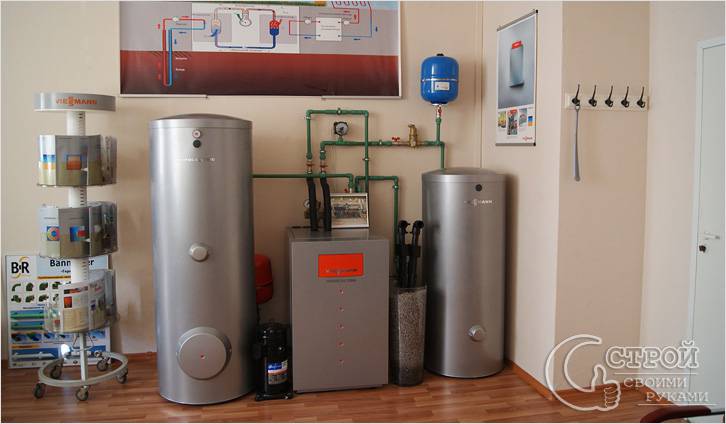
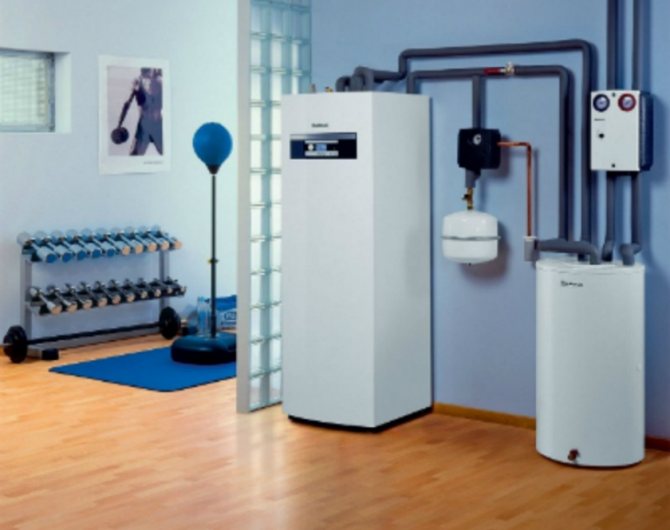
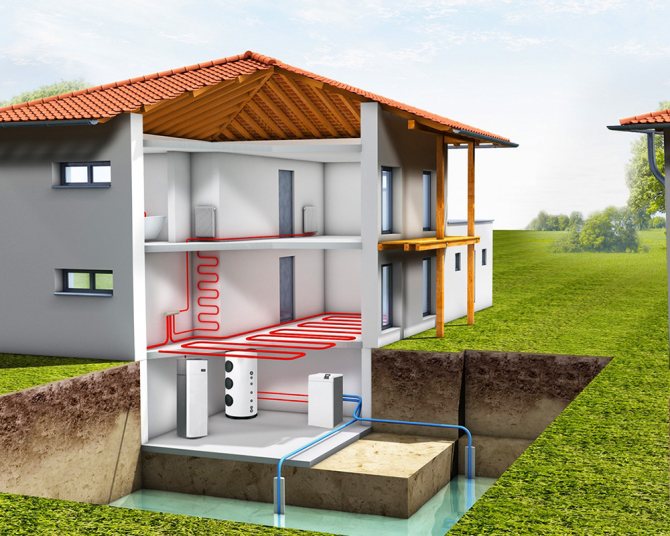
A heat pump is an interesting thing, but expensive. The approximate cost of equipment + external circuit devices is from $ 300 to $ 1000 per 1 kW of power. Knowing the "handiness" of the Russian people, it is easy to assume that more than one hand-made heat pump works in the vastness of our vast and diverse homeland. Most often, there are home-made devices that were made by "refrigerators". And this is understandable, because the heat pump and the freezer work according to the same principle, it is just that the system of heating plants is focused on collecting heat, not removing it, and the compressor is used with a higher power.
Read about how it works here.
What can be a source of heat for a heat pump
Heat for heating the room can be taken from the air outside. But here difficulties in operation will inevitably arise: temperature fluctuations, even average daily, are too large, not to mention the fact that the heat pump shows normal efficiency at temperatures above 0o C. And how many regions do we have such a picture in winter? In the spring, and even then not early, and not throughout the territory, and not all the time.
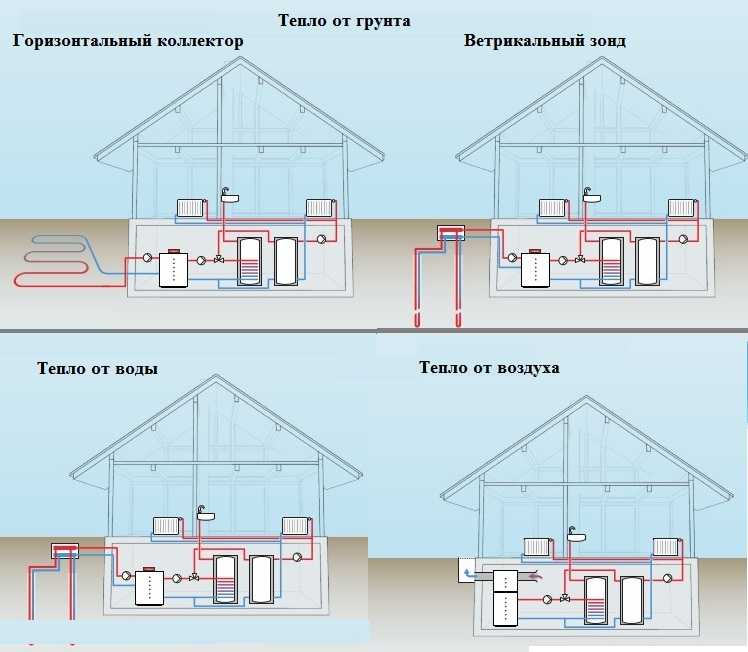
Any environment can be a source of heat for your heat pump-heated home
A heat source located in the water looks much more acceptable. If there is a river, a lake or a pond of a decent depth nearby, this is just great: you can simply drown the pipeline. It is only important that fishermen with donks do not fish there.
Another good option is a well, but there is a possibility that the water level will drop and you will have to look for another source. But so far everything is fine, it will work well: the average water temperature in the underground horizons is 5-7 oC. This is more than enough for the operation of the heat pump.
You may be surprised, but you can also use the sewerage system - the temperatures there are higher than in the wells. The pipeline can be placed in a cesspool or well, but on condition that it is covered with water at all times. And the pipe will need to be chemically resistant.
A horizontal underground collector is an extremely laborious task: it will be necessary to remove the soil from several hundred square meters to a depth below the freezing point. These are very large volumes that cannot be mastered alone or even with an assistant. And, as practice has shown, in our climatic conditions such systems are ineffective: winters are too harsh.
With vertical collectors, things are no better - you will hardly be able to do without drilling equipment. The number and depth of wells depend on the soil: the range of possible heat removal from a meter of a well is very large. From 25 W / m in dry crushed stone and sandy soil, up to 80-85 W / m in wet crushed stone and sandy soils or in granite. Accordingly, the difference in the length of the wells is 3 times and more.

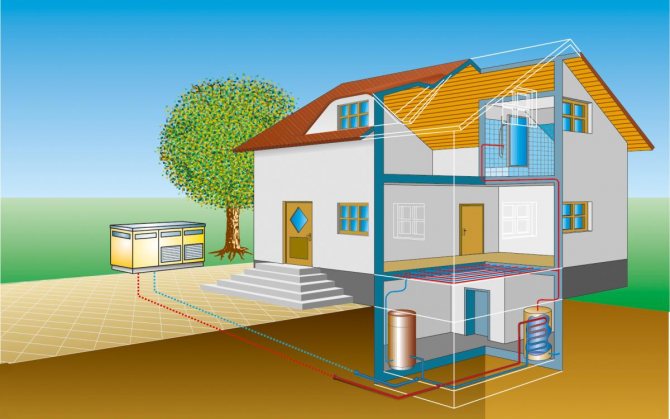
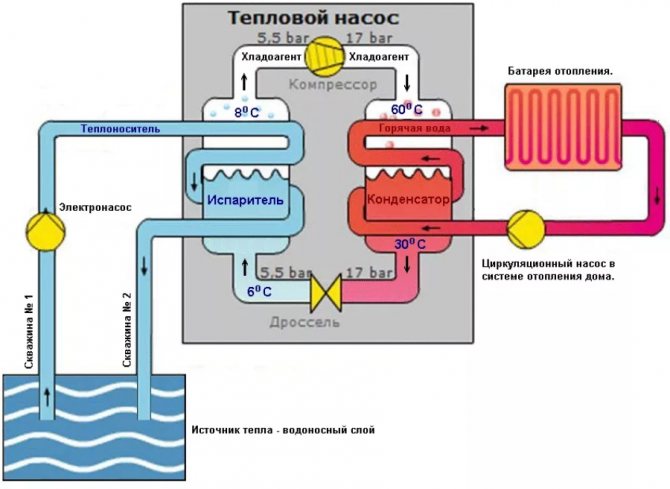
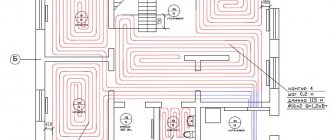
Here is a diagram of heating a house with a heat pump. When using, as in the described example, two wells and in the absence of a closed loop, the distance between the two wells must be at least 20 meters. And you need to take into account the direction of the flow so that cold water from the pump does not lower the temperature in the "donor" well
In the described example of a homemade heat pump, the heat source is a well with a good water flow rate. Water arrives so quickly that it covers the consumption for household needs and is enough to transfer the required amount of heat (the required water flow rate was calculated and the pump was selected accordingly).But the source of heat for this modification can be any of the ones described above, except for air. Having decided on the heat source, it will be possible to make a heat pump for heating the house.
Types of heat pumps
In order to clearly understand what a heat pump is, you need to know what is the heat carrier for it on the contours of its structure outside and inside the house. These coolants classify this device.


Types of heat pumps
The device receives energy for its operation from the following sources:
- water. The source can be a body of water, centralized water supply or a well, etc .;
- priming;
- air.
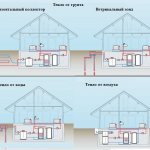
Indoors, the energy obtained with such a device is used not only for heating, but also in air conditioning, as well as heating water. The combination of various functions and elements used makes it possible to divide heat pumps into several types, which include:
- water-water;
- air-water;
- soil-water.
Water-air
The most efficient systems for heating are water-water systems. This efficiency is due to the fact that the temperature of the water used at great depths is constant and has rather high indicators. To obtain energy from this type of source, they can use:
- wells and wells, with the help of which groundwater is pumped;
- open water bodies, which include rivers and lakes;
- waste water that has been used in industry for technology.
A heat pump that uses energy extracted from an open-type reservoir will require the lowest cost. In this case, you will need to load pipes with a coolant and lower them into the water. In the case of groundwater, a more expensive structure is used, since its implementation is already more difficult. To dump water, you need to build a well. This water will pass through the heat exchanger.
Air-to-water or air circuit
An air-to-water heat pump combines pros and cons. The advantages include the uselessness in the development of wells of great depth and work associated with soil cleaning. The disadvantage of these devices is its low power in the cold season, which affects its lowest efficiency among other models. To use this device, it is required to mount the appropriate equipment on the house roof.
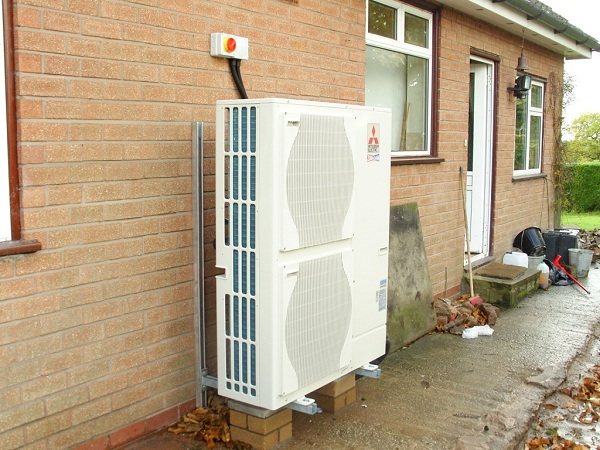


Air source heat pump
The advantage of this design can be attributed to its ability to reuse the leaving heat from the premises, which heats the heat pump in the form of smoke, water or air. In winter, alternative heating will be required to eliminate the lack of heat.
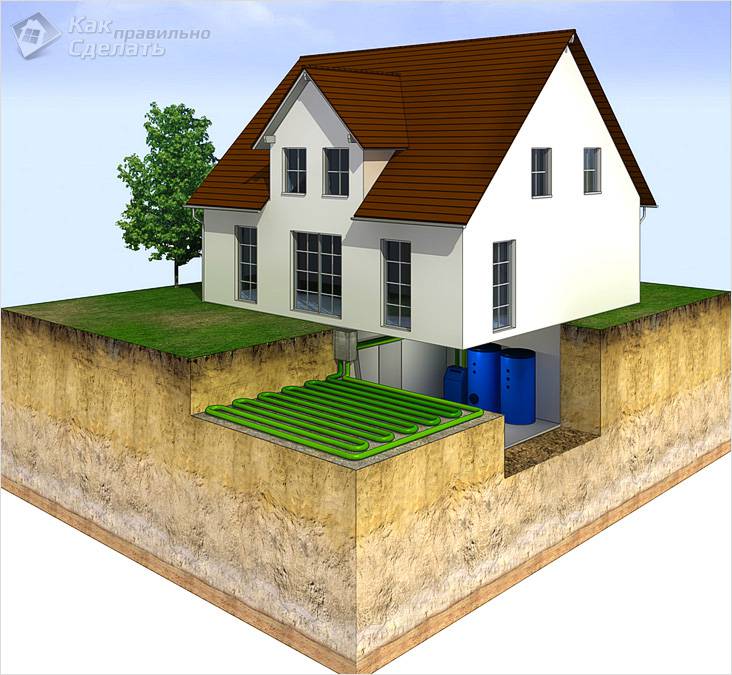
Ground-water
A heat pump of this type is also a very efficient source of energy for heating. This is due to the fact that the heat that is obtained from the ground 5 meters deep has constant values in temperature and is not affected by changes in weather conditions on the surface of the earth. On the external circuit, the coolant is a special safe composition called brine, which is safe from an environmental point of view.
The external circuit used for this type of heat pump can be horizontal or vertical type.
The pipes used for this system must be plastic. Horizontal execution requires a large area of land. After the pipes are laid under the ground, this plot of land cannot be used for agricultural needs.
It is allowed to grow a lawn or plants of the same age. For vertical execution, it will be necessary to develop several wells, the depth of which ranges from 50 to 150 meters, since at such a depth the soil has a stable and high temperature. Such a device is called a geothermal pump.To transfer energy from such depths, special probes are used.
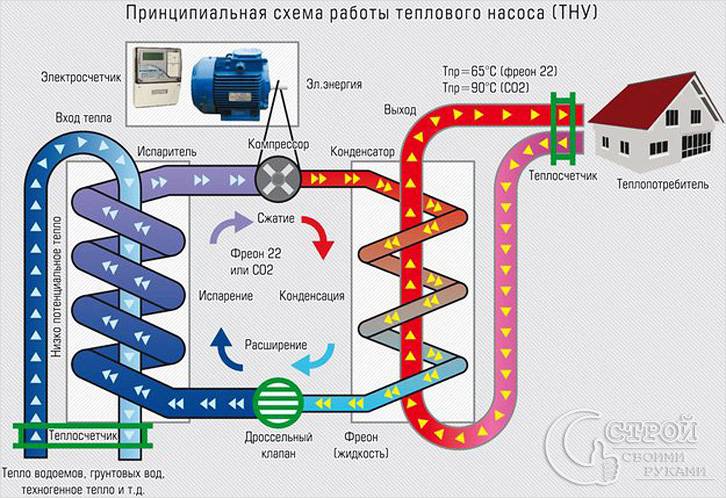
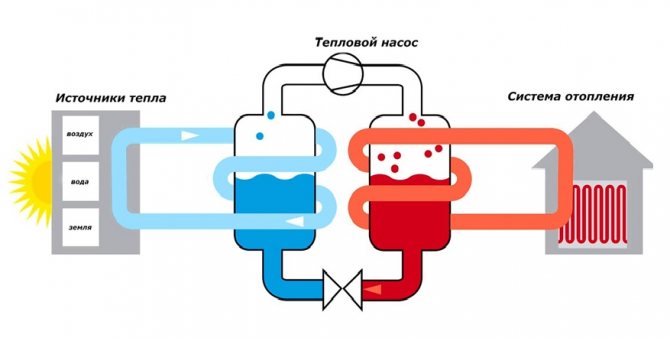
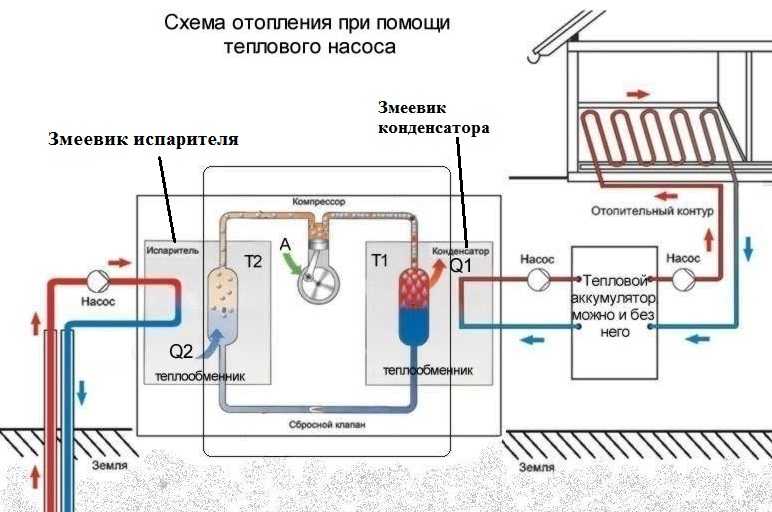
How the heat pump works
The environment around us, at temperatures over one degree, has a certain amount of energy. With the help of a heat pump, this energy can be used. Its principle of operation is based on heat transfer from a low potential source with thermal energy to a heat carrier, the temperature of which is much higher.

How the heat pump works
This is implemented as follows:
- The coolant enters the pipeline located in the ground. It heats up a few degrees.
- After that, the coolant that has passed into the evaporator transfers to the internal circuit the energy that was collected in the evaporator.
- Refrigerant is located in the external circuit, which turns into gas after heating in a heat exchanger.
- To increase the temperature of this refrigerant, it enters the compressor for compression at high pressure.
- The already heated refrigerant gas enters the condenser, which in turn gives off heat to the coolant in the heating system of the room.
- After the end of the cycle, the refrigerant that has lost heat turns into a liquid state and returns to its original position.
Refrigeration units work on a similar principle. Therefore, heat pumps can be used to condense air in hot weather years (split systems), as from the refrigerator.
From the operating experience of a do-it-yourself heat pump
As practice has shown, the performance of the presented option is low: 2.6-2.8 kW. There is no need to talk about the high efficiency of this heat pump: on an area of 60 m2 at -5 oC outdoors, it itself maintains + 17oC. But the system was considered and installed under the boiler - radiators, at an input temperature of + 45oC, simply cannot give out more. The system in the house worked old and the number of radiators was not increased, but so far in the cold they were warmed up by a stove.
If a regenerative heat exchanger is added to the structure, this will increase the efficiency by 10-15%. Given that the costs are low, you can do it. You will need two copper pipes 1.5 meters each. One with a diameter of 22 mm, the second - 10 mm. On a thinner one to increase the heat exchange area, a 4-core conductor (length 3-4 meters, diameter 4 mm) is wound, its ends are soldered to the tube so that they do not unwind. The wire wound tube is gently inserted into the larger diameter tube. It must be installed between the compressor and the evaporator. The refinement is insignificant, but it significantly increases the efficiency. True, under certain conditions it is unsafe: warm freon can get into the compressor, which will lead to its failure.
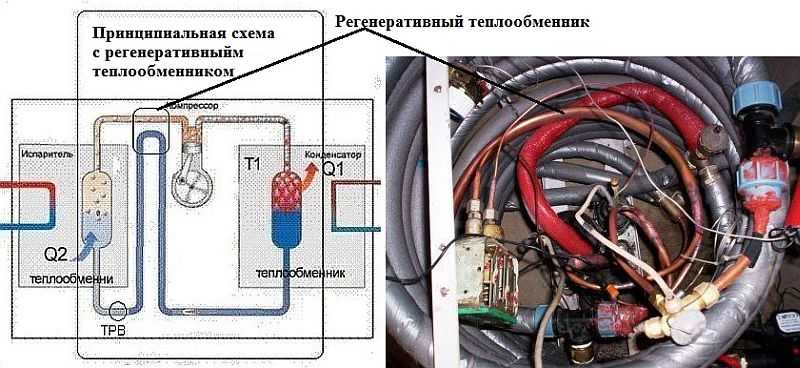

Improvement of the circuit: you can add a regenerative heat exchanger, which will increase the productivity by about 15-20%
The second option for increasing efficiency, safer and no less effective, is to build in an additional heat exchanger for heating water or glycol.
What to look for if you decide to make your own heat pump. There are a few things that can only be learned from experience:
- The starting currents of this particular installation were very decent. There were not always enough network resources to run the installation. Therefore, if you make a serious installation, it is better to take a three-phase compressor, and supply a three-phase input, respectively. Yes, not cheap, but for a stable start of a single-phase compressor, an electronic stabilizer of decent power is required, which cannot be called cheap either.
- A heat pump on a finished radiator system will not give a normal room temperature. They are designed for a different coolant temperature, which these installations, especially home-made ones, are extremely rarely able to give.Therefore, either upgrade the system (by adding at least the same number of radiator sections), or install water floors.
- If there are three rings of water in a well, this does not mean that it has a large debit. You need to know how much water he is able to give with its constant selection.
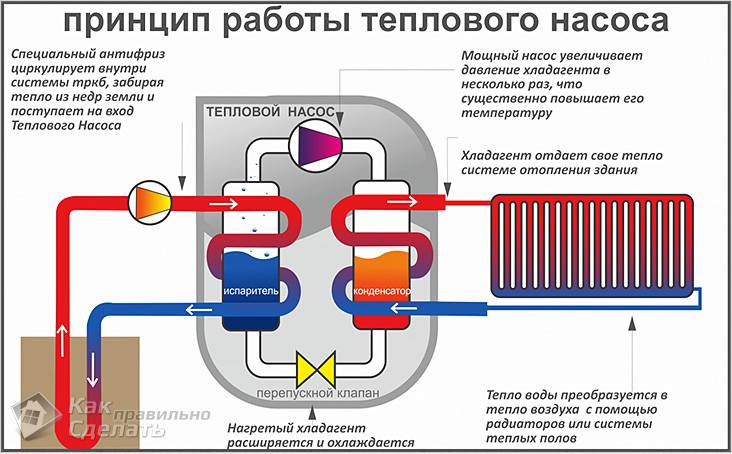
The principle of operation of the heat pump
The peculiarity of heat pumps is that they operate from natural energy sources. The pump does not need diesel, electricity or solid fuels to release heat energy.
The source of energy is water, atmosphere and soil. The pumps do not generate heat, but simply transfer it into the building. This uses a small amount of electricity.
In order to provide a house with heat, you only need a heat pump and a heat source. The principle of operation of the system resembles that of a conventional refrigerator, just the opposite. In this case, the heat is taken from outside and transferred to the house.
An important point: the main element in an alternative heating system is precisely the heat pump, therefore, its construction must be approached very carefully.
The pump consists of the following elements:
Features of the air-to-air heat pump:
- compressor, which is an intermediate element of the system;
- evaporator. The transfer of low-potential energy takes place in it;
- a throttle valve through which the refrigerant (freon) returns to the evaporator;
- condenser, where freon is cooled and heat energy is released.
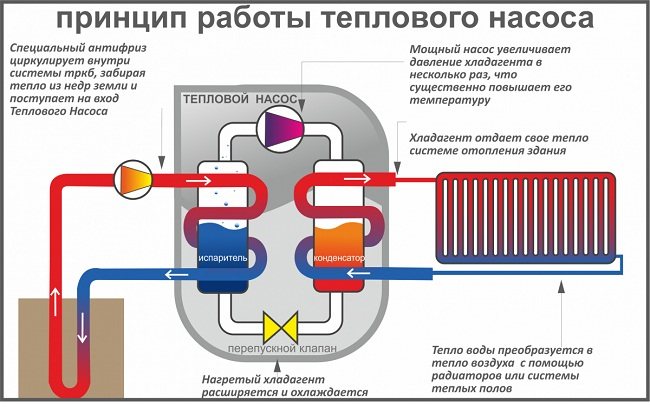
The pump works according to a certain principle. It looks something like this:
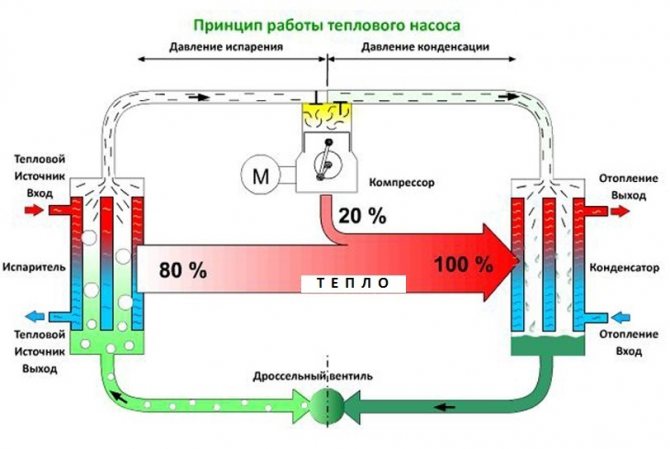

The principle of operation of the heat pump. (Click to enlarge)
- Low-grade heat, which is released from external energy sources, is transferred through pipes to the evaporator - to the first element in the pump design. Heat is transferred by heat carriers that are able to withstand low temperatures and not freeze at the same time.
- Here the heat is transferred to the refrigerant, which is circulated in a closed loop of the system. Freon is often used as a refrigerant.
- In the compressor, high pressure acts on freon, which significantly increases its temperature.
- At the next stage, the refrigerant enters the condenser, where heat is transferred to the heating system circuit. As a result, the heat goes into the room, and the freon, when cooled, returns to a liquid state.
- Through the pressure reducing valve, the freon goes back to the evaporator, where the process is repeated.
Based on the principle of operation of the pump, electricity is spent only on the operation of the compressor. As a result, this makes the heat pump the most economical way to transfer heat.
You may be interested in an article about the features of heat pumps for home heating. You can study a detailed classification of heat pumps in this article.
Outcomes
Undoubtedly, the cost of a heat pump from an air conditioner is several times lower than ready-made factory options, even those made in China. But there are a lot of nuances here: you need to take care of the source and amount of supplied heat, correctly calculate the length of heat exchangers (coils), install automation, provide guaranteed power, etc. But if you are able to solve these problems, then it is undoubtedly beneficial. Let me give you some advice: in the first year it is very desirable to have backup heating, and testing and trial run, it is better to carry out in the summer, so that there is time to revise the unit before the start of the heating season.
Pros and cons of heat pumps
To the pluses use of heating systems based on the use of heat pumps can be attributed the following:
- Profitability during operation;
- Environmental safety of installations;
- Fire safety of installations;
- Operational reliability;
- Autonomy of work.
The disadvantages include:
- High price;
- The complexity of the entire complex of works;
- The need for major repairs after the expiration of the service life, associated with significant material investments.