Rating: 1 172

Due to the fact that winters in our country are rather harsh, everyone needs a source of heat to heat their home. There are a huge number of different heating systems - from hot water to inverter heating. In order to make a decision to use one or another method, you need to familiarize yourself with each of them and consider all the positive and negative sides.
Water heating system
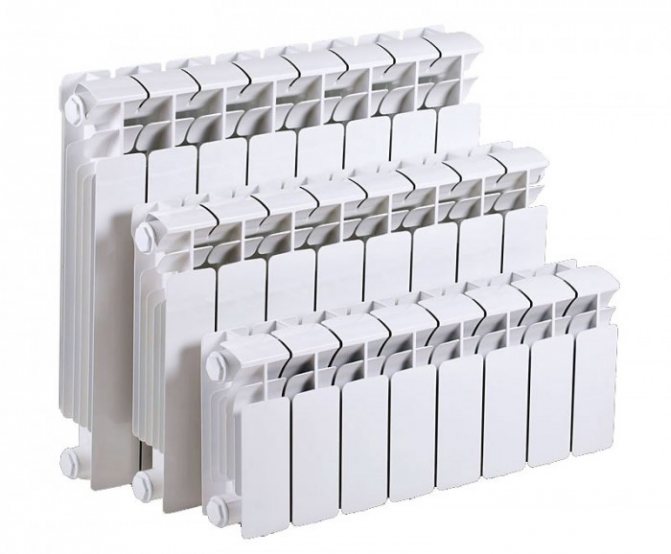
Water heating is one of the most common heating systems. It is subdivided into dependent and independent.
It is possible to distinguish several types of its wiring - one-pipe, two-pipe and collector. A single pipe heating system is also called a bifilar system.
The principle of its operation is quite simple. The energy carrier here is water. After going through the heating process, it moves along the pipeline in different directions. In this case, the water is in a different temperature regime. Standing heating by hydraulic connection of elements of heating devices refers to a one-pipe system, and for heat transfer devices - to a two-pipe system.
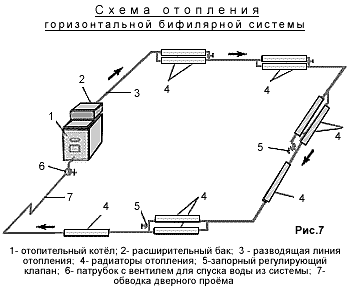

Diagram of a bifilar heating system
A dependent or open connection scheme is characterized by the presence of a vertical or horizontal riser. In this case, there is a similarity with the bifilar system. This kind of device implies that the process of heating the coolant takes place using elements that heat up autonomously. And they, in turn, are divided into several coils. According to experts, it is best to connect them to the ascending or descending part of the pipe.
In a two-furnace horizontal bifilar system, pipe heating devices are used, such as a convector, smooth or finned heating pipes, radiators made of concrete, steel, cast iron, etc.
A horizontal heating system does not allow individual temperature control of each heating element. In this case, the entire chain of devices is fully regulated.
As a rule, the use of a one-pipe system consisting of horizontal façade branches is limited to heating agricultural buildings and structures.
Device and technical characteristics
At first glance, the construction of an ion boiler is complicated, but it is simple and not compulsory. Externally, it is a steel seamless pipe, which is covered with a polyamide electrical insulating layer. Manufacturers have tried to protect people as much as possible from electric shock and expensive energy leaks.
In addition to the tubular body, the electrode boiler contains:
- The working electrode, which is made of special alloys and is held by protected polyamide nuts (in models operating from a 3-phase network, three electrodes are provided at once)
- Coolant inlet and outlet nozzles
- Grounding terminals
- Terminals supplying power to the chassis
- Rubber insulating gaskets
The outer shell of ionic heating boilers is cylindrical. Most common household models meet the following characteristics:
- Length - up to 60 cm
- Diameter - up to 32 cm
- Weight - about 10-12 kg
- Equipment power - from 2 to 50 kW


For domestic needs, compact single-phase models with a power of no more than 6 kW are used. There are enough of them to fully provide a cottage with an area of 80-150 square meters with heat. For large industrial areas, 3-phase equipment is used.An installation with a capacity of 50 kW is capable of heating a room up to 1600 sq. M.
However, the electrode boiler works most efficiently in conjunction with the control automation, which includes the following elements:
- Starter block
- Surge protection
- Control controller
Additionally, control GSM modules can be installed for remote activation or deactivation. Low inertness allows quick response to temperature fluctuations in the environment.
Due attention should be paid to the quality and temperature of the coolant. The optimal liquid in a heating system with an ionic boiler is considered to be heated to 75 degrees. In this case, the power consumption will correspond to that specified in the documents. Otherwise, two situations are possible:
- Temperature below 75 degrees - electricity consumption decreases along with the efficiency of the installation
- Temperatures above 75 degrees - electricity consumption will increase, however, the already high efficiency rates will remain the same
Internal heating system
The method of moving the coolant determines the differentiation of systems into operating on the basis of natural and forced circulation.
Natural circulation in several types: a system with an upper filling and, accordingly, a system with a bottom filling.
An installation with an upper filling operates as follows - water rises up through the supply riser, then, passing through horizontal pipes, it enters the radiators. Having given them heat, the water becomes heavier and moves back to the boiler.
Natural circulation heating system
Dead-end and associated systems differ in the direction of water movement in the main pipeline.
In a dead end, hot water moves in the opposite direction to cold water. Circulation rings, or rather their number, are a distinctive black dead-end system. If the heater is located close to the boiler, the length of the circulation ring becomes shorter. And vice versa. The further the main riser is, the greater its length. For this reason, experts advise installing the device while maintaining a minimum distance from the boiler. The ideal would be to install two small systems rather than one long one.
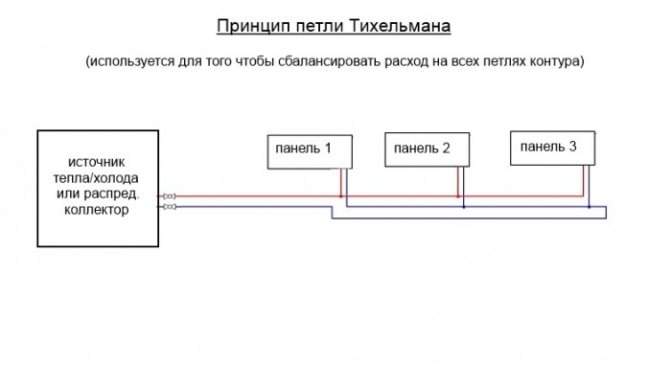
Tichelmann system
Two-pipe systems have a large number of varieties. One of them is the Tichelmann system. It was developed by engineer Albert Tichelman, and the installation got its name in honor of him. In another way, it is called "reversible type return system". In this case, the radiator heats up evenly, providing a fairly high efficiency. With proper balancing, the system will operate efficiently and smoothly.
Like any other, such a heating system has several disadvantages. During its installation, additional pipes are used, which entails additional costs, respectively. Pay attention to the fact that the pipes must be of a larger diameter.
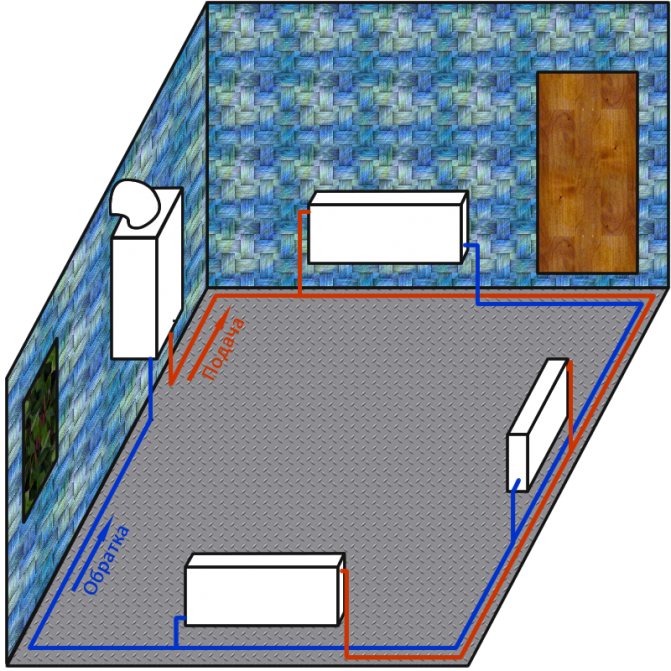

Tichelman heating system
Plus, such a device does not allow heating a room with a large area.
Also, the Tichelman scheme is not suitable for those who need to maintain an individual temperature regime for each room. In this case, you should turn your attention to the collector system.
A closed heating system (in another way it is called "ring") is a device in which water is constantly moving and circulating through a closed pipeline.
Output
Having studied in more detail the video presented in this article, you can get additional information about these types of heating radiators and their features. Also, having read the proposed text, one can come to the conclusion that such equipment is the most economical and is considered the best in terms of its safety.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to our channel Yandex.Zen
Cascade heating
A huge number of positive reviews have gained cascade heating. The principle of its operation is quite simple. To increase the productivity of such a system, several boilers are combined with the help of regulators. This ensures maximum efficiency in the use of equipment power.
Cascade heating system
The main advantages of a cascade heating system are:
- the system allows you to heat buildings with a large area, and is also capable of providing an apartment with hot water supply;
- energy consumption is quite small, with a large heating area, not a lot of fuel is consumed;
- the installation of such a system is very simple, and the small dimensions of the boiler make it possible to use the installation in both large and small rooms.
A new word in autonomous heating - capillary floors
Despite the abundance of proposals, it is rather problematic to find an acceptable way of organizing autonomous heating of an apartment. Some options are too difficult to install and maintain, others are excessively costly and cumbersome, and others are not allowed for use due to the design features of apartment buildings.
But relatively recently, in 2012, a fundamentally new solution appeared on the heating systems market - capillary warm floors. We have already studied the capabilities of these systems and have successfully implemented them at several client sites. We want to share with you our impressions and tell you about the features of capillary underfloor heating.


How capillary underfloor heating works
Capillary underfloor heating consists of an electronic control unit and thin tubes (capillaries) laid under the "clean floor" or directly in the screed. The control unit contains an electric heating element, a circulation pump and automation elements. You think this is a massive box crammed with electrical equipment? Far from it: the block is very compact - its dimensions are comparable to the size of a small book. The power grid is connected to this "volume" and capillaries filled with a coolant are supplied; usually distilled water.
Installation of capillary floors is reduced to the following steps: a heat-insulating layer is laid on a pre-leveled floor surface, to which a heat line is attached. The outputs of the tubes are connected to the fittings of the control unit, after which the system is filled with water through a hole specially provided for this (without forced injection). The next step is verification. If there are no violations in the tightness and functionality, the line is mutated into a screed, using bulk (self-leveling) mixtures for this. When the concrete hardens and gains strength, the floor is decorated. As in the case of conventional electric cable and water heat-insulated floors, materials with a low specific resistance to heat transfer can be used as a decorative coating; for example, block, panel or artistic parquet, engineered board or laminate, as well as tile.
About reliability
Since we are talking about a closed loop, there is no need to feed the system and worry about leaks: only a few liters of water will circulate throughout the entire system. There is also no need to fear that the line may burst: the system operates under a pressure of only 0.3 kgf / cm2. The tubes are made of corrosion resistant materials. The cement screed covering the heating lines performs the functions of protection against mechanical damage and a preservative coating, that is, the line will turn out to be almost eternal. But how reliable is the unit?
The capillary floor control unit is repairable, that is, any electronic or electromechanical component can be replaced if necessary.In addition, manufacturers of such heating systems provide rather long guarantees - the buyer has the right to count on free maintenance, up to a complete replacement of the control unit.
Comparative advantages
Capillary underfloor heating does not spoil the interior design: among the visible parts of the system there is only a control unit with digital display. It fits well into the surroundings, but if desired, it can be hidden in a built-in shield.
The described heating systems have no restrictions on their use: they can be installed in any room, up to bathrooms, baths, saunas, loggias and balconies. Flexible load regulation allows the use of capillary floors even with a lack of electrical power - this indicator for the described systems ranges from 0.1-3 kW.
Heat generation (and power consumption) control is automatic: the user just needs to set the desired coolant temperature in the circuit or the preferred air temperature in the heated room - the system will take care of the rest on its own. Another convenient option is turning on and off at user-specified time intervals: using warm floors in conjunction with multi-tariff electricity metering devices, you can save a lot of money.
Unlike electric underfloor heating, furniture can be installed over capillary structures: the tubes will not overheat and fail due to circulation.
conclusions
Capillary underfloor heating is a hybrid solution that combines the advantages of heating electric cables and water systems, but without their disadvantages. We are definitely in favor of capillary systems.


Capillary underfloor heating UNIMAT AQUA
The UNIMAT AQUA system is designed for heating small areas from 10 to 20 m². Powered by distilled water. Power 100 - 2400 W / sq.m.
Heating area:
UNIMAT AQUA is an innovative type of water underfloor heating and is an autonomous closed system through which a small amount of water circulates under low pressure through thin, like capillaries, heating tubes in a closed loop. Water heating in the system is carried out using an electronic control unit with a programmable power from 100 to 2400 W.
Purpose of UNIMAT AQUA kits
The UNIMAT AQUA system is designed to heat small areas from 10 to 20 m² and can be safely installed in any residential urban or suburban area.
Contents of the UNIMAT AQUA kit
To install UNIMAT AQUA capillary underfloor heating, you need to purchase the following items:
• The basic kit includes:
• KV-2400 control unit assembled - 1 pc.
• Connecting tube - 2 pcs.
• Mounting kit SK - 1 pc.
• Passport of the product - 1 pc.
Additional kit includes:
• PVC pipes (based on polyethylene series polymer) - 2 coils, the length of which depends on the heated area:
For a heating area "up to 10 sq. m "- 2 x 35 running meters.
For a heating area "up to 20 sq. m "- 2 x 70 running meters.
Supporting materials:
• Thermal insulation (if necessary).
• Waterproofing (if necessary).
• Damper tape.
• Reinforcing mesh and plastic clamps for attaching water pipes.
• Mounting box (from 10 cm wide).
• Distilled water (maximum volume about 6 liters).


1. Filling hole for water; 2. Water inlet; 3. Hole for water outlet; 4. Power button; 5. Setting selection button; 6. Temperature increase button; 7. Temperature decrease button; 8. Indicator of filling the system with water; 9. Timer indicator; 10. Error indicator; 11. Display panel of the current water temperature; 12. Display of the set temperature of water or environment.
Inverter heating
From the simplest and most common heating method - hot water, we have crept up to a more interesting method, such as inverter heating.
It has become widespread both among large enterprises and among ordinary homeowners who use it for domestic purposes. The main positive point here is accessibility, because gas is not available in every area, and electricity is installed everywhere.
In addition, to install it, there is no need to collect a huge amount of documents, obtain permits from various authorities, and so on.
Another advantage is its small size, therefore, such a device does not take up much space in the room. The price also pleases buyers, because it is much lower than the cost of buying and installing any other heating appliances and devices.
The principle of operation of inverter heating
Electricity is transmitted using the heating element of the boiler. In order to reduce the loss of thermal energy, it is necessary to insulate the room. You should also protect the equipment from corrosion to prevent damage and breakdown.
The device is based on electromagnetic induction. The boiler is equipped with a battery, so you can not be afraid of power outages, which is important for the owners of those houses where this phenomenon is quite frequent.
The boiler consists of two main elements:
- magnetic part;
- heat exchanger in which the coolant is heated.


Inverter Heating Boiler
Advantages and disadvantages
Such a heating system has a number of positive qualities:
- practicality and ease of use due to the absence of a heating element;
- high rate of heating of the coolant is achieved due to the presence of a built-in pump;
- the choice of fuel is very simple due to the fact that the heating elements do not have direct contact with water.
There are several main disadvantages that the device is not without:
- considerable price of an inverter boiler in comparison with heating elements;
- quite large (this installation is only suitable for large areas);
- to control the temperature and power of the boiler, it is necessary to install a special automatic system.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF COLD CEILINGS
For ease of understanding, the principle of operation of cold ceilings can be compared with a warm floor, only if the warm floor heats the room, the cold ceiling cools it.


Cold ceiling capillary mat
Capillary polypropylene tubes (with a diameter of 3.5 or 4.3 mm) are built into the surface of the ceiling or wall, structurally combined into mats. On top of the capillary mats, a layer of plaster with a thickness of 10-15 mm is applied.
Chilled water with a temperature of 16-18˚C circulates through capillary tubes. Thus, the room is conditioned. The small distance between the pipes and their parallel connection contributes to an even distribution of temperature over the cooling surface.
The room is cooled to cold ceilings due to natural convection (40%) and radiant cooling (60%). Natural convective currents lift warm air upwards, when it comes into contact with the ceiling, the air cools down, increases its specific gravity and without drafts, evenly goes down over the entire surface.
Radiant cooling works by transferring heat from heated surfaces, including human skin, towards cooler surfaces.
The source of cold is chilled distilled water with operating temperatures of +16 - 18 ° C. Water treatment is carried out by a chiller type refrigeration machine. Water circulation is provided by a circulation pump. In general terms, the cold ceiling air conditioning system consists of the following elements: CLINA capillary mats, polypropylene pipelines, a circulation pump, a Chiller refrigeration machine, shut-off and control valves, an automation and control system.
Heating system based on electrode boilers
The boiler is heated by electrodes. In the process of ionization of water, ions are formed, charged positively and negatively. As the particles approach the electrodes, energy is released. That is why the water heats up.
Since the current is constantly changing its direction, no particles remain on the heating plate, which means that scale will not appear.


Electrode boiler for heating
The advantages of such a system include:
What are the positive aspects of such heating:
- the level of efficiency is quite high;
- does not need manual temperature adjustment;
- profitability;
- installation and assembly can be carried out without investing extra funds;
- high speed of heating the room, due to the high level of heat transfer;
- if there is such a need, then it is possible to change the heat heater.
Features of installation of ion boilers
A prerequisite for installing ionic heating boilers is the presence of a safety valve, a pressure gauge and an automatic air vent. The equipment must be positioned in a vertical position (horizontal or at an angle is unacceptable). At the same time, about 1.5 m of the supply pipes are not galvanized steel.
The zero terminal is usually located at the bottom of the boiler. A ground wire with a resistance of up to 4 ohms and a cross section of over 4 mm is connected to it. Do not rely solely on RAM - it cannot help with leakage currents. Resistance must also comply with the rules of the PUE.
If the heating system is completely new, there is no need to prepare the pipes - they must be clean inside. When the boiler crashes into an already operating line, it is imperative to flush it with inhibitors. There is a wide range of descaling, scale and descaling products on the markets. However, each manufacturer of electrode boilers indicates those that they consider to be the best for their equipment. Their opinion should be adhered to. Neglecting flushing will fail to establish an accurate ohmic resistance.
It is very important to select heating radiators for the ion boiler. Models with a large internal volume will not work, since more than 10 liters of coolant will be required for 1 kW of power. The boiler will constantly run, wasting part of the electricity in vain. The ideal ratio of the boiler output to the total volume of the heating system is 8 liters per 1 kW.


If we talk about materials, it is better to install modern aluminum and bimetallic radiators with minimal inertia. When choosing aluminum models, preference is given to the material of the primary type (not remelted). In comparison with the secondary, it contains less impurities, reducing the ohmic resistance.
Cast iron radiators are least compatible with an ionic boiler, since they are most susceptible to contamination. If there is no way to replace them, experts recommend observing several important conditions:
- The documents must indicate compliance with the European standard
- Mandatory installation of coarse filters and sludge catchers
- Once again, the total volume of the coolant is produced and equipment suitable for power is selected
Anode-capillary system
This system is innovative. It is based on the process of polarization of water molecules under the action of alternating current. Heat loss is minimized here. This is the main feature of the anode-capillary heating system. The appearance of the electrolysis process in this case is practically excluded due to the absence of any impurities in the coolant, and the alloys from which the electrodes themselves are made have low electrolytic capabilities.
Anode-capillary boiler
Anode electrodes should be preferred as their use increases the productivity of the system.
History of appearance and principle of operation
During just 1 second, each of the electrodes collides with the others up to 50 times, changing their sign. Due to the action of alternating current, the liquid does not divide into oxygen and hydrogen, retaining its structure.An increase in temperature leads to an increase in pressure, which forces the coolant to circulate.
To achieve the maximum efficiency of the electrode boiler, you will have to constantly monitor the ohmic resistance of the liquid. At a classic room temperature (20-25 degrees), it should not exceed 3 thousand ohms.


Distilled water must not be poured into the heating system. It does not contain any salts in the form of impurities, which means that you should not expect it to be heated in this way - there will be no medium between the electrodes for the formation of an electrical circuit.
For additional instructions on how to make an electrode boiler yourself, read here