The use of heating systems with a liquid heat carrier in private houses today is based on several schemes of the system. One of the most reliable, simple and time-tested schemes is the gravitational heating system. Based on the laws of thermodynamics, gravitational heating has become widespread due to the small number of elements and the ease of work, both in terms of project calculation and practical installation. But, despite the seeming simplicity, for correct operation, it is necessary to take into account many points, which will be discussed in this article.
The principle of operation of the gravitational heating system of a private house
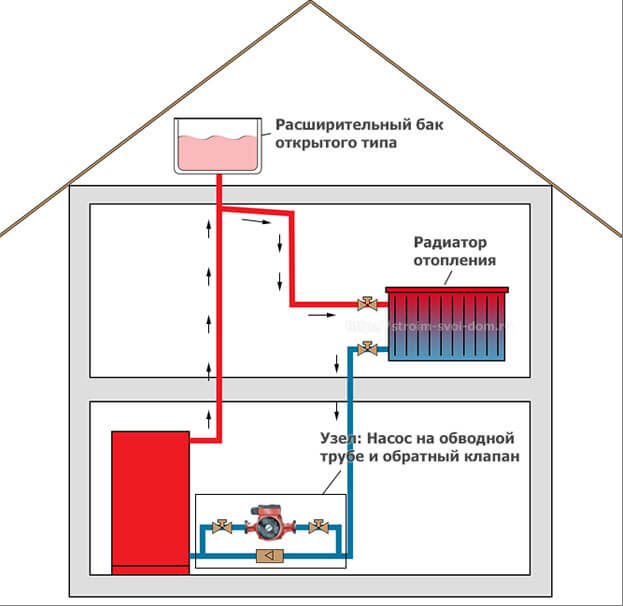
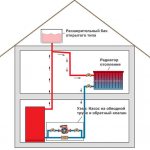
The gravitational heating system of a private house is based on two physical principles. The first is that substances have different densities at different temperatures. The second is that the pressure in the system is created due to the difference in the levels of the liquid, and the greater the difference between the upper and lower points, the higher the pressure in the system.
The first principle of a gravitational heating system is expressed in the fact that when heating a liquid heat carrier, and it does not have to be water, it changes its density. Water in its normal state at a temperature of 20 degrees has a density greater than that heated to 45 degrees; when heated to 80 degrees, the difference will be such that additional volume is required for water. In this case, the coolant of the same mass will occupy a different volume, because of which it begins to expand and be displaced outside the heat exchanger. In a confined space, after the start of the movement of the heated coolant, its place is taken by the cooled coolant. So, under the influence of heating, a flow arises, and the gravitational heating system begins to work.
The second principle of operation of this circuit begins to work from the moment the coolant begins to move. As it warms up, near water or antifreeze, the speed of movement increases, since the temperature rises quickly and the expansion of the volume forces the liquid to be forced out of the boiler water jacket at a higher speed. Leaving the volume of the boiler, the liquid escapes along a vertical pipe to the expansion tank. Having reached the level of the branch, the liquid fills the volume of the pipe and rushes along the pressure loop to the pipelines leading to the heating radiators, creating the necessary pressure. Considering the difference in height between the point where the liquid enters the pressure loop and the lower point of discharge, the pressure created additionally affects the cold heat carrier.
By gradually warming up, the system reduces the temperature difference between the cold and hot coolant, and thus, the speed of fluid movement in the system increases to its maximum and can even reach 1 meter per second.
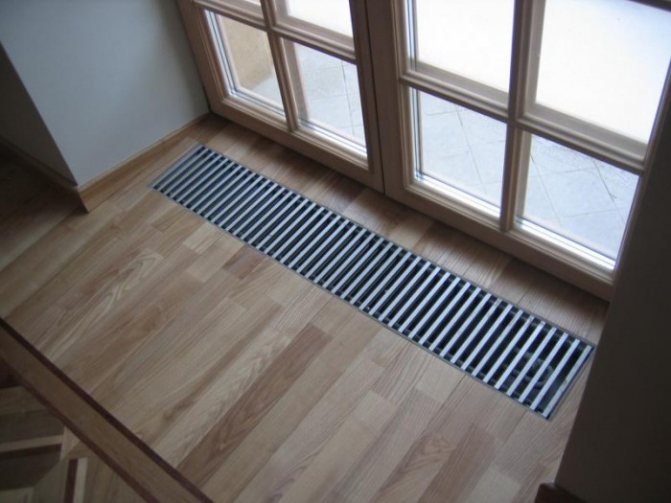
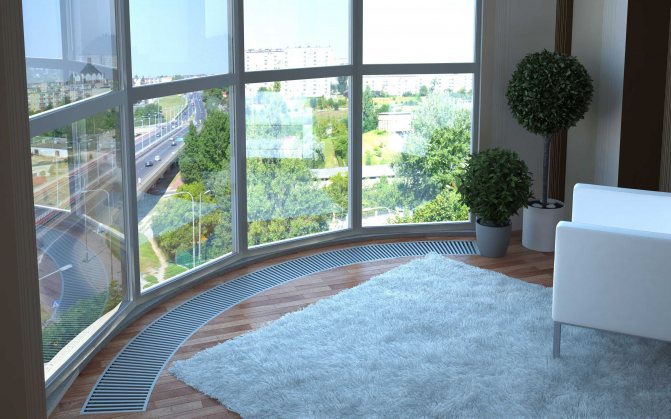
Types of floor convectors
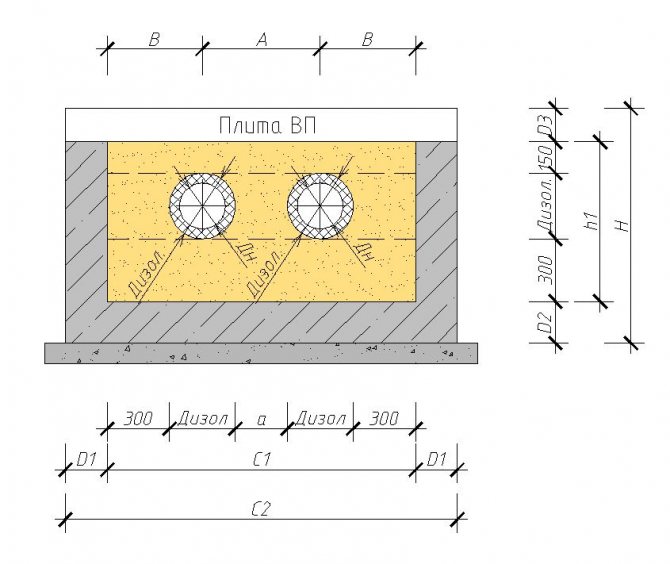
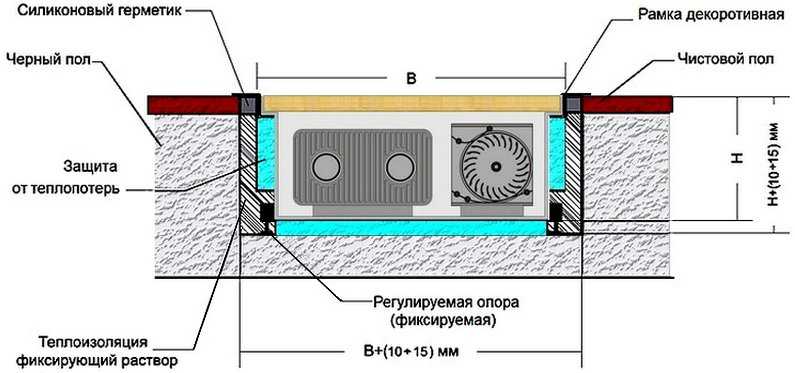
There are two types of built-in convectors - electric and water. Electric ones are independent of the heating system, but if there is no electricity, they do not work. Installation of electric convectors built into the floor is easier. If there is a niche under the case, supply the power, insert it, fill it with a solution, after the solution has dried, you can use it.
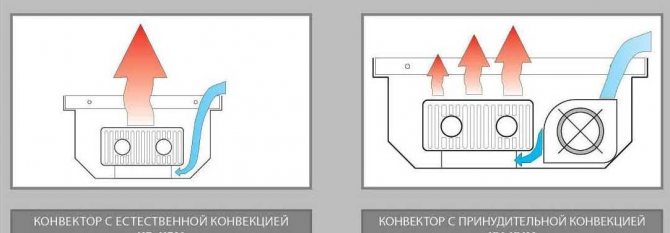

With a fan, much more heat dissipation
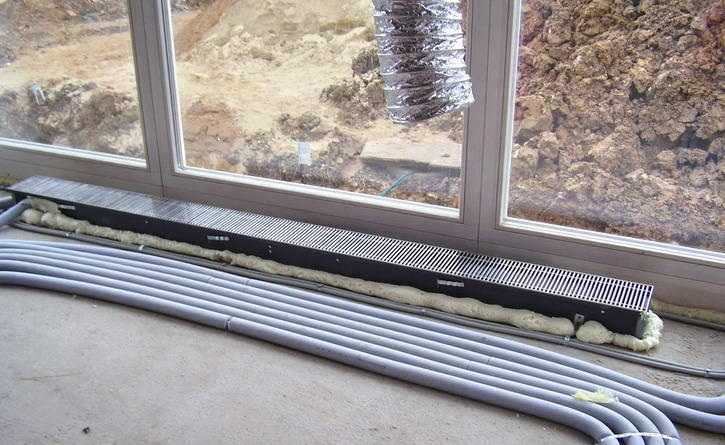
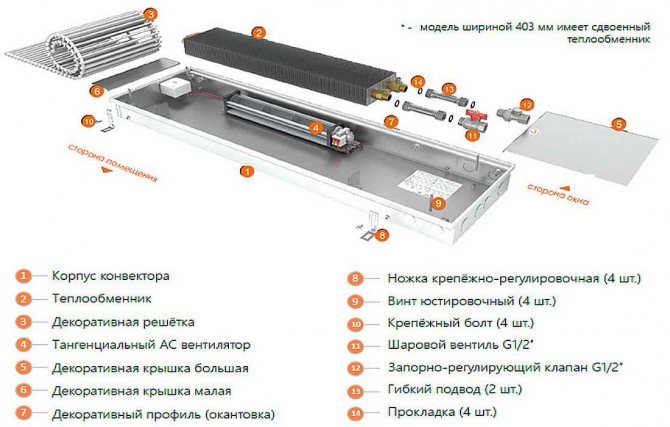
Water convectors recessed into the floor are connected to the heating system. At the same time, the heating pipes are laid on the floor. Radiation wiring is more effective - this is when a pair of pipes goes to each radiator - supply and return.With this method, somewhere in an apartment or in a private house, a water collector is installed, pipes from radiators are connected to it. With this scheme, a coolant of the same temperature is supplied to each of the devices. The reliability of such a scheme is higher - if something happens, only one device does not work. Minus - high costs at the installation stage - more pipes are needed.
Despite the complexity of installation and connection, floor heating is often done with water convectors. Still, heating costs are lower. Invest once during installation, then just enjoy the warmth. Here is the approximate logic behind this choice.
Gravity heating the advantages of a gravity heating system

Before considering the positive qualities of gravity heating systems with natural water circulation, it is worth considering separately all the disadvantages of the system. For many, the first and main drawback of the gravitational heating system is its archaism. Indeed, this is one of the most ancient heating systems using a liquid heat carrier. It was from this system that one and two-pipe wiring schemes were subsequently developed, it was this system that was used for mass installation, when the industry mastered solid fuel heating and, a little later, gas heating boilers. But on the other hand, the gravitational heating system is also one of the most reliable - its service life is on average 45-50 years. That is, exactly as long as it takes for the metal pipes to lose their tightness under the influence of the coolant.
The second point is the low efficiency of the gravitational heating system. Indeed, the scheme itself, based on the natural circulation of water, implies the inertia of the process of heating the room, until the heating boiler picks up the required power, and the temperature difference between the heated and cooled coolant reaches a minimum, it will take quite a long time. But on the other hand, even after the boiler stops supporting combustion, the circulation process continues, while a large volume of water in the system will cool down much longer than in a forced circulation system.
Another disadvantage can be written into its asset by the gravitational heating system due to its bulkiness. In practice, with the same area of the heated room, a system with forced circulation compared to gravity will take up much less space. In the gravitational heating system, in addition to batteries, pipes of the upper distribution will also be placed, without which the creation of the necessary fluid pressure is impossible.
And of course, the issue of temperature control in individual radiators, and the possibility of adjusting it. A gravitational heating system in the classic form with a one-pipe construction scheme cannot provide such a function due to the impossibility of shutting off a separate radiator.
But on the other hand, it is an ideal system for installation in homes where there is no electricity or there are constant problems with its supply. The gravitational heating system is capable of operating without electricity, since the main force of movement of the coolant through the system is not the circulation pump, but the thermal expansion of the volume of the coolant.
A large volume of coolant in the system allows for smooth heating of the room. On the other hand, such a volume of heated coolant cools down much more slowly than the volume of a forced circulation system. This is especially pronounced when there is a power outage or damping of fuel in the firebox. A forced circulation system cools down 3-4 times faster than such an archaic gravity heating system.
This property is often used when temporarily staying in the house - just instead of ordinary water, antifreeze is poured into the system, and even after complete cooling, neither pipes nor radiators are threatened with rupture due to freezing of water.
And of course, it just needs to be noted that such a system is simply trouble-free in operation. With proper operation, it can last for about 50 years, while it has only two risk factors. The first is the threat of boiler overheating, but even here it mainly depends on the human factor, and not on the system. The second is the freezing of the coolant, but in this case, the use of antifreeze reduces the risk of this accident to almost zero.
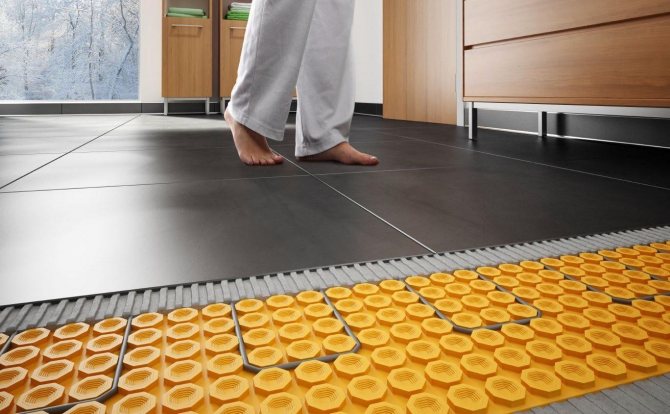
What is the best underfloor heating?
Today, there are two main types of underfloor heating - water and electric. The latter, in turn, is presented in three variations: rod, cable and film. Each has its own pros and cons.
The choice of a specific option directly depends on the conditions and the possibility of installation. Assessing the main advantages of a warm floor, not taking into account its specific type, the following can be noted:
- livability of the system. In simple terms, a warm floor is able to maintain the most comfortable temperature in the room for staying in it. Unlike traditional heating systems, there will be no room for local overheating or barely warmed up areas;
- underfloor heating aesthetics. There are no visible elements of the heating system. Here it is not required to link it to the arrangement of furniture inside the room. You can enjoy a warm floor without radiators and get more free space for decorating your home;
- versatility. You can use any energy source (electric or water heat-insulated floor), any type of heat carrier (in the case of a water-heated floor) and any floor covering;
- human safety and health. A significant advantage of a warm floor is the absence of dust circulation inside the room, which is a real salvation for people with allergies;
- profitability. Optimum temperature distribution can significantly reduce heating costs. Unlike traditional heating systems, underfloor heating does not heat the space above the ceiling, but the floor and the surface above it. Therefore, all rooms will have very comfortable conditions.
We recommend: How is the underfloor heating sensor installed?
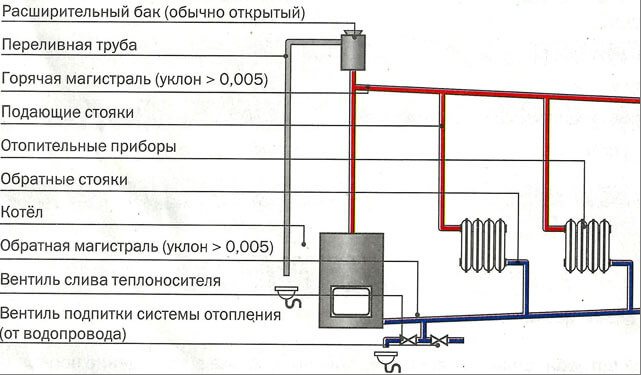
A simplified version of the heating system with natural circulation of the heat carrier

When choosing a private gravitational heating system, it is necessary to carry out a number of calculations in order to understand how the system will provide heating of the room. Under normal conditions, the volume of individual rooms and the power of heating radiators installed in them are taken into account in the layout of the piping layout. When installing radiators of the same rating, the gravitational heating system will heat up the rooms unevenly. The first radiator closest to the boiler will heat up more, and in the radiator farthest from the boiler, the coolant temperature will be significantly lower. That is why, when selecting heating devices, the former are installed with a lower power, and those that are farther must be more powerful.
It is important to choose the right expansion tank in the choice of structural elements. When calculating the volume of the expansion tank, it is customary to take the ratio 1/10 as the basis. That is, when the volume of water in the system is about 250 liters, the volume of the tank must be at least 25 liters.
The gravitational heating system is very demanding on the materials of construction. First of all, this applies to pipes and pipelines. The large volume of the coolant and the low pressure in the system require that the circulation be carried out with the lowest losses, and this is possible, either in steel or in polypropylene pipes. But here, too, there are certain limitations.So, steel pipes must be connected either by gas or electric welding, or by means of threaded connections. And if the first type allows you to provide a reliable connection practically without obtaining a weld inside the pipe, then the threaded method can create a large number of irregularities inside the pipeline. As for the polypropylene pipe, it has one significant drawback. This disadvantage concerns the ability of the pipe to withstand high temperatures - the maximum temperature that such a pipe can withstand is +95 degrees, which is not suitable for a pipe installed immediately after the boiler.
But even in spite of all these caveats, a simplified diagram of a gravitational heating system is significantly different from a forced circulation system.
Such a system must necessarily include:
- Heating boiler (a prerequisite for such systems is the presence of a boiler with a large volume of a hot water jacket);
- Large diameter water pipes 11/2 inches;
- Expansion tank with a capacity of 1/10 of the volume of liquid in the system;
- Supply pipes with a diameter of 1 inch;
- Radiators of different sizes to ensure uniform heating of the premises;
- Return pipe;
- Liquid drain cock;
- A thermometer and a pressure gauge in the boiler, and Mayevsky's taps in the radiators are installed as control devices in the system.
As you can see, the system has a small number of structural elements and is quite suitable for assembling it yourself.
Parsing the circuit
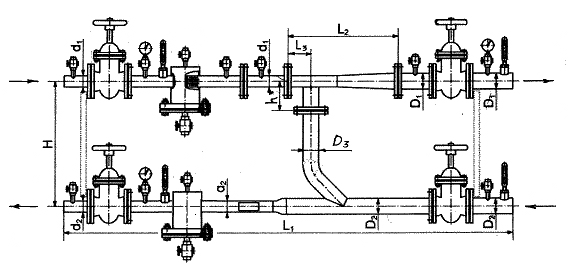
As you understand, the unit consists of filters, an elevator, instrumentation and fittings. If you plan to independently install this system, then it is worth understanding the diagram. A good example would be a high-rise building, in the basement of which there is always an elevator unit.
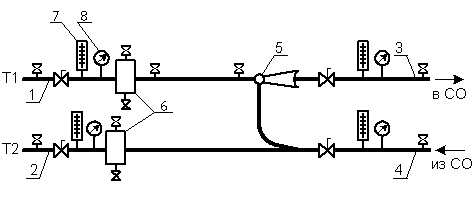

On the diagram, the elements of the system are marked with numbers:
1, 2 - these numbers indicate the supply and return pipelines that are installed in the heating plant.
3.4 - supply and return pipelines installed in the heating system of the building (in our case, this is a multi-storey building).
5 - elevator.
6 - this number denotes coarse filters, which are also known as mud collectors.
7 - thermometers
8 - manometers.
The standard composition of this heating system includes control devices, mud collectors, elevators and valves. Depending on the design and purpose, additional elements can be added to the node.
Interesting! Today, in multi-storey and apartment buildings, one can find elevator units that are equipped with an electric drive. This upgrade is needed in order to adjust the nozzle diameter. The heat carrier can be corrected by means of an electric drive.
It is worth saying that every year utilities are becoming more expensive, this also applies to private houses. As a result, system manufacturers supply them with energy-saving devices. For example, now the circuit can contain flow and pressure regulators, circulation pumps, elements for protecting pipes and water purification, as well as automation aimed at maintaining a comfortable mode.

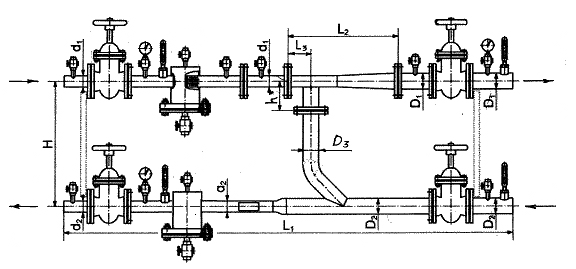

Another variant of the scheme of a thermal elevator unit for a multi-storey building.
Also, in modern systems, a thermal energy metering unit can be installed. From the name it can be understood that he is responsible for accounting for heat consumption in the house. If this device is not present, the savings will not be visible. Most owners of private houses and apartments tend to install meters for electricity and water, because they have to pay much less with them.
Basic schemes for heating houses
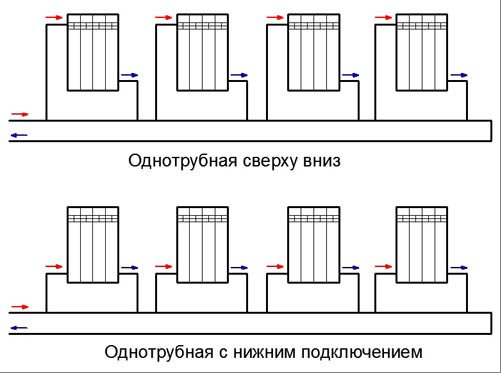

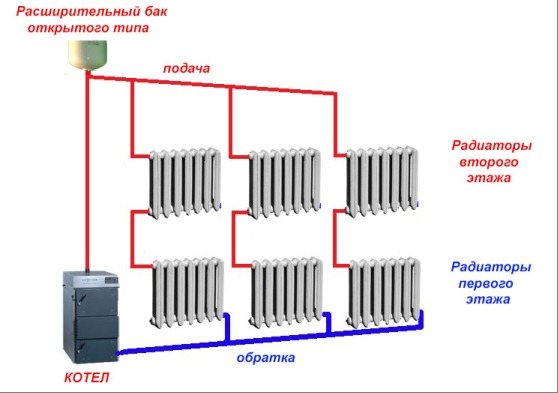
Today there are several types of gravitational heating systems. The most popular is the simplest system with a pressure loop and a slope of supply and return pipes.Here, a scheme is implemented in which the coolant circulates in a natural mode, and the expansion tank has an open top. The disadvantage of this type of gravitational heating system is its inertia and complexity in implementation. The complexity of implementation in this case means the need to maintain all parameters of pipe slopes. So, after the pressure loop is mounted, the piping should be done with an inclination of 0.05 degrees to the side of the boiler. This slope is sufficient to provide initial fluid movement. The same slope is ensured when laying the return pipeline.
Such schemes imply one-pipe options for building a security system. More advanced gravitational heating systems imply a two-pipe piping scheme. But for this it is necessary to ensure the correct laying of the main pipeline. For the normal functioning of such a system, the total length of the supply pipe should be about 25 meters, the maximum size of such a pipe can be 35 meters. A long pipe length will reduce the temperature of the coolant supply; for its laying, an additional slope will be required, which will require an additional volume of the attic space or volume inside the room in the project.
What to look for when designing a gravitational heating system
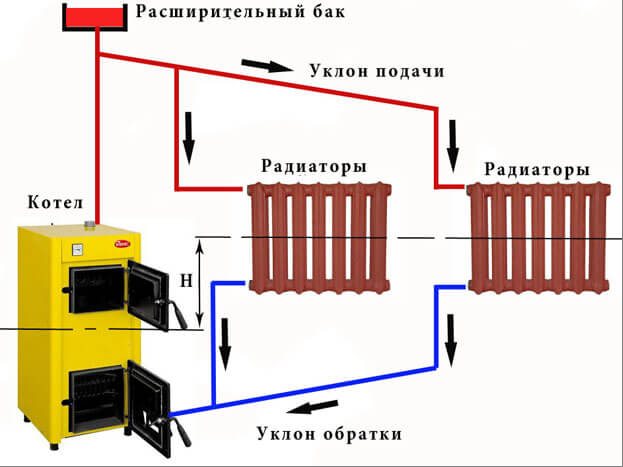

The main problem of the effective operation of the gravitational heating system in low-rise private houses is the incorrect location of the boiler and radiators relative to each other. One of the important parameters of the system is the value of the circulating head. It shows the distance from the center of the heater to the center of the boiler. The higher this indicator, the more efficient the whole system will work.
The inefficiency and low efficiency of heating boilers, both solid fuel and gas, installed in gravitational systems are often associated with a small difference in heights between the radiator and the boiler. So, under normal conditions, this difference is usually only 0.2-0.3 meters. This situation does not allow saving up to 25% of fuel. Most of the energy is spent on superheating the liquid. At the same time, if you increase the height difference by 0.5 meters and bring it to 0.7-0.8 meters, then the efficiency will increase by 6-11%, and with a difference of 2.0 meters, it becomes possible to save up to 20% of energy ... That is why, when designing gravity-type heating systems, the boiler is planned to be placed at the lowest point, most often in the basement.
At the same time, considering all the options and methods for installing heating systems in a private house, despite the seeming simplicity of implementing this project, it is recommended to entrust it to professionals. Experience and availability of special equipment will help to ensure quick and, most importantly, easy installation of all equipment, minimizing the risk of errors.
Which floor heating to choose?
Much depends on various parameters and conditions. For example, the area of the room and its location are of particular importance.
If we are talking about a private house, then here you can consider any type of underfloor heating, but it is still better to preliminarily assess the feasibility of each individual option in order to choose the most optimal one. As for the apartment, here you will have to face special restrictions.
It is extremely important to understand the purpose of the underfloor heating system. If additional heating is required, then you can take a closer look at mats or film floors.
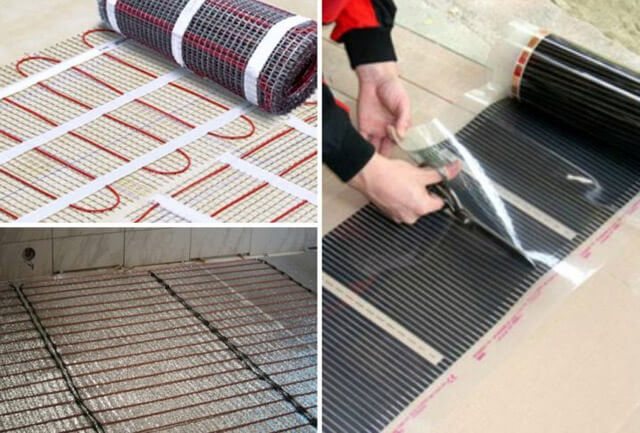


If the warm floor is to act as the main heating, then it is logical to consider a water system or a high power heating cable.
Product quality should also be a priority. You should not blindly trust advertising and buy systems from previously unknown manufacturers.Your best bet is to rely on certified products that, if used correctly, can last for years.
- Similar posts
- How to assemble a Valtec underfloor manifold?
- Do you need a mixer for an underfloor heating?
- What is the difference between Unimat underfloor heating models?
- How to install underfloor heating under the cork?
- Do you need a warm floor in the house?
- What are the advantages of Gulf Stream underfloor heating?