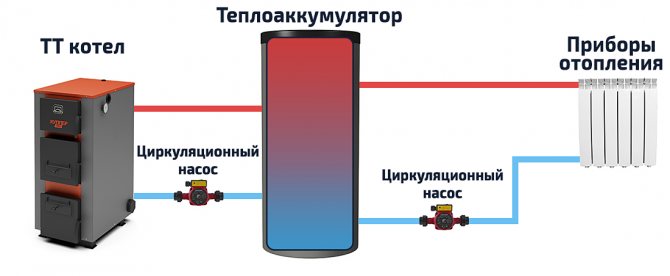
The heat accumulator is a sealed, as a rule, vertical cylindrical tank, sometimes additionally thermally insulated. He is an intermediary between the boiler and the heating devices. Standard models are equipped with a tie-in of 2 pairs of nozzles: first pair - boiler supply and return (small circuit); the second pair - the supply and return of the heating circuit, divorced around the house. The small circuit and the heating circuit do not overlap.
The principle of operation of a heat accumulator in conjunction with a solid fuel boiler is simple:
- After firing up the boiler, the circulation pump constantly pumps the coolant in a small circuit (between the boiler heat exchanger and the tank). The boiler supply is connected to the upper branch pipe of the heat accumulator, and the return to the lower one. Thanks to this, the entire buffer tank is smoothly filled with heated water, without a pronounced vertical movement of warm water.
- On the other hand, the supply to the heating radiators is connected to the top of the buffer tank, and the return is connected to the bottom. The heat carrier can circulate both without a pump (if the heating system is designed for natural circulation), and forcibly. Again, such a connection scheme minimizes vertical mixing, so the buffer tank transfers the accumulated heat to the batteries gradually and more evenly.
If the volume and other characteristics of the buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler are correctly selected, heat losses can be minimized, which will affect not only fuel economy, but also the comfort of the furnace. The accumulated heat in a well-insulated heat accumulator is retained for 30-40 hours or more.
Moreover, due to a sufficient volume, much larger than in the heating system, absolutely all the released heat is accumulated (in accordance with the boiler efficiency). Already after 1-3 hours of the furnace, even with complete damping, a fully "charged" heat accumulator is available.
Types of structures
| Photo | Buffer tank device | Description of distinctive features |
| Standard, previously described buffer tank with direct connection at the top and bottom. | Such designs are the cheapest and most commonly used. Suitable for standard heating systems where all circuits have the same maximum allowable operating pressure, the same heat carrier, and the temperature of the water heated by the boiler does not exceed the maximum allowable for radiators. |
| Buffer tank with an additional internal heat exchanger (usually in the form of a coil). | A device with an additional heat exchanger is necessary at a higher pressure of a small circuit, which is unacceptable for heating radiators. If an additional heat exchanger is connected with a separate pair of nozzles, an additional (second) heat source can be connected, for example, TT boiler + electric boiler. You can also separate the coolant (for example: water in the additional circuit; antifreeze in the heating system) | |
| Storage tank with an additional circuit and another circuit for DHW. The heat exchanger for hot water supply is made of alloys that do not violate sanitary standards and requirements for water used for cooking. | It is used as a replacement for a double-circuit boiler. In addition, it has the advantage of almost instantaneous hot water supply, while a double-circuit boiler requires 15-20 seconds to prepare it and deliver it to the point of consumption. |
| The design is similar to the previous one, however, the DHW heat exchanger is not made in the form of a coil, but in the form of a separate internal tank. | In addition to the benefits described above, the internal tank removes the limitations in hot water capacity. The entire volume of the DHW tank can be used for unlimited simultaneous consumption, after which time is required for heating. Usually, the volume of the internal tank is enough for at least 2-4 people bathing in a row. |
Any of the above types of buffer tanks can have a larger number of pairs of nozzles, which makes it possible to differentiate the parameters of the heating system by zones, additionally connect a water heated floor, etc.
HR batteries for UPS
Some batteries are specifically marketed by the manufacturer as batteries for UPS. With the same mass (and sometimes the same dimensions), these batteries, during short (10-30 minutes) discharges, give off more capacity than conventional batteries. The increase in the operating time of the UPS can be more than 50% (with discharge times of about 10 minutes).During long-term discharges, these "UPS batteries" have no advantage over conventional ones.
At CSB and some other manufacturers, such batteries are designated HR (from the English high rate - high rate, high power). These batteries can, of course, be used not only as batteries for UPS. They are beneficial for all applications where a compact power system with short battery life is required.
Reviews of household heat accumulators for boilers: advantages and disadvantages
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Much more efficient use of solid fuels, resulting in increased savings | The system is only justified with constant use. In case of intermittent residence in the house and kindling, for example, only on weekends, the system takes time to warm up. In the case of short-term work, the effectiveness will be questionable. |
| Extending cycle times and reducing the frequency of solid fuel filling | The system requires forced circulation, which is provided by a circulation pump. Accordingly, such a system is volatile. |
| Increased comfort due to more stable and customizable heating system operation | Additional funds are required to equip a heating system using an indirect heating boiler. The cost of inexpensive buffer tanks starts from 25 thousand rubles + security costs (a generator in case of a power outage and a voltage stabilizer, otherwise, in the absence of coolant circulation, at best, overheating and burnout of the boiler may occur). |
| Possibility of providing hot water supply | The buffer tank, especially for 750 liters or more, is of considerable size and requires an additional 2-4 m2 of space in the boiler room. |
| The ability to connect several heat sources, the ability to differentiate the coolant | To ensure maximum efficiency, the boiler must have at least 40-60% more power than the minimum required to heat the house. |
| Connecting a buffer tank is a simple process, it can be done without the involvement of specialists |
disadvantages
The large size of the storage tank makes it difficult to install in a standard residential building. The minimum buffer capacity is about 500 liters, and its installation will require 60 cm of free space at one and a half meters in height. The use of insulation for the construction works will take already 80 cm of living space. A tank for a ton of water will be one meter wide and two meters high, which is unlikely to allow you to carry it through the doors and put it in the room.


Installation of structures of this type requires the allocation of a separate room for the furnace. The final decision on the possibility of installation is made after the representatives of the construction organization visit the site.
How to choose a buffer tank


Calculation of the minimum required volume
The most important parameter that should be determined right away is the volume of the container. It should be as large as possible to maximize efficiency, but up to a certain threshold so that the boiler has enough power to “charge” it.
The calculation of the volume of the buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler is made according to the formula:
m = Q / (k * c * Δt)
- Where, m - the mass of the coolant, after calculating it is not difficult to convert it into liters (1 kg of water ~ 1 dm3);
- Q - the required amount of heat is calculated as: boiler power * period of its activity - heat loss at home * period of boiler activity;
- k - boiler efficiency;
- c - specific heat capacity of the coolant (for water, this is a known value - 4.19 kJ / kg * ° C = 1.16 kW / m3 * ° C);
- Δt - the temperature difference in the boiler supply and return pipes, readings are taken when the system is stable.
For example, for an average house with 2 bricks with an area of 100 m2, the heat loss is roughly 10 kW / h.Accordingly, the required amount of heat (Q) to maintain the balance = 10 kW. The house is heated by a 14 kW boiler with an efficiency of 88%, firewood in which burns out in 3 hours (the period of boiler activity). The temperature in the supply pipe is 85 ° C, and in the return pipe - 50 ° C.
First you need to calculate the required amount of heat.
Q = 14 * 3-10 * 3 = 12 kW.
As a result, m = 12 / 0.88 * 1.16 * (85-50) = 0.336 t = 0.336 cubic meters or 336 liters... This is the minimum required buffer capacity. With such a capacity, after the bookmark burns out (3 hours), the heat accumulator will accumulate and distribute further 12 kW of heat. For the example home, this is more than 1 extra hour of warm batteries on one tab.
Accordingly, the indicators depend on the quality of the fuel, the purity of the coolant, the accuracy of the initial data, therefore, in practice, the result may differ by 10-15%.
Calculator for calculating the minimum required heat storage capacity
Number of heat exchangers
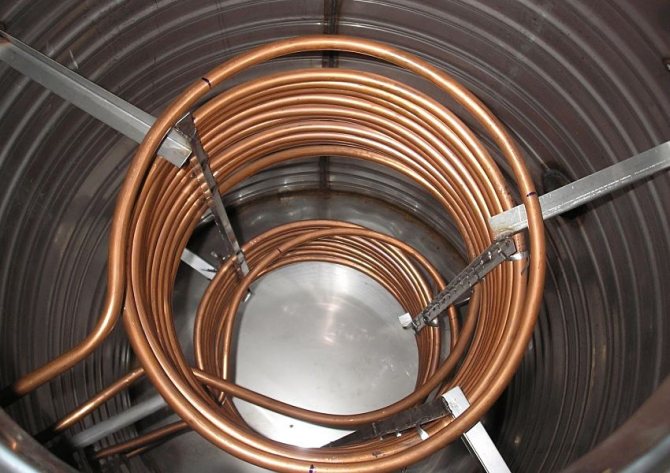


Copper internal heat exchangers of the storage tank.
After selecting the volume, the second thing you should pay attention to is the presence of heat exchangers and their number. The choice depends on the desires, requirements for CO and the tank connection diagram. For the simplest heating system, an empty model without heat exchangers is sufficient.
However, if natural circulation is planned in the heating circuit, an additional heat exchanger is needed, since the small boiler circuit can only function with forced circulation. The pressure is then higher than in a natural circulation heating circuit. Additional heat exchangers are also required to provide hot water supply or to connect underfloor heating.
Maximum allowable pressure
When choosing a buffer tank with an additional heat exchanger, you should pay attention to the maximum permissible operating pressure, which should not be lower than in any of the heating circuits. Tank models without heat exchangers are generally designed for internal pressures up to 6 bar, which is more than enough for the average CO.
Inner container material
At the moment, there are 2 options for manufacturing an internal tank:
- soft carbon steel - covered with a waterproof anti-corrosion coating, has a lower cost price, is used in inexpensive models;
- stainless steel - more expensive, but more reliable and durable.
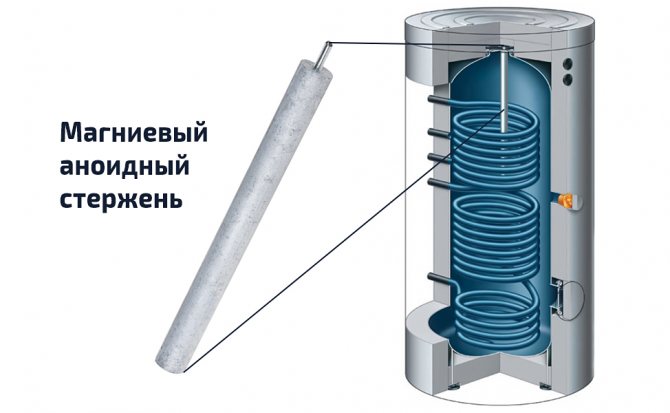
Some manufacturers also install additional wall protection in the container. Most often this is, for example, a magnesium anoid rod in the center of the tank, which protects the walls of the tank and heat exchangers from the growth of a layer of solid salts. However, such elements need periodic cleaning.

Other selection criteria
After determining with the main technical criteria, you can pay attention to additional parameters that increase the efficiency and comfort of use:
- the ability to connect a heating element for additional heating from the mains, as well as additional instrumentation, which are mounted with a threaded or sleeve (but in no case welded) connection;
- the presence of a layer of thermal insulation - in more expensive models of heat accumulators there is a layer of heat-insulating material between the inner tank and the outer shell, which contributes to even longer heat retention (up to 4-5 days);
- weight and dimensions - all of the above parameters affect the weight and dimensions of the buffer tank, so it is worthwhile to decide in advance how it will be entered into the boiler room.
Calculation of the heat accumulator
The calculation of the buffer storage capacity requires careful attention. First of all, it is necessary to determine for what purposes the container will be used.If to reduce the inertia during the operation of a solid fuel boiler, one formulas are used, for operation in the absence of electricity in heat pumps - others. First of all, consider a system with a solid fuel boiler.
Alternatively, you can apply the simplest formula, which allows you to approximately select the capacity of the tank, depending on the power of the boiler. For example, it is recommended to select the volume of the heat accumulator in the range of 40–80 liters per 1 kW of boiler power. This method is simple but not reliable.
Since during the heating season only a small part of the total heat demand is required, when using, taking into account the average outside air temperature during the heating period, you can select the optimal system mode. To do this, it is necessary to calculate the capacity according to which formula: V = 2246 * ((2.5-Qn / Q)) / (73-0.4 * T) * Qn (Qn is the calculated heating load for the object, T is the calculated temperature " return ").
The heat pump requires slightly different principles for choosing a buffer tank. Heat accumulators for such systems are selected based on different principles. For example, to optimize the operation of the system over time, you can use the ratio of 20–25 liters of usable volume of the heat accumulator for each kW of heat pump power.
A well-chosen and manufactured buffer tank will make it possible to arrange a comfortable heating system without unnecessary consumption of electricity, fuel and money.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Sunsystem PS 200
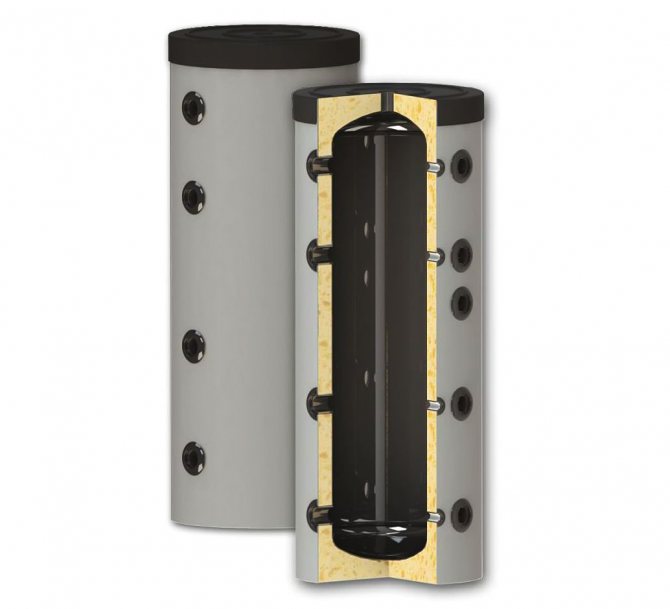


A standard inexpensive heat accumulator, perfect for a solid fuel boiler in a small private house with an area of up to 100-120 m2. By design, this is an ordinary tank, without heat exchangers. The volume of the container is 200 liters at a maximum allowable pressure of 3 bar. For a low cost, the model has a 50 mm layer of polyurethane thermal insulation, the ability to connect a heating element.
Price: an average of 30,000 rubles.
Hajdu AQ PT 500 C
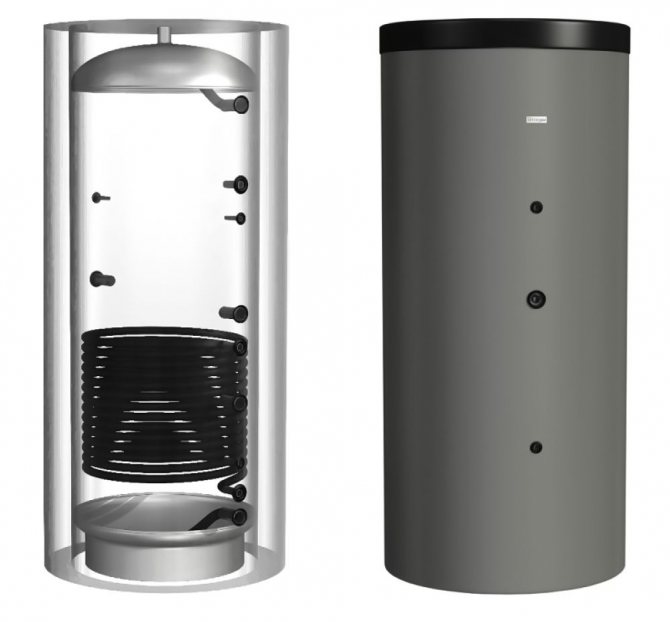


One of the best models of buffer tanks for its price, equipped with one built-in heat exchanger. Volume - 500 l, allowable pressure - 3 bar. An excellent option for a house with an area of 150-300 m2 with a large power reserve of a solid fuel boiler. The line includes models of different sizes.
From a volume of 500 liters, the models (optionally) are equipped with a layer of polyurethane thermal insulation + a casing made of artificial leather. Installation of heating elements is possible. The model is known for extremely positive owner reviews, reliability and durability. Country of origin: Hungary.
The cost: 36,000 rubles.
S-TANK AT PRESTIGE 300
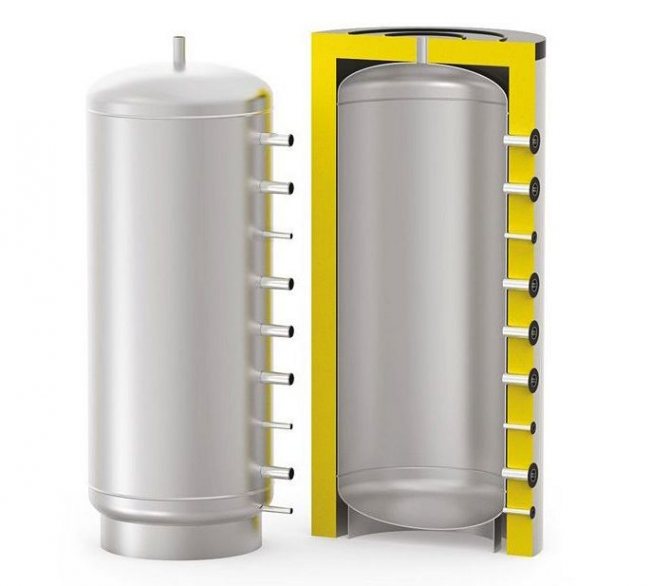


Another inexpensive 300 liter buffer tank. By design, it is a storage tank without additional heat exchangers with a maximum permissible operating pressure of 6 bar. The inner walls, as in the previous cases, are made of carbon steel. The main difference is a significant, environmentally friendly layer of thermal insulation made of polyester material according to the NOFIRE technology, i.e. high class heat and fire resistance. Country of origin: Belarus
The cost: 39,000 rubles.
ACV LCA 750 1 CO TP
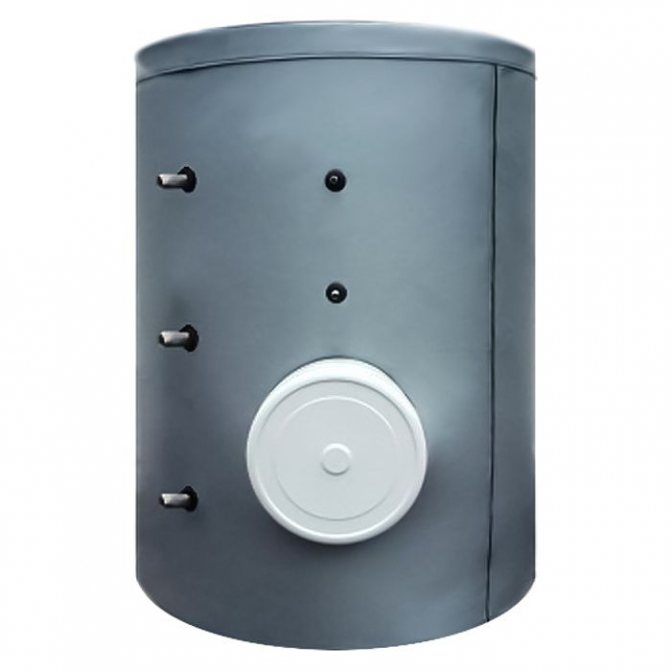


A high-performance, expensive 750 l buffer tank with an additional tubular heat exchanger for hot water supply, designed for boilers with a large power reserve.
The inner walls are covered with protective enamel, there is a high-quality 100 mm thermal insulation layer. A magnesium anode is installed inside the tank, which prevents the accumulation of a layer of solid salts (there are 3 spare anodes in the kit). Installation of heating elements and additional instrumentation is possible. Country of origin: Belgium.
The cost: 168,000 rubles.
Benefits
A significant advantage of storage tanks is the ability to connect them to several heating devices.
Adding a thermostat to the working circuit will allow you to adjust the priority of turning on the heaters, as well as turning them off in case of sufficient temperature.


Additional advantages of such designs include:
- increasing the safety of the structure due to its automation;
- regulation of the temperature of the building on each of its floors;
- minimum costs for connecting gas or solid fuel boilers;
- ease of additional installation of a heat pump or solar collectors.
Prices: summary table
| Model | Volume, l | Permissible operating pressure, bar | Cost, rub |
| Sunsystem PS 200, Bulgaria | 200 | 3 | 30 000 |
| Hajdu AQ PT 500 C, Hungary | 500 | 3 | 36 000 |
| S-TANK AT PRESTIGE 300, Belarus | 300 | 6 | 39 000 |
| ACV LCA 750 1 CO TP, Belgium | 750 | 8 | 168 000 |
The main types of batteries
There are 3 leading battery technologies: lead acid, alkaline and lithium ion. Each of these technologies has its own unique advantages and disadvantages that determine their application in different cases. See the links for more details on each of the battery types:
- lead-acid starter (automobile)
- AGM (sealed)
- sealed gel
- sealed gel with tubular electrodes (OPzV)
- jellied with spreading plates (OPzS series)
- traction (usually with liquid electrolyte)
- carbon
- nickel iron
Lead acid batteries


The most common type of AB are lead acid
, both with liquid electrolyte, and sealed (recently become more and more popular due to price reductions).
Special batteries with spreading plates
for use in autonomous power supply systems, they are often assembled from separate 2-volt batteries connected together. ABs of smaller capacity with a voltage of 6 and 12 volts are also used, but less often. These batteries are mainly produced in Europe and the USA. They are comparatively expensive. Recently, such Chinese-made batteries have appeared on the Russian market. With practically the same characteristics, Chinese batteries are significantly (one and a half to two times) cheaper.
Traction batteries
, both with liquid electrolyte and sealed, are designed for cyclic operation. The deep cycle modifications have similar parameters. They are more suitable for autonomous power supply systems. They are more expensive than conventional sealed batteries, but they also have a longer service life.
Sealed Lead Acid Batteries have the same principle of operation as conventional car starter batteries. This is the most mature technology, and for some unique parameters, no replacement has yet been found. These batteries should not be disposed of in landfills as they contain highly toxic lead and sulfuric acid. However, they are very easy to recycle and the lead can be reused. These batteries charge much more slowly than other batteries (about 5 times slower), but they are able to provide much more power to power powerful consumers.
The biggest disadvantage of lead acid batteries is their weight. Because of this, they have the worst performance in terms of specific energy density. However, the wide distribution of the elements used in these batteries and the simplicity of their production determine not only their widespread use, but also a much lower price.
Various types of lead-acid batteries are discussed in detail in the article "Types of lead-acid batteries".
Alkaline batteries


An acidic battery does not tolerate deep discharge, but does not mind recharging in portions at every opportunity.Alkaline, on the contrary, does not like to give high currents, but currents in the amount of about 1/10 of the capacity are ready to give out for a long time and to the point of exhaustion. That is, it not only allows a full discharge, but also welcomes in every possible way (because if you charge a fully discharged alkaline battery, it will not gain full capacity - the so-called "memory effect" is most pronounced in nickel-cadmium batteries). In short, you cannot charge / discharge an alkaline battery in portions - only "from and to". But with proper operation (in addition to charging / discharging, it implies flushing the cans and replacing the electrolyte once a season), alkalis serve up to 20 years (more precisely, 1000-1500 full cycles). Also, alkaline batteries do not charge well at low currents. That is, the current flows through them, but there is no charge.
This explains the fact that alkaline batteries are not widely used in autonomous power supply systems with renewable energy sources. Nickel cadmium and nickel metal hydride sealed batteries
can be used in some cases. Although they are much more expensive than acid ones, they have a very long service life and have a more stable voltage during the discharge process. They are usually used in portable or mobile power supplies. allow you to store more energy per kg of weight.
NiMh batteries hit the mainstream market in the 1980s as a cleaner alternative to nickel cadmium batteries. NiCd batteries use the highly toxic element cadmium in their composition, and since the mainstream consumer does not really think about disposing of used batteries, this posed a big problem for the environment. The disadvantages of NiMh batteries are their relatively high self-discharge, which results in a loss of approximately 30% of the energy within 1 month. They also charge up to 2x longer than lithium or nickel cadmium batteries.


Although the electrical parameters of NiMh batteries are not as good as those of NiCd, NiMH batteries are more stable and suffer less from the "memory effect" of NiCd batteries. They do not need to be fully discharged before recharging as NiCd batteries require this to prevent internal crystal growth that leads to cracking of the NiCd battery case. AA NiMh batteries are the same as conventional alkaline batteries and are therefore most popular for use in digital cameras and cameras, portable players, radios and flashlights.
Nickel-cadmium and nickel-iron batteries with liquid electrolyte are cheaper than sealed ones, but contain liquid electrolyte, emit gases during charging and require periodic maintenance and a special ventilated room. The cost of stored energy in a charge-discharge cycle is comparable to or even cheaper than sealed lead-acid batteries.
We recommend using nickel-iron batteries (usually they are used as traction batteries in electric vehicles, as well as on the railway) only in one case - as part of an autonomous diesel-battery system, in which the fuel generator is the only source of energy. We know from our experience that lead-acid batteries do not last long in such systems - deep cycles and chronic undercharging do their dirty work. Under these operating conditions, you can put up with such disadvantages of alkaline batteries as the impossibility of charging with low currents (you can set any from the generator, and even better if the current is large, it will charge faster), the memory effect (the cycles will be just deep) and low charge efficiency. For the generator system, the memory effect is not important - the batteries are discharged as much as possible in order to start the generator as rarely as possible.
As for the efficiency - if alkaline batteries can be charged with a high current, then its low efficiency will more than pay off with a more efficient operating mode of the generator. After all, for recharging lead batteries, it is required to charge them with low currents for a long time, i.e. almost idling of the generator. And in alkaline charging limits, this is the temperature of the batteries, as well as gas evolution.
We emphasize once again that alkaline batteries are not suitable for every backup or autonomous system. If there are solar panels or wind turbines, i.e. sources that produce different currents, incl. and it makes no sense to put small, alkaline batteries - the energy of small currents will simply be lost without benefit.
Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries
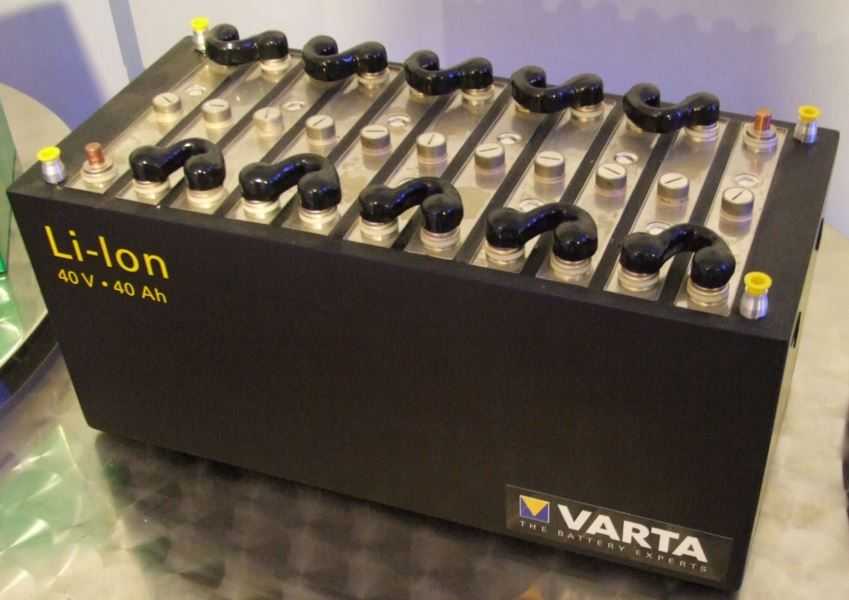


It is one of the newer technologies and is developing faster than others. There are several variations on the chemical processes of lithium-ion technologies, but their discussion is not covered here. Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in small electronic devices such as mobile phones, gadgets and audio players, electronic watches, PDAs and laptops. These batteries supply very well with low power for a long time. They have a very high specific charge density, which means they can store a significant amount of electrical energy in a small volume. However, this concentration of energy results in a certain vulnerability of lithium-ion batteries.
The process chemistry of lithium-ion batteries requires strict adherence to manufacturing techniques, and contamination in the manufacture of these batteries often results in battery degradation. Many may remember recalling thousands of Dell and Apple laptops in the summer of 2006 when their Sony-made batteries were found to contain contaminants that could cause them to overheat. Lithium batteries do not tolerate overheating, so they often have built-in electronic circuits that ensure their safety by preventing overcharging - the charge stops when the voltage reaches its limit.
The lithium polymer batteries that have been developed recently are the 'dry' version of lithium-ion batteries. They behave better at high temperatures (over 25C) and also allow the manufacture of extremely flat batteries, down to the thickness of a credit card. Due to the nature of their manufacturing technology, these batteries are very expensive and rarely justified compared to more conventional lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are best suited for power systems. See the link for detailed information on this type of battery. You can buy such batteries in our store.
Recently, relatively inexpensive lithium-iron-phosphate batteries manufactured by the Liotech plant have appeared on the Russian market. The produced capacities are from 250 A * h, therefore their use is limited by relatively powerful systems of autonomous or backup power supply. Also, there are mixed reviews about these batteries.
One of the latest developments is lithium titanate batteries. They have a service life of up to 25,000 thousand cycles.
Wiring and connection diagrams
| Simplified pictorial diagram (click to enlarge) | Description |
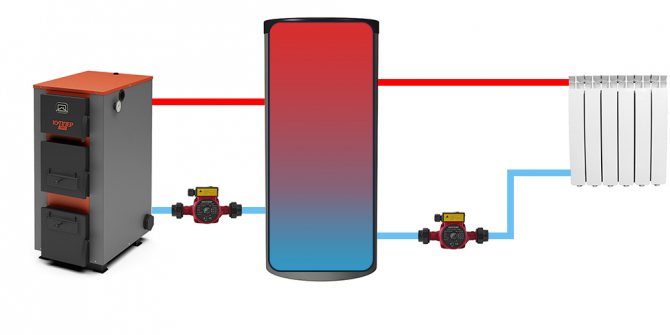
| Standard wiring diagram for "empty" buffer tanks to a solid fuel boiler. It is used when the heating system (in both circuits: before and after the tank) has a single heat carrier, the same permissible operating pressure. |
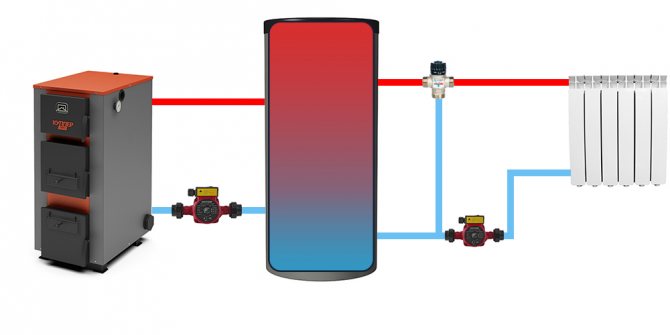
| The scheme is similar to the previous one, but assuming the installation of a thermostatic three-way valve. With such an arrangement, the temperature of the heating devices can be adjusted, which makes it possible to use the heat accumulated in the tank even more economically. |
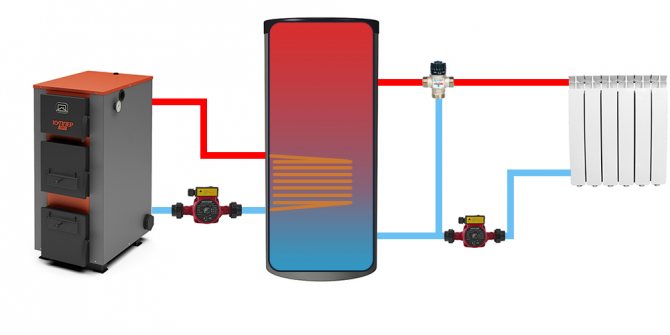
| Connection diagram for heat accumulators with additional heat exchangers.As already mentioned more than once, it is used in the case when a different coolant or higher operating pressure is supposed to be used in a small circuit. |
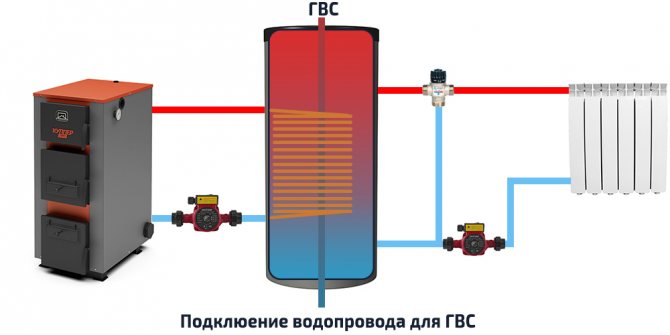
| Diagram of the organization of hot water supply (if there is a corresponding heat exchanger in the tank). |
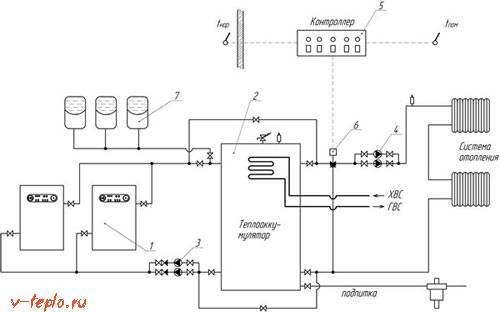
| The scheme assuming the use of 2 independent sources of thermal energy. In the example, this is an electric boiler. Sources are connected in order of decreasing thermal head (top-down). In the example, first comes the main source - a solid fuel boiler, below - an auxiliary electric boiler. |
As an additional source of heat, for example, instead of an electric boiler, a tubular electric heater (TEN) can be used. In most modern models, it is already provided for its installation by means of a flange or coupling. By installing a heating element in the corresponding branch pipe, you can partially replace the electric boiler or once again do without kindling a solid fuel boiler.
It is important to understand that these are simplified, not complete wiring diagrams. To ensure control, accounting and safety of the system, a safety group is installed at the boiler supply. In addition, it is important to take care of the operation of the CO in the event of a power outage, since there is not enough energy to power the circulation pump from the thermocouple of non-volatile boilers. The lack of circulation of the coolant and the accumulation of heat in the heat exchanger of the boiler will most likely lead to a rupture of the circuit and an emergency emptying of the system, it is possible that the boiler burns out.
Therefore, for the sake of safety, you need to take care of ensuring the operation of the system at least until the bookmark is completely burned out. For this, a generator is used, the power of which is selected depending on the characteristics of the boiler and the duration of combustion of 1 fuel insert.
Difference from the standard heating scheme
The system, equipped with a heat accumulator for hot water heating, works on a completely different principle. The device is not complicated, it is mounted quickly enough. Its installation will solve several important tasks at once for the life support of homeownership.
In order for the system to work differently, it is required to install a storage tank for the boiler with multi-layer effective thermal insulation between the boiler and the pipelines through which the water rushes to the radiators.
Inside the tank there are various heat exchangers for hot water supply and heating systems. The water heated by the boiler inside the accumulator will remain hot for a long time. It will be gradually distributed through two channels at once: water supply and heating.


Using the example of a tank capacity of 350 liters, one can imagine the fuel economy. An accumulator that meets the heating and hot water needs of one standard household may have:
- volume from 350 to 3500 liters;
- diameter from 0.7 m. to 1.8 m .;
- height from 1.8 m to 5.6 m.
Heat exchangers for hot water supply and heating system are installed in the accumulator. Safety devices require special attention:
- pressure gauge;
- valve group;
- air outlet nozzles,
In addition, the accumulator is equipped with temperature and pressure control devices. All this allows him to regulate important processes related to the provision of hot water and space heating.
How to connect
A person who has come across the device of heating systems many times should easily make a heat accumulator with his own hands and make further connections. Such work should not be too difficult for a beginner.

In words, the connection diagram can be described as follows:
- In transit through the entire tank, a return pipeline must pass through the heat accumulator, at its ends a one and a half-inch inlet and outlet must be provided
- First, the boiler return and the tank are connected to each other. Between them there should be a circulation pump that drives water from the barrel to the shut-off valve, expansion tank and heater.
- The circulation pump and shut-off valve are also mounted on the second side
- It is necessary to connect the supply pipeline by analogy with the previous one, but now the heat pumps are not installed
It is worth noting that in this way the heat accumulator is connected to a heating system operating on the basis of only one boiler. If their number increases, the scheme will become much more complicated.
The container must be additionally equipped with a thermometer, pressure sensors inside and an explosion valve. By constantly accumulating heat, the barrel can overheat over time. Overpressure must be relieved periodically to prevent explosion.
Heat accumulator and different types of heating systems
The heat accumulator can be installed in conjunction with various heating systems. Interacting with each of them, it provides a number of advantages and pays off quickly.
The most common are heat accumulators, installed together with heating equipment operating on solid fuels, in which the amount of residues is minimal. Having brought the efficiency to the maximum possible, they very quickly heat up the heating radiators, which soon wear out. It is better to save part of the generated energy and use it when the need really arises.


The double night electricity tariff is a problem for owners of electric boilers. Thus, in the daytime, the heat accumulator will accumulate heat in itself at a more favorable cost, and at night it will give it to the heating system.
Similar installations are used in multi-circuit systems, distributing water between the circuits. If the pipes are installed at different heights, it is possible to extract water at different temperatures.
Modernization options
Looking at the simplest heat accumulator with his own hands, a person with an engineering education will probably think about the options for its modernization. This can be done in the following ways:
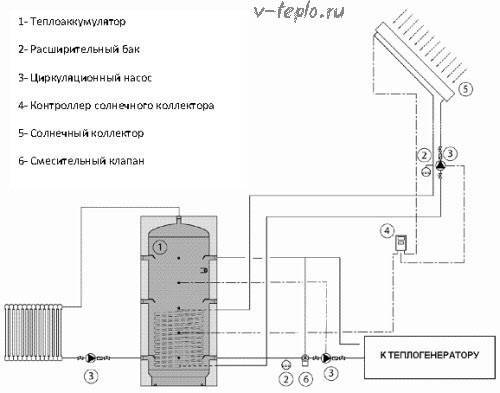

- Another heat exchanger is installed below, through which the energy received by the solar collector can be accumulated.
- It is possible to divide the inner space of the tank into several sections, communicating with each other, so that the stratification of the liquid by temperature is more pronounced
- To spend money on thermal insulation or not - everyone decides for himself. But a few centimeters of polyurethane foam will significantly reduce heat loss.
- By increasing the number of branch pipes, it will be possible to mount the unit to more complex heating systems with several circuits operating independently.
- An additional heat exchanger can be made in which drinking water will accumulate
Video - Heat accumulator in a house with a periodic firebox
https://youtube.com/watch?v=rgMQG7RLCew
Summing up
Absolutely everyone can collect heat accumulators with their own hands. There is no need for him to buy expensive equipment, and the simplest model consists of components that a good person always has in the garage or pantry.
All those who do not trust home-made devices can familiarize themselves with a wide selection of models in the markets. Their cost is more than acceptable, and the invested funds quickly pay off.