Duration of start-up and adjustment work when starting heating in mcdou
- commissioning tests in operational conditions, balance experiments (setting optimal modes, testing valve control in manual and automatic mode, checking automation settings, identifying deficiencies and working out proposals for their elimination), the result is an individual test report;
- comprehensive testing (72 hours of continuous operation - for all main equipment, 24 hours - for heating networks), its start is considered to be the start time of all systems at maximum load.
Some companies draw up all activities directly related to the preparation and testing of devices in a separate document - the PNR Methodology, which comes as an addition to the Program. In the Program, they include more general things of an organizational nature.
That is, there is an actual division of the entire complex of works into organizational, legal and technical components.
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of May 23, 2006 No. 307 "On the Procedure for Providing Utility Services to Citizens", the requirement for utility services for heating is uninterrupted round-the-clock heating during the heating period. The permissible duration of the heating interruption is not more than 24 hours in total within one month.
In case of failure to provide utilities or the provision of utilities of inadequate quality, the consumer notifies the emergency dispatch service of the contractor or another service specified by the contractor. A message about the failure to provide utilities or the provision of utilities of inadequate quality can be made by the consumer in writing or orally (including by phone) and is subject to mandatory registration with the emergency dispatch service.
The involved specialized organization issues a technical report, as a rule, within one month. proektoved.com Commissioning of heating systems Before putting the heating system into operation, it is necessary to perform a number of preparatory work, carry out tests and establish the interaction of various units with each other. All this is included in the commissioning of the heating system, the purpose of which is to identify and eliminate deficiencies and errors made during installation, as well as to bring the entire system in accordance with the standards established for it.
As a result of these works, the client receives a reliable, productive and efficient system. The cost of commissioning of heating is fully paid off by subsequent trouble-free operation and safety of the equipment. Scope of commissioning
Commissioning works are carried out after installation.
As part of the commissioning of refrigeration, the following types of test work are carried out:
- checking the correctness of assembly of all units and components of refrigeration equipment;
- filling the cooling system with all necessary working media (freon, nitrogen and oil);
- checking the functioning of protection and control means;
- starting the system and bringing it to the required operating mode;
- instructing (and, if necessary, training) of the operating personnel.
Important! The last point can be included in the commissioning program only by agreement with the customer. Procedure for commissioning heating and heat supply systems. The term "heat supply" is usually associated with the organization supplying the heat carrier, while the concept of "heating" is associated with its consumption and is applicable to organizations,operating heated rooms
Scheduled and unscheduled works on setting up heating networks
Scheduled checks include checks carried out at thermal power plants with the required frequency of PTETE:
- performance testing — one every 5 years (p. 2.5.4);
- development of hydraulic regimes of heating networks - one once a year for heating and once a year for summer periods (p. 6.2.60);
- regulation of subscriber inputs with adjustment of the size of throttling diaphragms - for each heating season (clause 6.2.60);
- correction of schemes, profiles of heating mains, gas-hazardous heat chambers - one once a year according to the actual state of heating networks (clause 6.2.5);
- hydraulic tests to determine the actual head loss - every 5 years (p. 6.2.32);
- tests for maximum temperature and determination of actual heat losses - once every 5 years (p. 6.2.32);
- hydraulic tests for strength and density of equipment are carried out once a year (p. 6.2.13);
- testing of air heating and supply ventilation systems, determining their compliance with passport and design parameters - once every 2 years or more (p. 9.4.14).
Extraordinary commissioning tests of thermal power plants are carried out in accordance with PTETE (clause 2.5.5), as a result:
- constant discrepancy between actual indicators and standard characteristics;
- changes in the modes of production, distribution and consumption of heat energy and network water;
- modernization and reconstruction.
Unscheduled commissioning is recommended when there is a lack of heating for end users. Problems are revealed during routine checks carried out by the maintenance personnel of the heating network or when complaints are received from the owners of the connected heat and hot water supply points. Also, unscheduled adjustments are necessary when:
- reconstruction of boiler houses, their merging into a single system;
- disconnecting consumption points or connecting new ones;
- transfer of heat supply from the central heating station to the ITP;
- reconstruction of the hot water supply system from open to closed.
- overheating of consumers or underheating.
The reliability of heat supply to consumers is ensured, in accordance with PTETE (clause 11.1), by the preparation and implementation of the main measures in the inter-heating period:
- elimination of the discovered deficiencies in the operating modes of the heat supply system;
- hydraulic tests for strength and density of pipelines of heating systems, equipment and communications of a boiler room, heating points and heat consumption systems;
- boring of heating systems in order to detect corrosion damage to pipelines;
- flushing of communications of boiler houses, heating networks, heating points, heat consumption systems;
- tests of heating networks for heat and hydraulic losses, maximum temperature of network water;
- development and implementation of operating modes of heat supply systems.
The presence of seals on the installed design washers and cones of elevators is checked and recorded, on the basis of PTETE (clause 11.5), in the act of readiness of heat points for the heating season.
Heating regulation works with shut-off valves
Throughout the entire process, the water entering the system must be at a constant temperature. Regulation, as a rule, is carried out according to temperature differences by changing the volume of supplied water, which depends on the type of heating system and heat input.
Temperature drops depend on the volume of consumed water and this value is inversely proportional. Thus, in order to increase the differential to the required value, the coolant flow rate should be reduced. To do this, either close the valve located at the inlet, or reduce the flow itself.
The more water passes through the heating devices, the higher the speed of its movement and, accordingly, the coolant cools less.As a result, the average temperature in the radiator rises and the heat transfer of the device increases. After completing the adjustment in the heating unit, individual risers of the structure are subject to adjustment. In case of problems, the repair is carried out so that it is possible to activate the control valves for the heating system on the risers or the balancing valves (for more details: "Control valves for heating radiators, valve installation").
One of the ways to adjust the heating system is shown in the video:
When there are only taps on the heating risers, only preliminary adjustments are made. In this case, it is taken into account that the closer the riser is to the inlet, the more the tap should be opened. This is necessary so that the shut-off valves for heating on the nearest riser pass a minimum volume of water.
At the same time, on the riser farthest, you need to open the tap, such as in the photo. First, they check the quality of heating of the farthest riser in terms of location and end with the one that is closest.
Usually, in two-pipe systems, due to the pressure, the devices on the upper floors overheat. If this drawback is not present on the lower floor, then it is necessary to adjust the heating radiators of the upper ones. If there is a double adjustment valve, it is possible to reduce the flow area. In the absence of such taps, the heating batteries are adjusted by installing throttle washers.
In two-pipe heat supply systems, the uniformity of heating radiators will increase with increasing water consumption. The most important parameter for heating structures is the working pressure (read: "Pressure losses and pressure drop in the heating system - we solve the problem"). To lower it, use a pressure regulator in the heating system, and to increase it, use circulation pumps.
The temperature of the coolant when regulating the device cannot exceed 50-60 ° C. After completing the adjustment, the water temperature must be brought to 90 ° C, and the heating of the radiators must be checked again at this temperature regime. It is advisable to contact a specialist for the adjustment of heating systems.
Main menu
Hello! In this article I will consider a typical, let's say, case of adjusting and adjusting the internal heating system of a building. Namely, heating systems with an elevator mixing unit. According to my observations, there are about 80-85 percent of such ITPs (heating units) of the total number of heating units. I wrote about the elevator in this article.
The adjustment of the elevator unit is carried out after the adjustment of the ITP equipment. What does it mean? This means that for normal operation of the elevator, you at the heating point must know the operating parameters from the heat supplying organization in terms of pressure and temperature in the supply pipeline (supply) P1 and T1. That is, the temperature in the supply T1 must correspond to the temperature according to the temperature schedule of heat release approved for the heating season. Such a schedule can and should be taken in a heat supply organization, this is not a secret behind seven seals. And in general, every consumer of heat energy should have such a schedule without fail. This is the key point.
Then the supply pressure P1. It should not be less than what is necessary for the normal operation of the elevator. Well, usually the heat supply organization still maintains the working pressure for the supply.
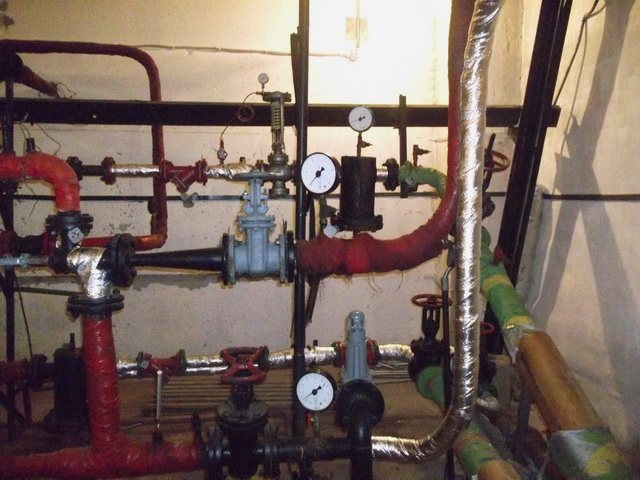

Further, it is necessary that the pressure regulator, or the flow regulator, or the orifice plate were correctly adjusted, adjusted. Or, as I usually say, "exposed". I'll write a separate article about this somehow. We will assume that all these conditions are met, and you can start setting up and adjusting the elevator unit. How do I usually do it?
First of all, I try to look at the design data on the ITP passport.I wrote about the ITP passport in this article. Here we are interested in all the parameters that relate to the elevator. System resistance, pressure drop, etc.
Secondly, I check, if possible, the correspondence of the fact and working data from the ITP passport.
Thirdly, I look and check the element-by-element elevator, mud collectors, shut-off and control valves, manometers, thermometers.
Fourthly, I look at the pressure difference between the supply and return (available pressure) in front of the elevator. It must correspond or be close to the calculated one calculated by the formula.
Fifthly, according to the pressure gauges after the elevator unit, in front of the house valves, I look at the pressure loss in the system (system resistance). They should not exceed 1 m.wst. for buildings up to 5 floors, and 1.5 sq.m. for buildings from 5 to 9 floors. This is in theory. But in fact, if you have a pressure loss of 2 m.w. and above, then most likely problems will arise. If you have a scale of divisions on the manometers after the elevator unit in kgf / cm2 (a more frequent case), then you need to look at the readings like this, if the pressure gauge readings are 4.2 kgf / cm2, then the return should be 4.1 kgf / cm2. If the return flow is 4.0 or 3.9 kgf / cm2, then this is already an alarming signal. Of course, here you need to take into account that pressure gauges can give measurement errors, anything can happen.
Sixth, I check the mixing ratio of the elevator. I wrote about the mixing ratio here. The mixing ratio must correspond to the calculated one, or be close in value to it. The mixing ratio is determined by the temperatures of the coolant, which we take either from the instantaneous readings of the heat meter, or from mercury thermometers. And here it must be borne in mind that the greater the temperature difference in the heating system, the more accurately you can calculate the mixing coefficient. Accordingly, the smaller the temperature difference in the system, the higher can be the error in determining the mixing ratio of the elevator.
It is not often, but it happens that the pressure difference between the supply and return before the elevator (available head) is insufficient to provide the required mixing ratio. This, I would say, is a difficult case. If the heat supply organization cannot (or does not want) to provide you with the required pressure drop, then most likely you will have to switch to a circuit with a circulation pump.
The adjustment of the elevator can be considered satisfactory and complete if the adopted nozzle size provides the required flow of heating water and the mixing ratio of the elevator.
After adjusting the elevator unit, they begin to adjust the heating system of the building. First, they look at the wiring diagram of the heating system in the building (if there is one, of course). If not, I view the heating wiring for the building visually. Although a visual inspection is necessary in any case. Here you need to find out which wiring, upper or lower, which heating devices are installed, whether they have control valves, whether there are balancing taps on the heating risers, thermostats on heating devices, whether there are devices for removing air at the upper points.
Setting up the heating system includes checking and adjusting the system both horizontally (distribution of the coolant along the risers) and vertically (distribution of the coolant over the floors).
First, we check the heating of the lower points of all risers. You can do it by touch. But in this case it is better for the water temperature to be 55-65 ° C. At higher temperatures, it is difficult to tell the degree of warming up. The lowest points of the heating pipes are usually located in the basement of the building. It is good if at least some kind of control valves are installed on all risers. This is generally necessary, but unfortunately, it does not always happen in fact. It is great if balancing valves are installed on the risers.Then cover the overheating risers with control valves.
But it is better, of course, to check the distribution of water along the risers by measuring the temperatures in the supply and return. Although this is a more time consuming option.
So, for example, the return temperature T2 in a two-pipe system should be taken taking into account the cooling of the supply water temperature. If according to the schedule T1 = 68 ° С, but actually T1 = 62 ° С, T2 according to the schedule is equal to 53 ° С. In this case, the design temperature is T2 = 62- (68-53) = 47 ° C, not 53 ° C.
In general, as a result of adjustment along the risers, there should be approximately the same temperature difference between the water inlet and outlet from all risers.
Further, the adjustment is carried out for individual heating devices. I have manual direct control valves at many sites.


A very good thing to adjust. It is even better if you have thermostats installed on your heating devices. Then the adjustment is carried out in automatic mode. We measure the temperature of heating devices using a pyrometer.
The adjustment of the elevator unit and the heating system is considered satisfactory if a uniform temperature of the heated rooms of the building is achieved.
On the topic of the device and setting of heating points, I wrote a book "The device of ITP (heating points) of buildings." In it, using specific examples, I examined various ITP schemes, namely, an ITP scheme without an elevator, a heating station scheme with an elevator, and finally, a heating unit scheme with a circulation pump and a variable valve. The book is based on my practical experience, I tried to write it as clear and accessible as possible. Here is the content of the book:
1. Introduction 2. ITP device, circuit without an elevator 3. ITP device, elevator circuit 4. ITP device, circuit with a circulation pump and an adjustable valve. 5. Conclusion
You can view the book at the link below:
Construction of ITP (heating points) of buildings
Recalculation for heating when setting up the heating system
The purpose of individual tests is to prepare for complex testing in the presence of a working committee.
Complex tests are actions carried out after the acceptance of the mechanisms by the working commission, and directly the complex testing itself. At the same time, the interconnected joint operation of all installed equipment is checked at idle speed, then under load, after which the technological mode envisaged by the project is reached.
Although not spelled out by law, in recent years, the customer has increasingly requested that a commissioning program be drawn up for testing. This gives confidence that not a single nuance will be missed, and that the operation of all systems will comply with the approved standards and project documentation.
What is crimping for?
After completing the installation of the heating system, pressure testing is a mandatory stage of commissioning. By increasing the pressure inside the heating system, you can notice weaknesses and shortcomings even before starting up, you can find sources of leaks that leak elements. The fact is that during the operation of the heating system, the water inside it heats up and expands, increasing the pressure, which means that there may be a breakthrough in weak points. It is safer to spot such deficiencies early on. To avoid a lot of damage.
The same applies to the heating season. After half a year of downtime, the elements of the system can weaken, and without checking and adjusting, an emergency situation can occur during hot water supply.


Methods for adjusting the heating system
It often happens that mistakes made during the installation of the heating system can only be detected after the equipment is put into operation. Among the reasons for the occurrence of failures in the heat supply of the house is the incorrect determination of the required amount of coolant.When there is little liquid in the system, it will be cold in the room, and if there is a lot, the air overheats and does not pass into other rooms.
Adjustment of the heating structure is required to adjust the operation. If it is not produced, then the service life of the equipment will be significantly reduced.
The heating system is regulated by one of two methods:
- in a qualitative way - by changing the temperature of the coolant;
- quantitatively - with it, the volume of the liquid is changed.
Qualitative regulation is carried out at the heat source, and quantitative regulation is carried out directly on the heating structure. Before proceeding with its implementation, determine the volume of the consumed liquid and the temperature of the coolant, using special devices for this - a water meter and a flow meter.

When there are no such devices, then the actual flow rates are compared with the calculated data. Most often, two-pipe heating systems are installed that can provide warmth and comfort in the house. You will also need shut-off and control valves for heating.
Heating system regulation
After setting up and starting up the heating system, regulation of the heating system, at the same time, it is imperative to check the heating of heat-using installations in hydraulic and thermal modes during operation of the heat source. It is also important to carry out work in order to identify the correspondence of the actual flow rates of the coolant with the planned ones. If discrepancies are found in the calculations, then the diameters of the nozzle holes of the throttle diaphragms should be corrected.
After completing all stages of work, it is necessary to check the efficiency of the functioning of the entire system.
The productivity of the heating network is characterized by the following indicators:
- reducing the consumption of electricity spent on pumping the coolant by turning off unnecessary pumping stations and reducing the consumption of network water;
- reduction of fuel consumption due to elimination of overheating of heating systems;
- the ability to connect additional heat consumers to the heating network.
strongly recommends using the services of specialists when starting, setting up and adjusting the heating system. This guarantees the normal functioning of the heating system, its high efficiency and operational reliability.
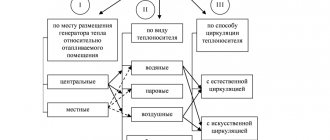
What are the types of heating systems for an apartment building
Depending on the installation of the heat generator or the location of the boiler room:
- An autonomous system in an apartment, where the heating boiler is installed in a separate room or in the kitchen. The costs of purchasing a boiler, radiators and related piping materials return quickly, since such an autonomous system can be adjusted based on your own considerations regarding the temperature regime in the house. In addition, the individual pipeline does not lose heat, but, on the contrary, helps to heat the premises, as it is laid through the apartment or around the house. An individual boiler does not need to be adapted for the reconstruction of centralized heating - once a heating scheme is drawn up and implemented, it will work for a lifetime. And, finally, an already working circuit can be supplemented with parallel or series-connected circuits, for example, a "warm floor";
- The option of individual heating, which is designed to service the entire apartment building or the whole residential complex, is a mini-boiler room. An example is the old boiler houses serving the block, or new complexes for one or more houses on different sources of energy - from gas and electricity to solar panels and thermal springs;
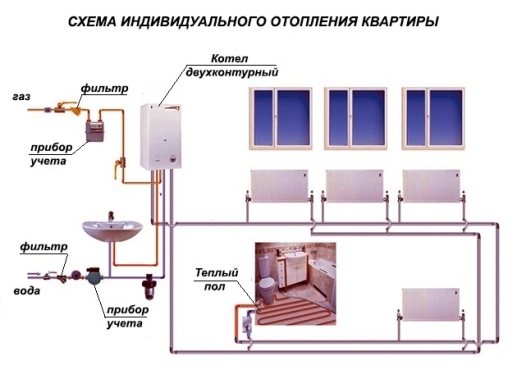

A centralized heating scheme in a multi-storey building is the most common working solution to the problem so far.

Heating schemes depending on the parameters of the working fluid:
- Heating on ordinary water, in the pipes of which the coolant is not heated above 65-70 0 C. This is a development from the field of low-potential systems, but most often old schemes work with the temperature of the working fluid reaching 80-105 0 C;
- Steam heating, where not hot water moves in pipes, but steam under pressure. Such systems are a thing of the past, and today they are practically not used in the delivery of heat and heating of any type of apartment buildings.

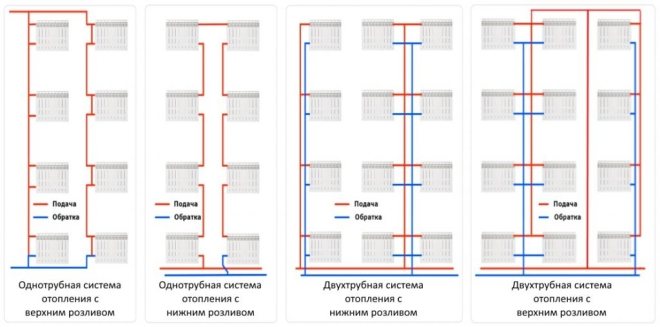
Based on the piping diagram:
- The most common is a one-pipe heating system for a multi-storey building, where both supply pipes and return pipes are one thread of the heating main. Such a scheme can still be found in "Khrushchev" and "Stalin" buildings, but in practice it has a big drawback: batteries or radiators connected in series in the circuit do not provide uniform heat transfer - each next heating device will be slightly colder, and the last radiator in the pipeline will be the coldest. For at least approximately the same heat distribution throughout the rooms, each radiator next in the circuit must be equipped with a larger number of sections. In addition, in a one-pipe heating scheme in a five-story building, it is impossible to use radiators that do not correspond to the design parameters, and devices for regulating heat transfer - valves, etc. regulation;
- The Leningradka scheme is a more perfect solution, but according to the same one-pipe scheme. This circuit has a bypass (pipe jumper) that can connect or disconnect additional heating devices, thereby regulating heat transfer in the room;

A more advanced two-pipe heating system in an apartment building began its existence with the construction of buildings according to the project of the so-called "Brezhnevka" - a panel house. The supply and return flow in such a scheme work separately, so the temperature of the working fluid at the inputs and outputs of apartments in a 9-storey building is always the same, as in radiators or batteries. Another plus is the ability to install a regulating automatic or manual valve on each heating device; The beam (collector) scheme is the latest development for atypical housing. All heating devices are connected in parallel, and taking into account the fact that this is a closed OO system in an apartment building, the piping can be made hidden. When implementing the beam scheme, all adjusting devices can limit or increase the supply of heat in a metered manner.
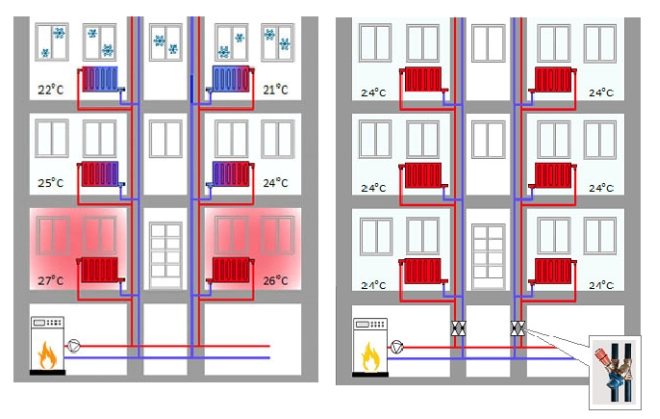
Regulation of the heating temperature in the heating unit of an apartment building
On the territory of Russia, the central heating system of an apartment building is usually used, the coolant to which is supplied from a city boiler house or CHP. In this case, the water circuits are equipped according to different schemes, since they are one-pipe and two-pipe. Usually, heat consumers are not very interested in such nuances, but if it is necessary to repair an apartment and change old batteries for new modern heating radiators, it is advisable for owners of residential real estate to understand such subtleties.
The cost of autonomous heating in an apartment building is rather big, so it is preferable to put into operation one powerful boiler house, capable of providing a residential neighborhood with heat and hot water.
Through the main pipelines, the coolant from the central boiler room is supplied to the heating unit of an apartment building and is further distributed to apartments. In this case, additional adjustment of the degree of hot water supply is carried out directly at the heating point, for which circular pumps are used. This method of supplying the coolant to the end consumer is called independent (in more detail: "Centralized heating is both pros and cons").
In addition, dependent heating systems are used in apartment buildings. In this case, the coolant is transported to apartment batteries without additional distribution directly from the CHP. In this case, the water temperature is regardless of whether it is supplied through a distribution point or directly to consumers.
The types of heating systems in an apartment building are open or closed (in more detail: "Open and closed heat supply system - advantages and disadvantages in comparison").
In the latter version, the heat carrier from the CHPP or the central boiler house, after entering the distribution point, is supplied separately to heating radiators and to hot water supply. In open systems, such a separation is not provided for by the design, and heated water for the needs of residents is supplied from the main pipe, therefore, outside the heating season, consumers are left without hot water supply, which causes many complaints about utilities.
Commissioning of heat supply
In terms of the importance of the procedure, the heating supply PNR can be compared with the installation of equipment or design. At the time of launch, all its components are monitored, as well as the readiness of the equipment, its effectiveness and efficiency.
Pressure testing as a fundamental step in the preparation of a heating system
When the main phases of the installation process are completed, it is necessary to do commissioning work - to check the efficiency of heating, its serviceability, and also to bring the equipment to operating indicators. One of the initial stages of heating supply is considered to be pressure testing. This procedure ensures the comfort of living in the room, in which the heating system functions correctly.
Pressure testing consists of the following sequential steps:
- Checking communications using excess pressure;
- Pump testing;
- Checking the reliability of pipelines is a fundamental stage in the PNR of heat supply, which is considered mandatory;
- Monitoring the tightness of pipe coils;
- Hydraulic checks.
Pressurized communications are left under pressure for a day
It should be noted that during the temperature drop, the load in them will slightly decrease - you should not be afraid of this. This is a traditional physical process when, when a substance cools, it contracts.
Even a person who does not have much knowledge in this area can cope with the heating supply PNRM - the procedure is simple and does not ask for specific abilities.
Test run with PNR heating systems
The heating system is tested before the heating period begins. Flush the pipes before filling them with water. The process removes very small particles of metal and polymer materials stuck during pipe processing.
The run of the liquid with the PNR of heat supply is done according to the schedule for the start of heating work. The test is carried out at a temperature of 60-70 degrees, depending on the period of the year: the frozen pipes must be warmed up in advance.
The test duration is 7 hours, and the equipment test should show good results. All fittings must withstand the test load: this means that the pipes are ready for continuous operation.
By running test testing, the basement floors of the building are monitored. Specifically here, problems may arise due to the difference in pressure indicators. For the release of air during the PNR of heat supply, specialized opening devices are used, by means of which the remnants of the substance that has appeared are removed.
The final step is to check the boiler and adjust it, after which we proceed to the application of heating completely.
Thermal test of the heating system.
Heating up a heating system is a thermal test that shows the efficiency and quality of heating the premises.The system starts up and warms up to 60-70 degrees, depending on the type of pipes and the season of the year. This process usually lasts about 7 hours. After a while, the temperature is measured in different elements of the heating system, as well as the air temperature in the room. All indicators should be as close as possible to the standards. If the test revealed the inefficiency of some elements of the system, installation regulation is carried out, as a result of which the level of circulation of certain elements of the system is adjusted.
Commissioning of electrical equipment


Commissioning works accompanying electrical work is a set of works, including checking, adjusting and testing electrical equipment in order to ensure the electrical parameters and modes specified by the project. Qualified commissioning work carried out by the electrical installation staff will be able not only to reveal possible violations during electrical installation work, shortcomings in the operation of the equipment before its operation, but also ensure its guaranteed operation for quite a long time.
The need for heating
The need to heat your own home has always existed, but the ways to achieve this goal were very different. For hundreds of years, classic Russian stoves have been used in Russia, and a little later, fireplaces appeared. The traditional heating structures have been replaced by modern appliances and heating systems, which are superior in quality and efficiency to their predecessors.
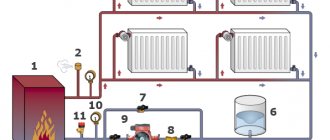
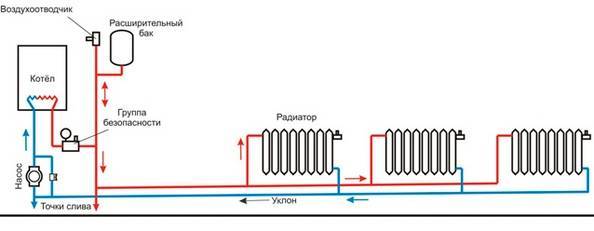
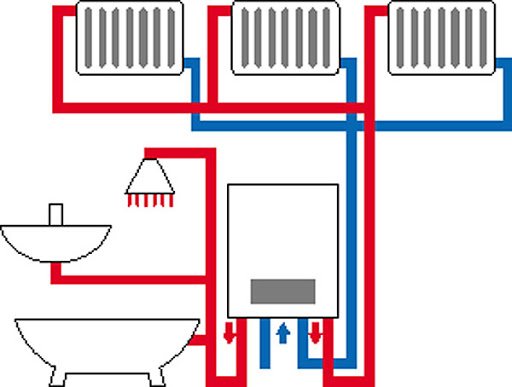
At present, a heating system is a structure, which, as a rule, consists of the following main elements:
- heating boiler;
- pipeline;
- heating devices.
There is a heating agent inside the heating system. In most cases, water is used to heat private households, since in the event of a leak, it does not pose a threat to people and the environment from an environmental point of view. Of all types of liquid heat transfer fluids, it is water that accumulates heat best of all and, when it cools, gives it away.


In addition, it flows well and moves almost instantly within the elements of the system. Water is always available in the water pipes and can be added to the heating structure at any time.
The functioning of the system consists in the movement of the hot coolant through it using a circulation pump. The water is first heated in the boiler and then distributed through pipes, from which it enters the radiators.
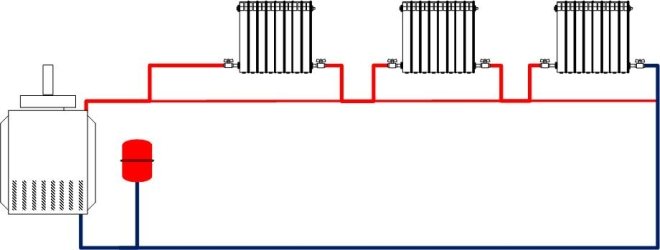
Two-pipe diagram of heating systems
In two-pipe schemes, the supply of hot coolant to the radiator and the removal of the cooled one from the radiator are carried out through two different pipelines of heating systems.
There are several options for two-pipe schemes: classic or standard, passing, fan or beam.
Two-pipe classic wiring

Classic two-pipe wiring diagram for the heating system.
In the classical scheme, the direction of movement of the coolant in the supply pipeline is opposite to that in the return pipeline. This scheme is most common in modern heating systems, both in high-rise buildings and in private individual ones. The two-pipe scheme allows you to evenly distribute the coolant between radiators without temperature loss and effectively regulate heat transfer in each room, including automatically by using thermostatic valves with installed thermal heads.
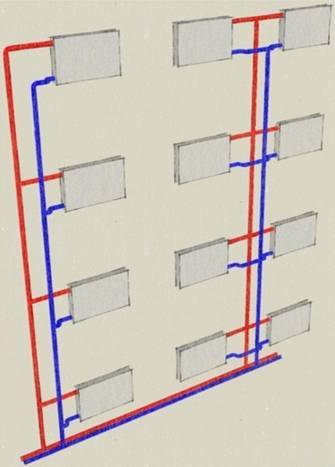

Such a device has a two-pipe heating system in a multi-storey building.
A passing scheme or "Tichelman's loop"
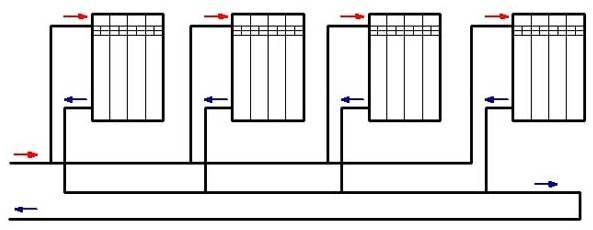

Accompanying heating wiring diagram.
The passing scheme is a variation of the classic scheme with the difference that the direction of movement of the coolant in the supply and return is the same. This scheme is used in heating systems with long and remote branches. The use of a passing circuit allows you to reduce the hydraulic resistance of the branch and evenly distribute the coolant over all radiators.
How to adjust the temperature


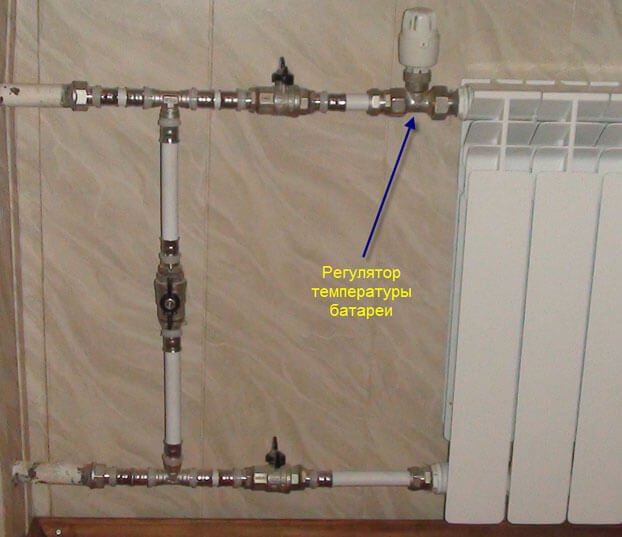
The difference in the temperature of the coolant inside the supply and return risers should be 15-20 degrees. This indicator can be adjusted using special equipment - mixers, taps and servo drives. Mixers are a crane with two or three working positions. The pipe of the supply riser is connected to one of the inputs, the outlet pipe is connected to the second. The third is used to regulate the temperature in a separate section of the line. Mixing units are equipped with a temperature sensor and a control unit. The sensor gives a signal about the temperature of the water inside the riser, and the control unit regulates the valve, due to which the two-pipe heating system is regulated. You can adjust the heating of water in radiators with your own hands, using taps for this. But the servos will eliminate the need to do this, since with their help, the heating of the risers will be automatically adjusted. The servo drive includes a thermostat that sets the desired temperature value. After that, the servo drive will begin to measure the incoming coolant flow and, if necessary, reduce or increase it.
Important! It is impossible to regulate the pressure with the help of thermostats, since they limit the flow of water only in one section of the system, without affecting its general condition and the heating of the remaining risers
Adjustment methods


The balancing procedure consists in adjusting the shut-off valves. This is done in two ways:
- Adjustment of each valve and temperature measurements after each correction of their position;
- Dividing the system into modules and adjusting them separately. In this case, each section of the room receives its share of the total heat given off by the system.
Before balancing, the heating system is diagnosed by opening all stopcocks and a test run; thus, it will be determined in which part of the circuit the unbalance has occurred.
- Regulators of flow and pressure of the coolant;
- Balancing and bypass valves.
The required control components are installed based on the type and complexity of the system. So, with a one-pipe circuit, ordinary taps are enough. In this case, the balancing of the heating system is carried out by simply twisting them until the desired temperature is reached. Balancing valves are required for two-pipe circuits. They, firstly, provide more accurate regulation, and secondly, they allow you to connect a special device to measure the characteristics of the coolant supply - pressure, flow rate and temperature.
Setting up the heating system: procedure
Setting up the heating system carried out in order to ensure the normal functioning of heating equipment. The heating system setup process consists of three stages:
- At the first stage, the heating system is calculated, the systems are surveyed and tested, and a work plan is developed to ensure the efficiency of the system.
- At the second stage of commissioning, it is necessary to choose a method for regulating the flow rate of the coolant and installation of the appropriate equipment. The second stage includes the implementation of all measures developed at the first stage.
Depending on the specific conditions, the flow rate of the coolant can be regulated in several ways:
- the choice of the diameter of the throttle diaphragms and the place of their installation;
- installation of throttle diaphragms or control valves on the risers, which will allow balancing the heating system;
- choice of automatic devices regulating the flow rate and temperature of the coolant.
- At the third stage, it is necessary to check the correctness and efficiency of the adjustment made, additional adjustments, and also to identify the operating modes, the magnitude of the heat load.
The correspondence of the actual water flow rates to the calculated values in the risers and in the radiators testifies to the correct adjustment of the heating systems. Such water flow rates are determined by the readings of instruments, and by a calculation method by measuring temperatures. With proper adjustment, the water flow rate will vary within 0.9 - 1.15.
We set up the heating system of a country house ourselves


In my previous article, I wrote that one of the most effective ways to modernize heating systems in private buildings is to switch from an open heating system to a closed one. The heating system of a residential building improved in this way has many advantages, which together ensure its simple operation, you just need to turn on the boiler at the beginning of the heating season and turn it off at the end of it. Everything!
However, in order for the heating system of a country house to work in this mode (turned it on, “forgot” for six months, turned it off), you need to correctly configure and adjust its operating parameters. This is what my article will be about. I will make the main calculations, conclusions and calculations using the example of my heating system, but the reader can always use this information, drawing an analogy with his own case.
Features of the heating device in an apartment building
Depending on what kind of heating wiring you have in a multi-storey building, when choosing a boiler for installing an autonomous heating system, give preference to boilers with an isolated combustion chamber. Boilers of this type have a ventilation system in their structure, which can independently regulate the supply of fresh air. It is convenient if the boiler is characterized by a cyclical rhythm of operation, which ensures gentle disposal of combustion products that enter the air. The released carbohydrate oxide should not exceed the permissible limits.
Calculation of heating in an apartment building
As you can see, the advantages of switching to heating an apartment building are obvious. Installation of this type of equipment will allow you to become independent from housing and communal services companies. Determine on your own the time of the end and start of the heating season and the optimum air temperature for yourself, adjusting the heating in an apartment building is a simple process. And, which is not unimportant, - saving the family budget.
PNRM. Heating system
NDP of your chosen company;
- they have relevant experience;
- terms of service and warranty.
In this case, the following requirements must be met:
- Activities related to the commissioning of engineering systems (including commissioning of air conditioning systems) must be carried out within the time frame established by the standards.
- The equipment is put into operation under the strict control of the specialists of the contractor company.
- Upon completion of the entire complex of commissioning, you should receive a documented guarantee of their high-quality implementation.
- The guarantee for them is provided from the moment of the final commissioning of the object.
Commissioning tests mean work performed on already installed (assembled) equipment, ready for start-up and commissioning.
Attention
Home »Heating» Heating system PNR Program of commissioning activities In the implementation of many projects, capital construction or reconstruction of buildings and structures is carried out with the installation of new equipment or specialized processes.Such works include the installation of fire extinguishing systems, power supply, air conditioning, ventilation, fire alarm
Obligations of the customer
Implementation of general, operational and technical management of the quality of construction, installation, commissioning and testing of equipment; carrying out pre-start and start-up operations on equipment, assemblies and block; the work of the acceptance commissions; elimination of equipment defects, construction and installation.
Ensuring the organization and conduct of pre-installation audit of equipment and apparatus.
Provision of commissioning works at all stages:
- financing of works;
- by qualified operating personnel (starting with unit testing);
- working tools and materials in the required quantities;
- exemplary devices, design and factory technical documentation.
Ensuring the safety of equipment and installations, the experimental control system, as well as documentation, equipment and apparatus of organizations involved in the commissioning of the power unit and a mode that excludes access by unauthorized persons.
Provision of personnel of commissioning and research organizations with office and laboratory premises, housing and other household services.
Development, together with the general contractor, of measures to ensure safe working conditions, and the adoption of general measures for safety and fire safety at the power unit.
Duration of commissioning when starting heating in mcd
Important
Flushing of heat consumption systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as installation, overhaul, routine repairs with replacement of pipes (in open systems, systems must also be disinfected before commissioning). Systems are flushed with water in quantities that exceed the design flow rate of the coolant by 3-5 times, while complete clarification of the water should be achieved
When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the air mixture should not exceed 3-5 times the design flow rate of the coolant. For flushing, tap or industrial water is used.
Connecting systems that have not been flushed, and in open systems, flushing and disinfection is not allowed. Diaphragms and nozzles of hydraulic elevators must be removed during flushing of the heating system.
After flushing, the system must be immediately filled with coolant.
Advantages of an individual heating system in an apartment building
- The device of the heating system of an apartment building allows utilities to reduce tariffs for services provided. In addition to financial savings, the consumer himself will be able to increase or decrease the temperature for heating the room at the right time. So, adjusting the heating system of an autonomous-type apartment building is an effective way to establish the optimal temperature regime.
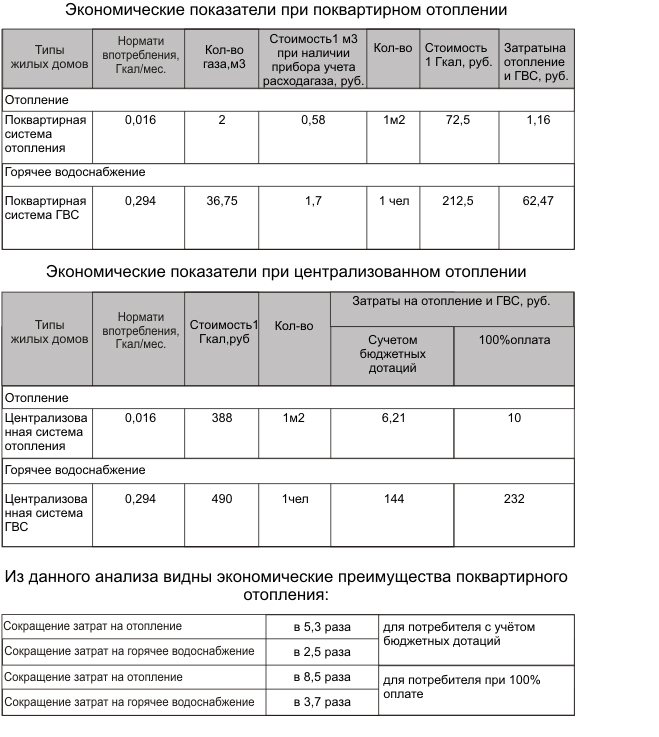

Economic indicators when using apartment and district heating
- Individual heating of residential premises allows developers to slightly reduce the cost of square meters when commissioning an object. This is due to the fact that builders bear large costs when laying communications. In addition, the heating device in an autonomous-type apartment building enables developers to develop new territories remote from population centers with all the infrastructure;
The fact of significant savings in natural gas has been proven, on which the in-house heating system of an apartment building operates. Compared to such a method as heating an apartment with electricity, natural gas is economical.
- Using an autonomous heating system, it becomes possible to minimize the waste of heat on the way to the consumer.There is no need to additionally insulate the heating mains, through which hot water is supplied to the apartments of consumers, and the balancing of the heating system of a multi-storey building is done easily and relatively quickly;

The double-circuit boiler not only heats the apartment but also provides hot water supply
For those who rarely stay in their apartments, the best solution is to insulate the outer surfaces of the room, which will allow you to keep heat for a long time and avoid the destruction of the structure under the influence of moisture;
- Special attention can be paid to the ventilation system. When adjusting the heating system of an apartment building and, in particular, gas-powered equipment, it is important to understand that it is necessary to remove decay products with high quality. It is in new buildings that there are all the necessary conditions for the implementation of the plan. Modern ventilation and cleaning systems are installed here. So, flushing the heating system of an apartment building will be done without problems, since the design already provides for it. To install autonomous heating for an apartment in an apartment building, it is important to coordinate everything with the city authorities and be sure to provide a project for the placement of equipment.
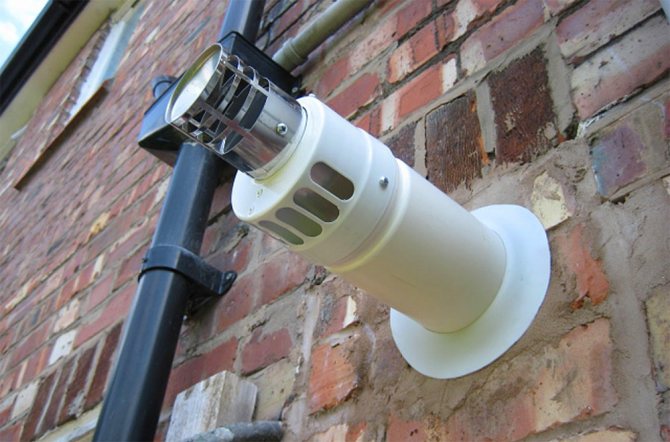


The chimney of the parapet boiler can be brought out directly through the wall of the apartment to the street
Commissioning of heating systems
Before putting the heating system into operation, you need to do a number of preparatory work, carry out checks and establish the mutual action of the most different units among themselves. All this is included in the commissioning of the heating system, the purpose of which is to detect and remove the minuses and errors committed when the installation work is being carried out, and also to bring the entire system in accordance with the standards established for it. As a result of these works, the customer receives a good, efficient and effective system. The cost of adjustment and start-up of heat supply is fully reimbursed by the next trouble-free operation and safety of the equipment.
Scope of work on commissioning and commissioning
- Commissioning work is done after the installation work has been carried out. They include:
- Connecting the boiler to the gas main (if a gas boiler is used);
- Setting up security systems;
- Installation of an electric voltage stabilizer and connecting a boiler to it;
- Coordination of the operation of the boiler and the indirect device (if used);
- Connection of thermal converters and their adjustment;
- Testing and pressure testing of heating systems;
- Filling the system with a heat carrier;
- Bleeding air from the system and balancing it;
- system start-up;
Upon completion, a report is drawn up on the commissioning of the heating system, which lists the scope of the work performed and draws conclusions regarding the subsequent operation and improvement of the equipment.
The essence of the system check processes and its launch
As you can see, commissioning consists of a huge number of operations, very important of which are associated with testing the heating system. Let's consider in more detail one of the main stages of commissioning - pressure testing of the system. It should be performed to detect all suspected areas of leakage. The essence of the procedure consists in injecting water or air into the system under pressure, a couple of times higher than the working one. During crimping, all connections must be checked very carefully. If air is used during the test, the joints of the pipeline must be smeared with a soap-based solution.
Another stage of verification is thermal testing of the system. Its purpose is to warm up all radiators with water at a temperature of 60-70 ° C for 7 hours. At the same time, the degree of heating of the radiators, the temperature of the heat carrier at the outlet and inlet to the boiler and the air temperature are monitored.If all indicators are as close to the design ones as possible, the system has successfully passed the thermal test. If not, then a subsequent adjustment is made. Before filling the system with test water, it should be flushed to remove equipment preservatives and other debris from the pipes.
To start the system, you need to fill it with a heat carrier, bleed air and start the boiler. To fill the system with a heat carrier, a make-up valve is opened, the location of which can be found in the documentation for the equipment for the boiler room. When the system pressure can reach the required value, the valve is closed and the first start-up of the boiler is carried out. After turning on the circulation pump, bleed air from it by slightly unscrewing the screw in the very center. When water flows out from under the screw, it must be rolled up to the end. Then the electronics will start up all the boiler systems, and for some time the air will be removed from the system, which will be reported by gurgling sounds. When the operation of the system is getting better, you need to check the pressure, and if necessary, bring it to normal by replenishing the amount of heat carrier.
After the first start-up of the heat supply, you can adjust the system using taps to adjust the heating devices. It is necessary to ensure that the energy of the heat carrier is sufficient to warm up the last heater in the circuit. This adjustment can take a couple of days and is performed during operation. There is no need to worry about this, because in general the system is already debugged and does not stop working in normal mode.
Duties of the head commissioning organization
3.2.1. Ensuring the fulfillment of its scope of commissioning work on the equipment in accordance with the agreed distribution of volumes between the contracted commissioning organizations.
3.2.2. In addition to performing its scope of commissioning works:
- distribution of the scope of adjustment work (when drawing up a coordination plan);
- coordination of actions of all participants in commissioning works: development of engineering support for commissioning, participation in the development and approval of a combined schedule of construction, installation and commissioning works, development or approval of working and technical programs for commissioning in accordance with the instructions of Appendix 3, participation in the formation of consolidated commissioning teams, including separation of row-nodal foremen from its staff;
- control of the results of commissioning by all participants, participation in the work of acceptance committees;
- providing round-the-clock duty of leading specialists to provide operational technical assistance during the period of launch operations on equipment;
- submission to the launch headquarters of questions and proposals concerning the organization and progress of construction, installation and commissioning works;
- generalization, together with the organizations-co-executors, of the results of commissioning and, on their basis, prompt issuance to the customer, design organizations and manufacturing plants (in the copy - to the relevant central chapters) of proposals for improving the technology, schemes, modes and designs of equipment and monitoring their implementation;
- generalization of the operating experience of similar equipment and the issuance of a proposal to the customer for implementation;
- development, together with the customer, of instructive and technical documentation.
The head commissioning organization together with the customer bears the main responsibility for the timing and quality of commissioning and commissioning.
3.2.3. The instructions of the head commissioning organization in terms of the technology and the timing of commissioning are mandatory for all organizations participating in the equipment commissioning.
3.2.4.The main form of activity of the head commissioning organization is the conclusion of a single contract agreement for the implementation of the entire complex of commissioning works with the involvement of other commissioning organizations on a subcontract basis.
3.2.5. Additional performance of the "head" functions by the commissioning organization is paid in accordance with the "Regulations on the relationship of organizations-general contractors with subcontractors" approved by the decree of the USSR State Construction Committee and the USSR State Planning Committee of 07/03/87, No. 132/109 and the contract with the customer.
3.2.6. In the absence of a head commissioning organization, its functions in the part of distribution, control and coordination of work are performed by the customer or, in the case of turnkey delivery of the facility, by the general contractor.