What is a radiator and what is it for?
A radiator is a part of a car that is installed in the engine compartment. It provides constant engine cooling.
How does it work, what is it for, what types of radiators are there, why does it fail, how to care for it and how to choose the best modification? Let's deal with all the nuances in more detail.
General concepts, purpose
During the operation of the car, all its mechanical components heat up. In some compartments, this figure reaches more than one hundred degrees. And the main unit, which will quickly fail due to the high temperature, is the motor.

The moving parts of the engine must be cooled to prevent deterioration. For this, the engineers of each car manufacturer develop and install a cooling system.
_
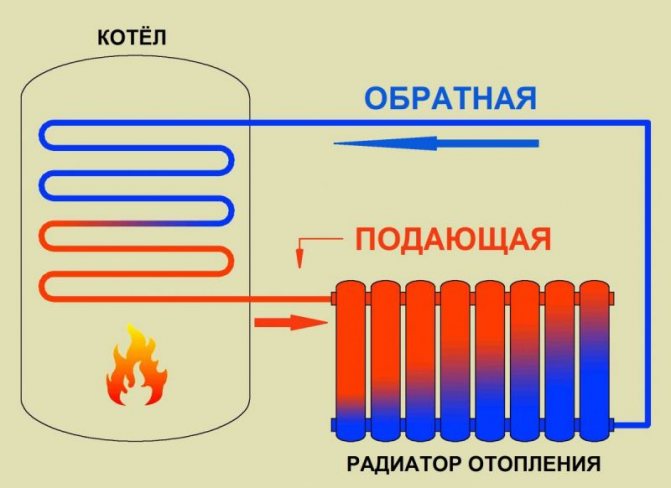
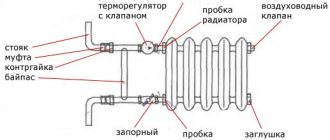
The cooling radiator is a metal heat exchanger filled with antifreeze (or antifreeze) inside. Rubber pipes are connected to it, which are attached to the corresponding motor necks.
The cooling of the motor works according to the following principle. The started internal combustion engine rotates the impeller of the water pump. Thanks to this, antifreeze begins to circulate in the system (in a small circle). When the temperature of the liquid reaches 80-90 degrees, the thermostat is triggered and a large circulation circle opens. This allows the engine to warm up faster to the desired temperature.
The following 3D animation clearly demonstrates how the system works:
Car engine cooling system. General device. 3D animation.
Disadvantages of cast iron radiators
Despite all the above advantages, cast iron radiators also have some disadvantages, among which it is especially important to mention the following:
- during long-term operation, rust accumulates inside the units;
- the heat transfer surface of the equipment is small, and the thermal conductivity of cast iron is very low, therefore, in order to heat a living room with high quality, cast iron heating batteries must consist of at least ten sections;
- in view of the fact that the mass of the coolant and the cast iron batteries themselves in the centralized heating system in an apartment building is very large, it will be necessary to install a volumetric pipe system that cannot be hidden in the wall;
- due to the fact that the volume of the coolant is very large, it will take a lot of time to heat the room. And the increased inertia of cast-iron equipment will not allow equipping the radiator with a mechanism for regulating the generated heat;
- it is rather difficult to install such devices in ready-made heating systems equipped with automatic devices, which does not allow you to control fuel consumption;
- the rate of heat transfer to the cast iron battery is very low.


What is it for in the car
The car engine works by burning fuel in the cylinders. As a result, all parts become very hot. When the temperature of the metallic elements rises, they expand. If they are not cooled, this will lead to various problems in the power unit, for example, cracks in the cylinder head, in the cooling jacket, cylinder head deformation, excessive thermal expansion of the pistons, and so on. Ignoring such problems will lead to costly ICE repairs.
To stabilize the temperature, all internal combustion engines in their design have a cooling jacket, through which fluid circulates with the help of a pump.The heated antifreeze is fed through the highway to the car's radiator. In it, the liquid is cooled, and then flows back to the engine. This process allows you to maintain the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine.
If there was no radiator in the design of the cooling system, the liquid in it would quickly boil. In the car, this part is installed in the front of the engine compartment. This is necessary so that more cold air enters its plane.
The efficiency of heat exchangers depends on the following factors:
- the number of tubes - the more there are, the better the antifreeze will cool;
- cross-section of tubes - oval shape increases the area of contact with air, which increases heat transfer;
- forced airflow - especially useful in urban driving mode;
- cleanliness - the more debris there is between the fins of the heat exchanger, the more difficult it will be for fresh air to get onto the hot pipes.
Convector type radiators
The device outwardly resembles an oil cooler, but its body is less convex and is equipped with two grilles - lower and upper. Cold air enters through the first, and the second, occupying from 15 to 20% of the surface, is equipped with guiding curtains and is designed to release heat.
Heating elements located inside the radiator are surrounded by metal plates that increase the useful area of the heating elements. Electric heating elements are made of stainless steel. Their tubes with magnesite inside are hermetically sealed.
Heating with the use of electric convectors occurs due to convective exchange according to the scheme: solid - gas and convective-radiant heat propagation, when it is transferred both by a radiation source and by convection.
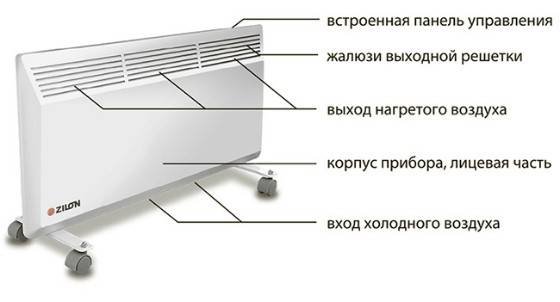

Convector radiator circuit
The advantages of this type of electric battery are significant:
- High reliability. There are no moving parts and coolant in the design, which greatly increases the resource reserve;
- Availability of alternative mounting options - permanently on the wall or installation on the floor, if there are legs or casters;
- Safe, convenient operation due to the presence of a thermostat and protection against fire, overheating. Even when the heating element is heated to 1000 degrees, the outer surface does not heat up by more than 65 degrees;
- No need to strengthen the power supply of the house and grounding device;
- Unlike other types of electric heating, they do not burn oxygen;
- The line includes models for operation in high humidity conditions;
- Autonomy;
- Efficiency 95%;
- High heating rate of heating elements - on average 30 sec.
Convector-type electric batteries also have disadvantages:
- High power consumption, which makes it irrational to use them for heating large areas;
- Annual reduction in efficiency.
Radiator design
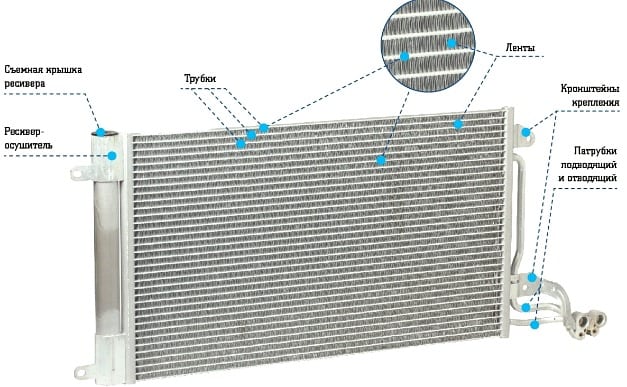

The material from which car radiators are made is metal (aluminum or copper). The walls of the heat exchanger are very thin, due to which the antifreeze quickly gives off its temperature and cools.
The design of the radiator consists of thin tubes welded together in the shape of a rectangle. This element is mounted on two tanks (one at the inlet, the other at the outlet). Additionally, plates are strung on the tubes, which increases the heat transfer area. Air passes between the ribs and quickly cools the surface of the part.
All heat exchangers have two openings: inlet and outlet. The pipes of the system are connected to them. To drain the liquid from the cavity, the heat exchanger is equipped with a plug installed at the bottom of the structure.
If the car is driving on a highway, there is enough air flow to cool the antifreeze naturally (blowing the ribs). In the case of traffic in the city, the air flow is not so intense. For this, a large fan is installed in the cooling system behind the radiator.In older car models, it was directly driven by a motor. Modern machines are equipped with an antifreeze temperature control system and, if necessary, includes forced airflow.
How radiators are made - see the following video:
How car radiators are made
The principle of operation and the device of the heating radiator
There is no difficulty in the operation of heating radiators. The water heated to the required temperature moves into the room through the pipe system, and then enters the heating devices, from which, in turn, the air in the dwelling is heated.
In the event that the method of heat transfer is convection, that is, accelerated, then the heating device will be called a convector. And if heat transfer is based on the principle of radiation, which means space heating due to a surface heated to a certain temperature, then such a mechanism will be called a radiator.
It is not uncommon for manufacturers to manufacture heating batteries of a combined type, which are panel-type convector-radiators.
Despite the temperature readings in the heating devices, these units will produce about 60% of the heat by means of energy radiation, and the remaining 40% will be produced by convection. This allows you to minimize the convection of heated air and makes possible high-quality heating of the objects in the room. Such a device to some extent resembles the construction of a warm floor.
Types of radiators
There are several types of heat exchangers. Each of them is designed for its own purpose, but they work according to the same principle - fluid circulates inside them to ensure the exchange of heat. Heat exchangers are used in the following vehicle systems:
- cooling;
- heating;
- climatic.
There are two categories of radiators most commonly used in the automotive industry.
- Tubular lamellar. This is the most common modification found on older cars. The heat exchanger in them consists of horizontally arranged tubes (circular section), on which thin plates are strung. Most often they are made from an aluminum alloy. These modifications were installed on older vehicles. The main disadvantage is poor heat transfer due to the small area of contact with the air flow.
- Tubular tape. They use long tubes (oval section), folded in the form of a coil. The material used for their manufacture is either an alloy of copper and brass, or aluminum. Such modifications are installed in many modern cars. Copper models have excellent thermal conductivity but are very expensive. Therefore, more often the cooling system is equipped with aluminum counterparts.
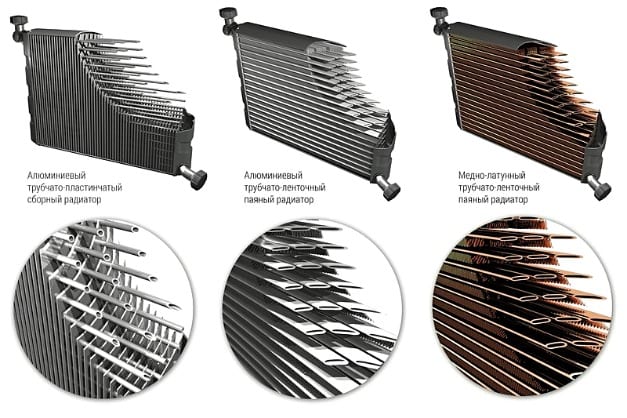

Among the first category, there are two more types of radiators. These are single-pass and multi-pass models. They differ from each other in the principle of circulation.
- One-way. The coolant enters the heat exchanger cavity from one side and is evenly distributed over all tubes. They have a significant drawback: the antifreeze in the cavity is distributed unevenly, due to which the efficiency of heat exchange is lost.
- Multi-pass. The cooling elements are divided into several sections. This design increases the overall length of the line, which improves the heat transfer process.
Manufacturers of bimetallic radiators.
Quite good pseudo-bimetallic batteries are offered by the Russian company Rifar. Its products, having conquered the Russian market, were exported. Produces seven types of radiators. Popular models are Rifar Flex, Monolith. The radiators are white. The number of sections in the battery is from 4 to 14 pieces. Rifar gives a guarantee for products from 10 to 25 years.
The German company TENRAD offers a fully bimetallic design in its products.
Innovative solutions of German engineers are protected by patents, including in the Russian Federation. TENRAD BM radiators are manufactured with a spacing of 500 and 350 mm connecting pipes.


Reliable batteries are offered by the Italian company Global Style. The technical characteristics of their products can be called the benchmark in the industry. These models include the Global Style Extra and Global Style Plus radiators. But elitism comes at a price, Global Style batteries are not cheap. Radiators are produced with a center distance of 350 and 500 mm, with the number of sections from 6 to 14 pcs. The manufacturer offers a 10 to 20 year warranty.
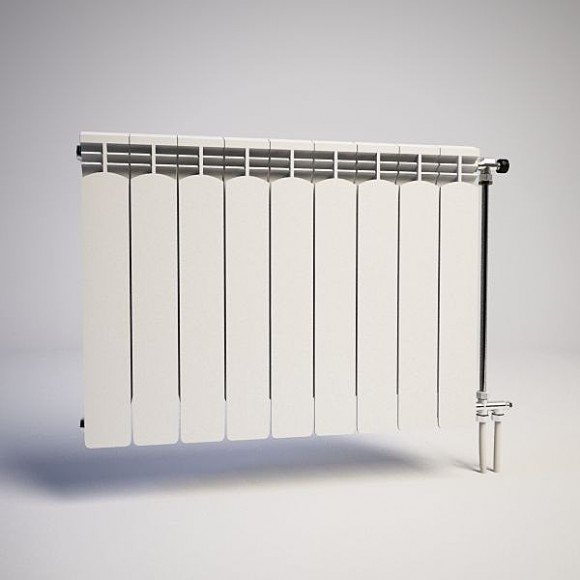


The British company BiLUX offers highly efficient bimetallic radiators. Available in 200, 350 and 500 mm center-to-center models. The design of the batteries is highly reliable, with a 10-year manufacturer's warranty.
Damage to radiators: causes, prevention
Like any part, the radiator in the car can also fail. Here are five main reasons.
- Mechanical damage. Since this part is installed in front of the vehicle, foreign objects often fall on it. For example, it can be stones from a car in front. Even a minor collision from a car can damage the radiator, which will compromise the tightness of the cooling system.
- Oxidation of metal. Although all elements of the heat exchanger are made of stainless materials, the radiators are not protected against scale build-up inside their cavities. Due to the use of low-quality coolant, metal parts of the motor can oxidize, which clogs the line and prevents the free circulation of antifreeze.
- Natural wear and tear. Constant heating and cooling leads to "fatigue" of the metal, which reduces its strength. Vibrations in the engine compartment destroy the connecting seams, which can lead to leakage.
- Excessive line pressure. If a poor-quality plug is installed on the expansion tank, over time, the pressure relief valve stops functioning. Due to the heating of the antifreeze to a temperature above 100 degrees, the volume in the system increases. Most often, seams on plastic elements diverge. But the walls of the old heat exchanger become thinner over time, which leads to depressurization and leaks.
- Coolant freezing. This can happen in the case of using the wrong antifreeze or plain water. In the cold, water crystallizes and expands. From this, cracks appear on the walls of the tubes.


Most of these problems can be prevented by applying preventive methods. To prolong the service of the radiator, the owner of the car can take the following measures.
- Do not fill the system with normal water. In an emergency, you can use distilled, but in the near future you need to change it to antifreeze. This liquid boils at temperatures above 115 degrees. In addition, it contains lubricant, which has a beneficial effect on the pump impeller and other metal parts of the system.
- Change the antifreeze in a timely manner, and when the level decreases, add it. Replacement must be done at least 50-70,000 km. mileage (for antifreeze, this interval is from 150 thousand). But if the coolant has changed its color and turned black, this is a clear signal for system maintenance.
- Install a radiator made for the given car model.
- Perform routine maintenance on the entire cooling system.
- Keep the fins of the heat exchanger clean.
- During the replacement of the antifreeze, periodically flush the inner walls of the coil.
Device, classification and features of the main types
Today they produce a variety of radiators for heating:
- tubular and lamellar;
- steel and aluminum;
- cast iron, cast and sectional;
- welded;
- plain and colored;
- wide and narrow etc.
There are Italian devices, Finnish and Chinese, German, as well as Russian-made products.
Device
You should also talk about the heating radiator device. It is a convection-radiation heating device that receives heat from the coolant circulating in the system. This heat carrier is most often water.
Water passing through the radiator heats the walls of the channels, which, in turn, transfer heat to the outer walls of the device. Obviously, the heating efficiency depends on the intensity of heat transfer from the water to the room air by the radiator material.
This intensity depends on several parameters:
- thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the material from which the device is made;
- surface area in contact with water;
- surface area in contact with air;
- outer surface color.
Radiator heating is carried out by convection and heat radiation. The efficiency of convection depends on the heating surface area, and the radiation efficiency depends on the area and color (the darker, the more intense).
Given these points, one can understand the logic that guides the production of these devices. First of all, it is aimed at increasing the contact area of the outer surface with air. For this, a breakdown into sections, all kinds of linings, lamellar grids and blades is used.
In addition, they use materials with high thermal conductivity, use thin walls for better heat transfer, increase the cross-sectional area of the pipes, due to which it is possible to create a flat heating radiator that has no less heat transfer than a volumetric cast-iron analogue, but at the same time fits perfectly into the interior.
As you can see, thermal conductivity is one of the main performance criteria. This indicator depends only on the material from which the emitter is made. Let's take a look at the main use cases for different materials.
Cast iron
A cast iron radiator is perhaps the most recognizable and widespread heating device. It is used to work in central heating systems, both in residential buildings and in offices and industrial premises. Great for multi-storey buildings.
This popularity and prevalence is explained by a number of advantages that this material has:
- Significant thermal power per unit length of the device;
- Compactness (although comparison with modern devices will be disadvantageous);
- Corrosion resistance and unpretentiousness to the quality of the coolant, which is important in central hot water supply systems, especially in our country;
- Thermal inertia due to the significant heat capacity of cast iron and the massiveness of the device made from it;
- Sufficiently high strength of the material to withstand hydraulic shocks during tests and start-ups of the heating system after the summer break;
- Durability, allowing cast iron devices to be used for over 40 years.
However, today, cast iron appliances are gradually being replaced by other materials.
This is due to a number of disadvantages inherent in cast iron models:
- High weight of cast iron products, which makes it difficult to transport and install devices. It is also quite difficult to change the device;
- Low thermal conductivity due to the porous structure and massiveness of cast iron. To heat the surface of the battery, a coolant with a high temperature is required, up to 70 - 80 C, otherwise the battery remains barely warm;
- Inter-section spacers tend to degrade;
- Radiator nipples are destroyed during long-term operation (more than 40 years);
- The inner walls are porous and rather rough, which leads to a drop in heat transfer due to plaque, and also impedes the movement of water;
- Require periodic painting;
- They are bulky enough and do not fit well with modern interior design styles;
- Take up a lot of space.
Advice! To enhance the appearance of the cast iron battery, you can use a guardrail or various covers and panels that hide the radiator and adapt it to modern design styles.
The main manufacturers of cast iron radiators are KONNER (China), MS-140 (Russia), Tokio (China).
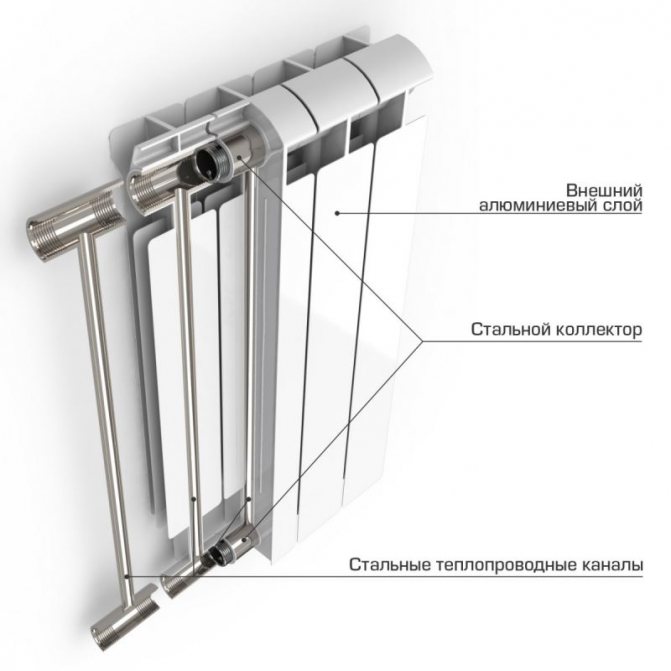
Aluminum
Aluminum is a metal with high thermal conductivity. Therefore, devices made of this material are highly efficient. It also becomes possible to equip the device with a branched system of protrusions, ribs and plates, which increase the area of the heated surface.
Aluminum radiators have the following advantages:
- Low density of aluminum, due to which the products are lightweight, which facilitates their transportation and installation. The change of such devices and their repair is also facilitated;
- Compactness of batteries, due to their efficiency and high thermal power;
- High working pressure - more than 12 atm. The crimping pressure of aluminum products is more than 18 atm .;
- High level of heat transfer, superior to those for cast iron, steel and stainless steel;
- Large cross-sectional area of intercollector tubes used in aluminum devices, which increases heat transfer from water to metal and contributes to better circulation of the coolant.
However, there are also a number of disadvantages. The most significant of them is the high chemical activity of aluminum, due to which there is an increased corrosion status of the material in contact with oxygen and water.
Increased corrosion is also observed when aluminum comes into contact with other metals, especially if stray currents are present in the heating system. Therefore, for aluminum products, special shut-off valves are used that take this feature into account.
Aluminum is saved from rapid deterioration as a result of interaction with water and air with an oxide film that almost instantly covers the metal when interacting with air.
However, if the integrity of this film is violated as a result of interaction with water, hydrogen is released, which, accumulating, increases the pressure in the radiator and can lead to its rupture.
To prevent this effect, polymer enamel is used for aluminum heating radiators.
Important! When buying an aluminum device, be sure to pay attention to the presence of a polymer coating on surfaces in contact with water. This coating allows the battery to be used for heat transfer fluids with a pH-factor of 5 to 10, typical for our systems, and also reduces hydrodynamic resistance and prevents buildup and blockages.
There are three main types of aluminum batteries:
- with solid sections;
- with a mechanically connected set of sections and;
- mixed.
The first type is distinguished by high strength of welded joints, ductility and resistance to external shocks and water hammer from the side of the system.
Sectional radiators allow replacing a damaged section, which is connected by means of threaded nipples. You can also build up the battery with your own hands during operation. The price of these advantages is the loss of reliability and the roughness of the inner surfaces of the sections.
Which is better: repair or change


All motorists can be roughly divided into two categories. The first believe that a failed part needs to be replaced with a new one. The latter are sure that everything can be repaired. And fixing radiators is a frequent topic of controversy.
The Internet is replete with all kinds of advice on how to fix the leak yourself. Some use special compounds. Others fill the system with crack bridging agents. Sometimes some methods help to prolong the life of the part for a while. But in most cases, these techniques only clog the cooling system.
It makes sense to repair copper models, because they are easy enough to solder. In the case of aluminum analogs, the situation is different. They can be soldered, but this will involve expensive welding. Therefore, the cost of repairing a leaking radiator will be almost identical to the price of a new part. It makes sense to agree to this procedure only in the case of an expensive heat exchanger model.
In most cases, repairs are only a temporary measure, because high pressure constantly builds up in the cooling system, which will lead to repeated depressurization of the line. If you carry out timely maintenance and cleaning of the system, you will often not need to change the radiator. Therefore, when a part breaks down and precious coolant poured onto the ground, it is better to replace this unit than to constantly throw away money to purchase another canister.
What it is
An electric battery refers to two different designs.
Liquid electric battery
From the verbose descriptions on the manufacturers' websites, you can still extract bits of useful information and, in general, understand how this device works.
- The circuit is based on a conventional heating element, a tubular heater. Since the solution is positioned as energy-saving, it usually has a low power - up to a kilowatt. Models with peak consumption of 300-500 watts dominate.
- The coolant is water or oil. There are also sealed structures with a non-replaceable coolant, and open ones, into which any liquid can be poured through the plug.
- The aluminum body, thanks to the ribbing, provides a solid heat exchange area, and due to the thermal conductivity of this metal, the same temperature throughout this area.
- The electric heating battery works at full capacity only until the target temperature is reached. When it is reached, the heating is turned off, as soon as the temperature drops, the heating element turns on again.
- Microprocessor control of a miniature electric boiler provides the most rational operating mode, due to which huge savings are achieved.
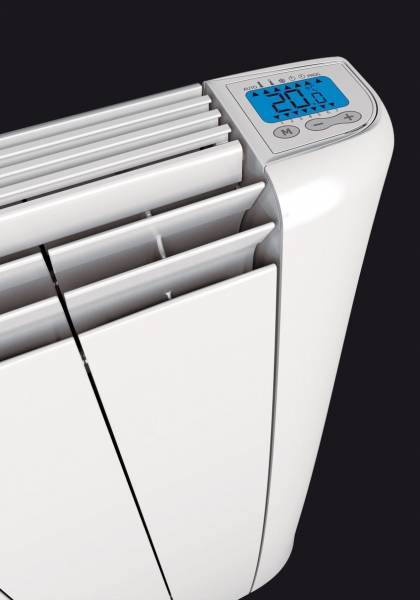


There is a digital thermostat in the circuit.
Ease of connection will make it easy to mount the heating system yourself.
Dear reader: wait laugh. So far, we are only citing the advertising assurances of the manufacturers.
Liquid-free electric battery
The manufacturers of the second type of miracle devices explain that the likelihood of water or oil leakage always stays with you as long as you use a liquid heater. The truth is in a liquid-free one, where a low-temperature heating element in an aluminum casing will warm you even more economically and safer.
At the same time, microprocessor control continues to save, save and save again.
The author will dare to quote a few more fragments of the technical descriptions.
- Battery housings are made of aircraft-grade aluminum, which allows the use of pressure up to 80 kgf / cm2 and maintains an oxide film that protects aluminum from corrosion (see the article Aluminum radiators - a reliable component of the heat supply system)
- Batteries are assembled on threads, in contrast to poor quality brazed and cast designs.
- Older models are bimetallic radiators - obviously with steel core sections.
The price of younger models is about 6,000 rubles. Seniors - 10,000.
If desired, you can assemble a kit from a purchased separate radiator and heating element.
We will try to adhere to the maximum objectivity to the last and will not comment on any of the four points. The author will say politely: none of the points in this section of the article is associated with anything that even remotely resembles common sense.
How to properly operate?


One of the most important conditions for the correct operation of a radiator is to keep it clean and to prevent excessive pressure in the system. The second factor depends on the expansion tank cap.
The first procedure can extend the life of this component. However, it must be done correctly.
- The manufacturer categorically prohibits the reuse of used coolant. Even if you clean it, it has already lost its properties, and therefore it will already be useless.
- If the antifreeze is very dirty, before pouring a new one into the system, it must be flushed with distilled water (in no case use ordinary water). It does not contain salts and impurities that can build up inside the coil and reduce the cooling efficiency.
- When cleaning the outside, it is important to take into account that the fins of the heat exchanger are very thin and therefore even small forces can bend them. Subsequently, this will interfere with the natural blowing of the radiator pipes. If the procedure is performed using a mini-washer, you need to adjust a small head. The jet should be directed perpendicular to the fins to prevent accumulated dirt from moving into the heat exchanger. Then it cannot be purified in any way.
Overview of aluminum battery manufacturers
Many models of aluminum radiators from different manufacturers are sold on the market today. Therefore, you can easily select such aluminum heating radiators which are best suited in terms of technical parameters, external performance and financial capabilities.
You can buy the required model on the market, in a specialized store. Also, the sale of aluminum heating radiators is carried out via the Internet. The advantage of such a purchase is time savings. If you have any questions regarding the parameters of the equipment, you can ask the online consultant or call the phone number indicated on the website and talk to the manager.
It should be noted that prices for heating radiators are aluminum, steel or cast iron models, in the online store, as a rule, below the market average. Therefore, many people prefer to order heating devices on the Internet.
Both imported and domestic products are on sale. Naturally, prices for domestically produced aluminum heating radiators are lower than for foreign counterparts. But this does not affect the quality of the products. Since many modern domestic batteries are manufactured using Italian technology. Among domestic producers, the companies Rifar and Thermal should be distinguished. They produce durable aluminum heaters at an affordable cost.
Since Italian aluminum heating radiators have always been famous for the highest quality, they are in great demand on the market, despite their high cost. Here it should be noted the products of the firms Fondital, Sira and Global. These companies also produce bimetallic heating radiators. Hungarian-made heating devices are also popular. True, they are inferior in quality to Italian models. Quite good aluminum batteries are produced by the Hungarian company NAMI.
Which radiator is better?


In most cases, the answer to this question depends on the material capabilities of the motorist. Copper-brass models lend themselves to inexpensive repairs. Compared with aluminum analogs, they have better heat transfer properties (the heat transfer coefficient of copper is 401 W / (m * K), and of aluminum - 202-236). However, the cost of a new part is very high due to the price of copper. And one more drawback - a lot of weight (about 15 kilograms).
Aluminum radiators are cheaper, they are lighter compared to copper versions (around 5 kg.), And their service life is longer.But they cannot be properly repaired.
There is another option - to buy a Chinese model. They are much cheaper than the original part for a particular car. Only the main problem with most of them is their short service life. If an aluminum radiator copes with its functions for 10-12 years, the Chinese analogue is three times less (4-5 years).
For details on breakdowns and maintenance of radiators, see the following video:
Engine cooling radiator. Malfunctions. Cleaning.
Rate publication
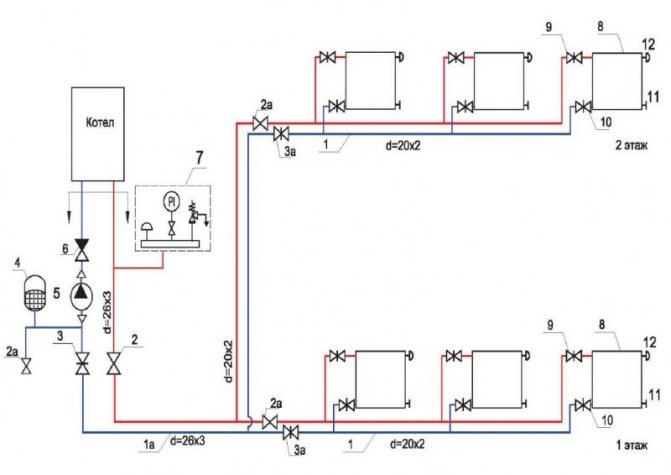
Connecting radiators
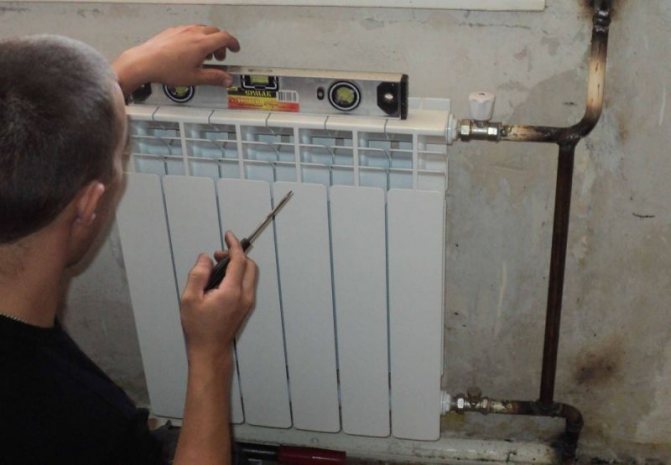
In any heating system, the plan and the project are important. The same aspect will include the connection diagram for heating radiators. A heating radiator drawing can be in several versions. This can be an individual diagram or a diagram made based on the method of piping in the field and the efficiency of the heat transfer indicator.
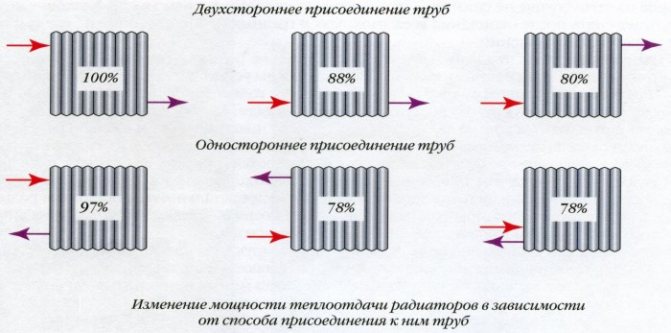

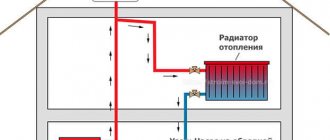
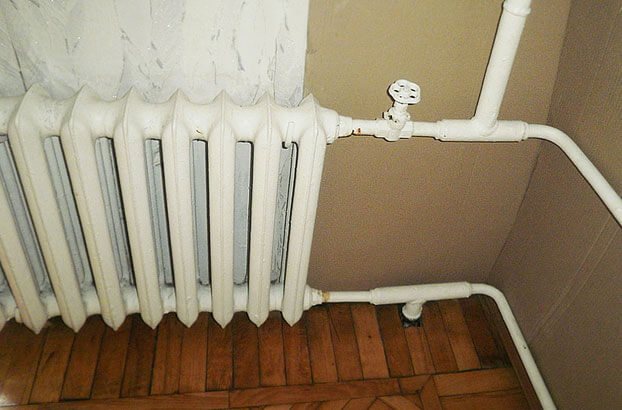
One-way connection is common. So, the designation of heating radiators in the drawings will show that all pipes are connected to the batteries only on one side. This scheme is the most convenient, especially in high-rise buildings.
Another option - the marking of heating radiators shows that the connection is made diagonally, that is, crosswise. The peculiarity of this principle is that the pipe that supplies heat is connected to the radiator from the upper part on one side, and the outlet pipe is connected to the lower part from the opposite side. It is important here how the heating radiator is arranged: such a scheme is suitable if the batteries are long, have many sections. The heat carrier will be evenly distributed over the entire area of the radiator, thus, the heat transfer will be excellent.
There is also a bottom connection. So, the inlet and outlet pipes are connected to the lower pipes, which are located on opposite sides of the radiator. This kind of scheme will lose to the previous two. After all, it provides heat transfer efficiency by about 10-15 percent. However, such a scheme would be an ideal solution when the heating system is hidden in the floor.
It's no secret that heating devices such as cast-iron batteries have been used in almost all residential buildings for quite a long time. They are common today, but the development of technology contributes to the fact that these units are being replaced by more modern and functional radiators.


- bimetallic;
- steel;
- aluminum batteries (in more detail: "Aluminum heating batteries - technical characteristics, installation").
In order to figure out how the installation of cast-iron heating batteries should be carried out, it is necessary to study what technical characteristics these devices have, and also consider on what principle the calculation of cast-iron heating batteries should be carried out.
How to disassemble an aluminum battery?
Sometimes there are situations when you need to disassemble the battery. For example, it is necessary to add additional sections to the radiator or replace one of the sections that has leaked. In any case, you need to know how to disassemble an aluminum radiator correctly.
Battery parsing algorithm:
- dismantle the radiator. To do this, you must first shut off the flow of the coolant into the system. The threaded connection is untwisted with a wrench;
- remove the radiator and put it on the floor upside down;
- disassemble the device into separate sections. The sections can be disconnected using a radiator wrench. Insert it into the grooves of the nipple-nut of the upper hole and make a few turns counterclockwise. Do the same with the bottom hole. The section is disconnected.
Convection radiators [edit | edit code]
Many radiators, in addition to dissipating part of the heat by radiation, remove another part of the heat by natural or forced (fan) convection and are a combination of a radiator and a convector. Convection heaters are heating radiators with ribs on the pipes. Convection heaters quickly heat up the room. Such heaters are often installed in industrial premises: in garages, workshops, warehouses. Modern convection heaters are made of copper and aluminum. The coolant comes into contact only with copper, and heat-conducting plates and a housing are made of aluminum.
Convection heaters create the effect of an air heat fan and mix well the air layers in the room, but this can also be a negative factor, since drafts are created in the room, dust does not settle, being constantly in the air.
Automotive radiator - design of the heat transfer system
As for their design, they are divided into the following types: pipe and welded. Round tube versions are a panel assembly with round aluminum tubes threaded onto them. Their main advantage is an acceptable pricing policy due to their low cost. The disadvantages include low strength, small heat transfer surface and the need for high quality gaskets, which are not always available.
Oval tube radiators in the mid-range are slightly better in service. This is possible due to the oval cut, which increases the area that gives off heat. Disadvantages: low strength, the need for high quality gaskets. Soldered radiators, which are distinguished by higher strength and heat transfer, also have a cost that not everyone can afford. Thus, it is not so important which car radiator, aluminum or copper, you choose, the main thing is a competent combination of the device and the material of the radiator.
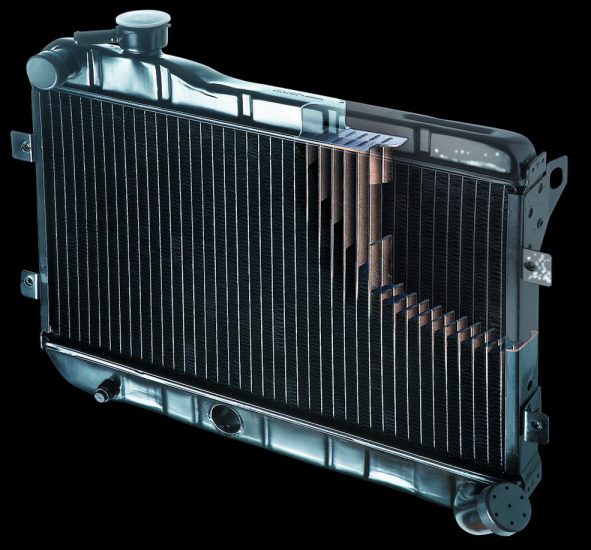


The radiator is one of the key and most important elements of a liquid cooling system. The main task is to dissipate heat into the atmosphere, which was removed from the engine by the coolant. The radiator of the engine cooling system can be considered the most important part of the power unit itself.
Devices similar to a modern radiator were installed on the earliest versions of cars with internal combustion engines, since without the specified cooling element, the operation of the power plant becomes simply impossible. This device is directly responsible for maintaining the normal operating temperature of the engine within strictly specified limits. Such protection protects the motor from overheating, which will inevitably disable almost any internal combustion engine.
Read in this article
How to assemble a radiator?
The assembly of aluminum heating radiators is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- put the battery on a flat surface;
- inspect each threaded connection for chips, cracks and thoroughly clean with sandpaper. Degrease the ends using gasoline. The gaskets can be washed in soapy water;
- connect sections. For this, it is necessary to put the seals on the nipple-nut and attach on both sides of the section of the device. Make a couple of turns with a wrench in the upper and lower holes. When the key stops turning, you can pull it out using the lever;
- the unused hole should be covered with a plug. And on the other hand, attach the Mayevsky tap to remove excess air from the system. Now the radiator can be connected to the system according to the selected scheme.
The history of the radiator
The water cooling system appeared at the dawn of engine building. The radiator concept was first used on the first production car, the Benz Velo, which went on sale in 1886.This idea of the device was continued to develop by Wilhelm Maybach, who designed a product with honeycombs. The development has found application in the design of the Mercedes 35HP model. Over the next decades to the present day, the radiator device has not undergone global changes, having remained almost in the same form as in the days of Maybach.
Thanks to this effect, the coolant entered the radiator. The thermosyphon effect is based on the fact that the density of water decreases when heated. Due to this property, heated water rushes upward. As a result, the heated liquid ended up in the device, penetrating there by passing through the upper branch pipe.
The water was cooled inside the radiator, and the density of the liquid increased again. This led to the fact that water fell into the lower part of the radiator, and from there it penetrated back into the engine jacket through the lower branch pipe. The main disadvantage of systems with a thermosyphon effect was that they could not provide adequate cooling against the background of the constantly growing power of the internal combustion engine. Such systems quickly supplanted solutions that were based on the use of a centrifugal water pump (pump).
Radiator service
Considering what a radiator is, it must be said about the principles of its maintenance. In some car models, cleaning the radiator is easy. In some brands of cars, this process will be expensive. Therefore, it is easier to buy a new radiator right away.
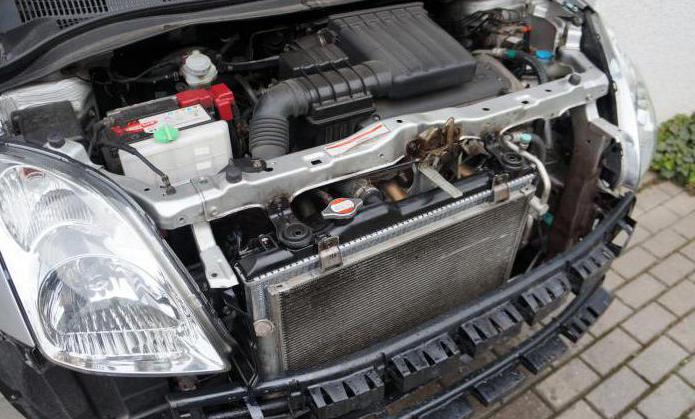


In the summer, the vehicle's cooling system requires special attention. It is during this period of time that the probability of its contamination with dust, fluff, etc. is high. In addition to external factors, the radiator can accumulate an oil film. It is this that leads to a decrease in air circulation, as well as a decrease in the cooling capacity of the system.
Knowing the characteristics of the radiator of your car, you can make the right decision in the process of its maintenance. Over time, any cooling system will require repair. To prevent this from happening as long as possible, it is necessary to properly adjust the cooling system in the summer, to protect it from contamination.