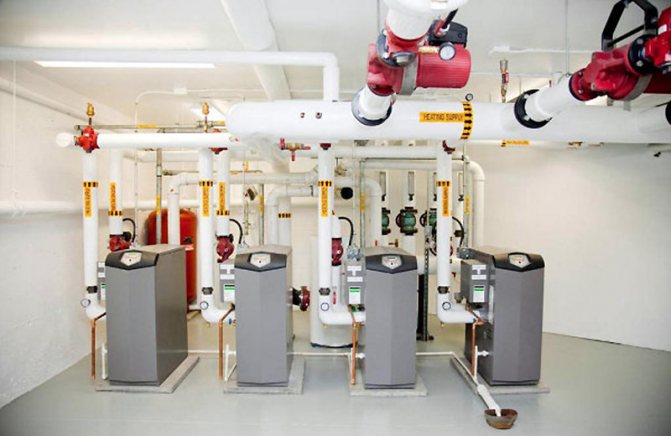
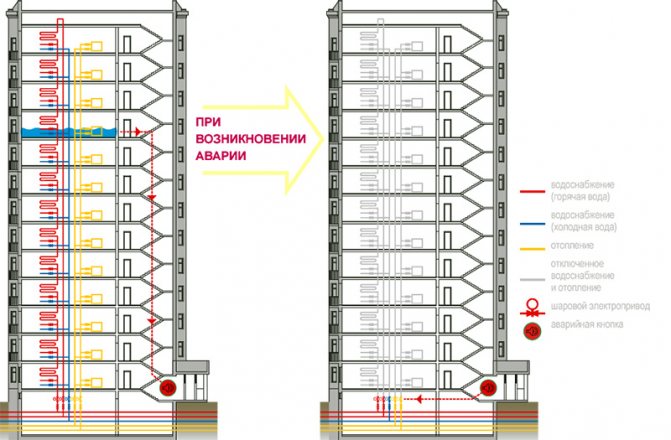
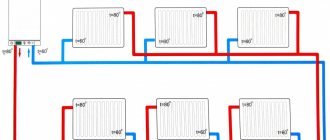
The heart of the heat supply system is the elevator unit
Today we have to find out how the water supply and heating of a residential building are arranged. The object of the study will be the most popular in Soviet-built houses, which make up more than 90% of the housing stock of our boundless and immense, open heat supply circuit with hot water withdrawal for households directly from the heating main.
How it works
First, some general information.
Hot water supply and heating of an apartment building begins with the introduction of the heating main into the house. Through the foundation, two lines are started from the nearest heat chamber - supply (through which industrial water, it is also a heat carrier, enters the building) and return (water, respectively, returns to the CHP or boiler house, giving off heat).
In the thermal chamber at the entrance to the house (as an option - at the group entrance to several houses located in close proximity to each other) there are cut-off valves or taps.

Heat chamber at the stage of installation
The heat point, also known as an elevator unit, combines several functions:
- Provides a minimum temperature difference between the supply and return of the heating system;
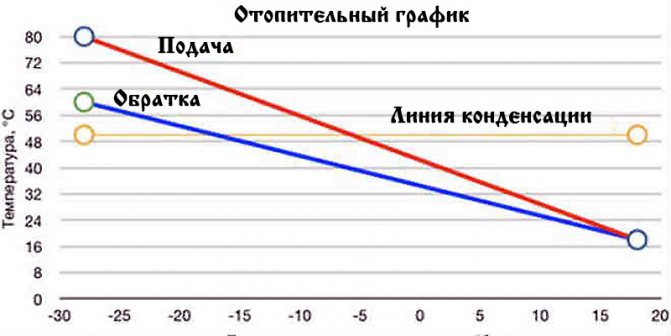
Reference: the upper peak of the supply temperature is 150 degrees, while, according to the temperature schedule, the return flow must return to the CHP plant cooled down to 70 ° С. However, such a difference would mean extremely uneven heating of heating devices, therefore, water from the elevator enters the heating circuit with a more modest temperature - up to 95 degrees.
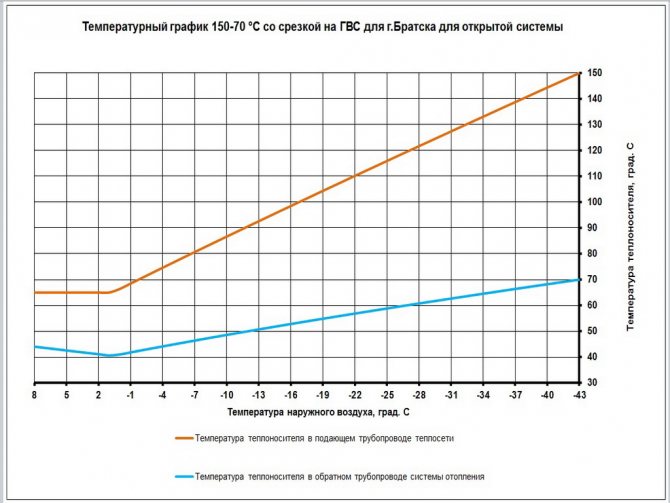

Temperature graph of the supply and return lines of the heating main depending on the outside temperature
- Organizes the supply of hot water to the hot water supply system and its shutdown on a scale of the house in case of accidents and current repairs;
- It makes it possible to stop and reset the heating system;
- Allows you to take control measurements of temperature and pressure;
- Provides cleaning of the coolant and water for hot water supply from large contaminants.
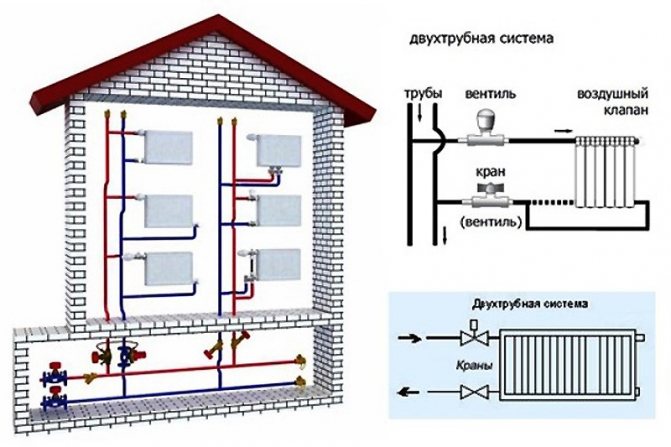
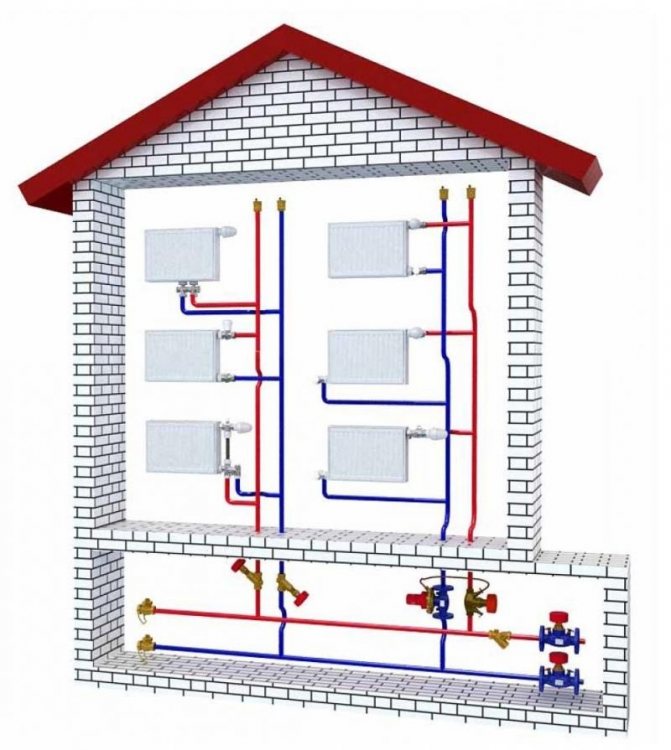
The heating system can be organized:
- With top filling: the filling of the supply takes place in the attic or technical floor under the roof of the house, and the return filling is located in the basement or underground. Each heating riser is disconnected independently of the others by two taps at the top and bottom of the house;
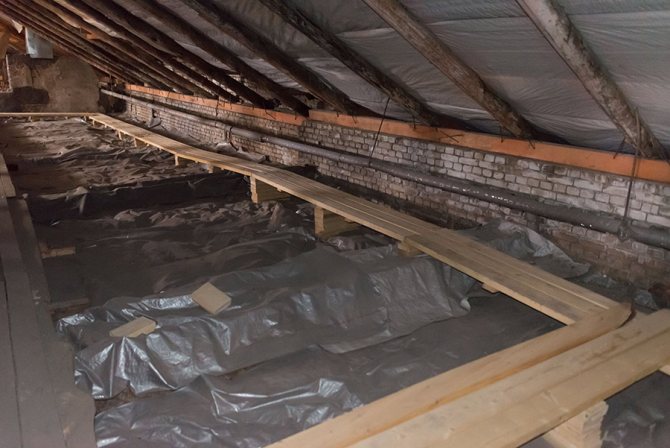


Top filling: heating supply is distributed in the attic
It is curious: there is also a reverse scheme - with feeding in the basement and pouring the return in the attic. However, it is much less popular and, as far as the author knows, is used mainly in small buildings with their own boiler rooms.
- With bottom filling: supply and return are bred in the basement; heating risers are connected to the filling one by one and are connected in pairs by jumpers on the top floor or attic. Each jumper is supplied with an air vent (Mayevsky valve or a conventional valve) to bleed the air lock.
The DHW system in buildings built in the 70s and in older houses is usually dead-end - completely identical to the cold water supply system. From a practical point of view, this means that hot water has to be drained for a long time during the drawdown before it is heated, and heated towel rails installed on the hot water supply pipes are heated only during the drawdown.


Dead-end DHW system: water needs to be drained for a long time before it heats up
In newer buildings, hot water supply and heating of a residential building function according to the general principle - water circulates continuously through the circuits, ensuring a constant temperature of heated towel rails and instantaneous heating of water during parsing.
To learn more about how the heating and water supply system of residential buildings is arranged, the video in this article will help you.
Central heating system structure
The main structural elements of a central heating system are:
- A source of thermal energy, which can be large boiler houses or heat and power plants (CHP); they heat the coolant through the use of some type of energy source. At the same time, water is used in boiler houses to transfer heat energy to consumers, while in CHP plants it is first heated to the state of steam, which has higher energy performance and is sent to steam turbines to generate electricity. And the already spent steam is used to heat the water that enters the heating system of an apartment building.
One combined heat and power plant is capable of replacing several boiler houses, as a result of which not only construction costs are reduced and significant areas are freed up, but the overall environmental situation is significantly improved.
It should be noted that large centralized heat supply schemes have, as a rule, several heat sources connected by backup lines and ensuring the reliability and maneuverability of their operation.
Figure 1 - General scheme of central heating
The elements
Now let's move on to a detailed acquaintance with the nodes of systems that provide water supply and heating in apartments.
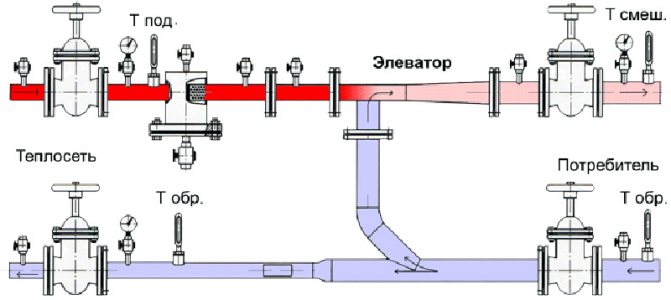
Elevator unit
Its heart is a water-jet elevator, in the mixing chamber of which hotter and higher-pressure water from the supply is injected through a nozzle into the relatively cold water from the return. At the same time, it involves a part of the coolant from the return pipeline entering through the suction (jumper between the supply and return) into the re-circulation.
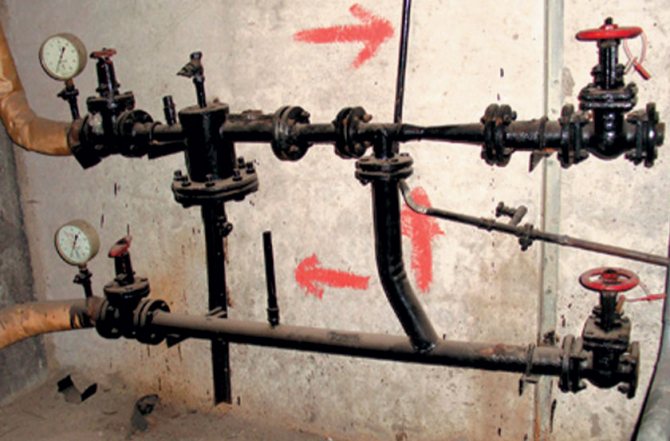

Direction of water circulation through the elevator unit
At the same time, the pressure at different points of the elevator unit is distributed like this:
- Feed to the elevator - 6-7 kgf / cm2;
- Return flow - 3-4 kgf / cm2;
- The mixture (on the supply line after the elevator) is 0.2 kgf / cm2 higher than on the return line.
Let us emphasize again: the entire coolant in the heating circuit sets in motion a difference of only 1/5 of the atmosphere, corresponding to a pressure (read — the height of the water column) of 2 meters. This explains the relatively slow circulation of the coolant, the absence of hydraulic noise in the radiators and the relatively large (15-25 degrees) temperature difference between the radiators in the house.


The mixture pressure is almost the same as the return pressure
There may be several elevator nodes in the house; however, usually only one of them is equipped with hot water connections. Tubes of the dead-end system are located on the supply and return to the elevator and suction and are connected to the general filling. At the same time, only one of the tie-ins is open: otherwise, the bypass created by them between the supply and return will extinguish the difference necessary for the operation of the elevator.


The simplest elevator with a dead-end DHW system
DHW with recirculation requires the wiring of two dispenses around the house.
In the elevator unit, they can be connected in three ways:
- From supply to return. The water flow through the hot water system is limited by a washer (steel pancake with a hole of a fixed diameter), installed on one of the flanges of the tie-in on the return line;
- From serve to serve. Two tie-ins are mounted on the supply line up to the elevator. Between them, a retaining washer is placed on the flange with a hole diameter 1 mm larger than the diameter of the elevator nozzle;
Note: the washer creates a minimum pressure drop between the tapping, with little or no effect on the operation of the water jet elevator.
- From return to return. The tie-in device and washers are the same as in the previous case, but on the return pipeline.
Please note: DHW switches to the return pipe when the flow temperature reaches 80 degrees Celsius. The current SNiP temperature of hot water supplied from an open heating system is limited to 75 ° C.
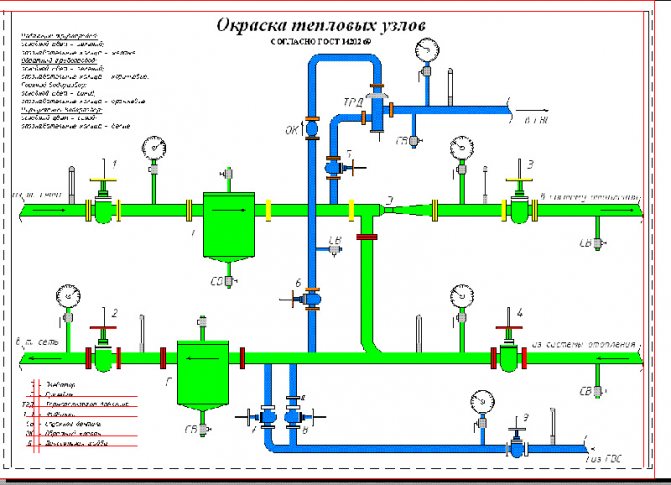
In addition to the elevator and hot water connections, the elevator unit includes:
- Mud traps (always at the feed inlet, optionally at the return) with flush valves;


Sump on the feed of the elevator unit
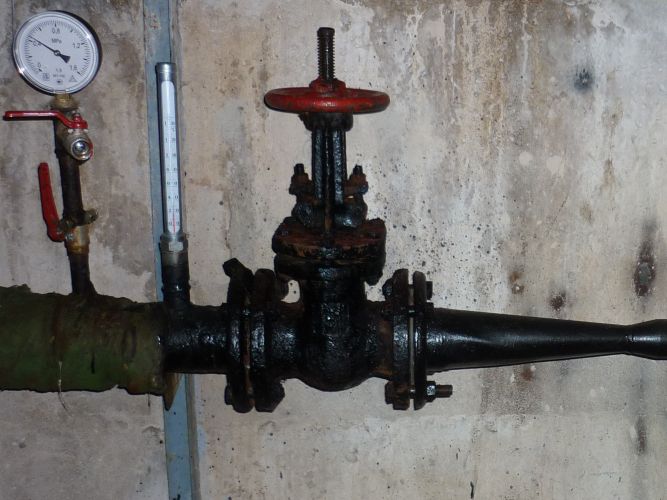
- Control valves for measuring pressure. They can be equipped with pressure gauges, but if the elevator unit is located in the basement of an economic purpose, the pressure gauges are often removed to avoid theft;
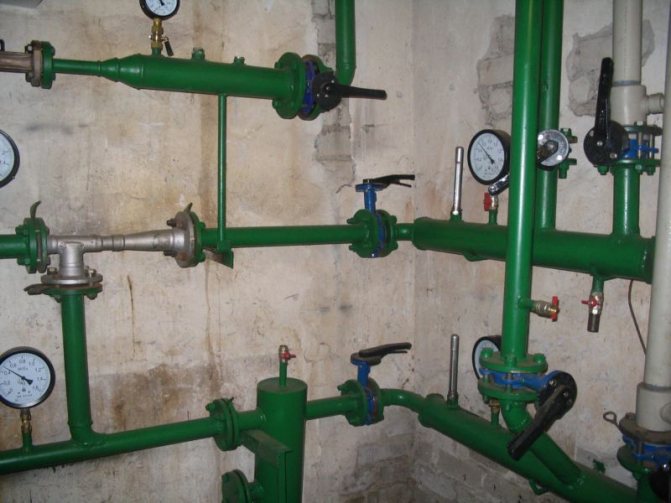


Permanently installed pressure gauges
- Oil pockets for temperature measurement;
- Heating system discharges. They open to the floor of the substation or, which is much more reasonable, to the sewer. Discharges allow you to completely drain the heating and water supply systems of apartment buildings. In addition, they are used for annual hydropneumatic heating flushing;


Once a year, the heating system is flushed with a compressor
- Gate valves or ball valves at the inlet of the elevator unit, for heating after the elevator and at all hot water connections. Optionally, intermediate valves can be present in the substation, allowing, for example, to drain the elevator to dismantle the nozzle without turning off the hot water supply.
Heating spills
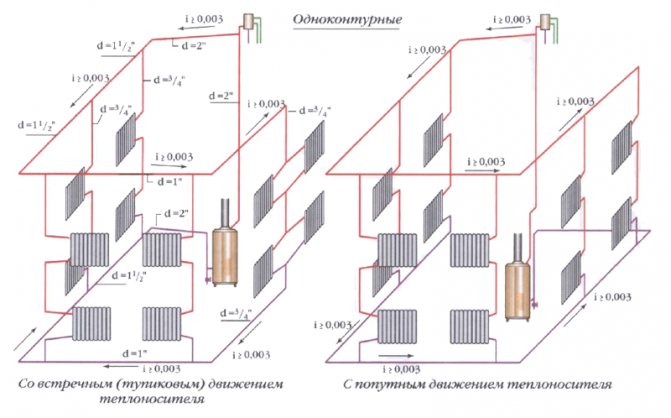
If the heating and water supply scheme for an apartment building is implemented with heating spouts in the basement, they are mounted horizontally, without slopes. Typical filling diameters are 32 - 50 mm. Risers are connected by welding, less often by threaded connections, on tees.


Bottom heating outlet: two pipes are laid around the perimeter of the house in the basement
It is curious: in the houses of the Stalinist construction, galvanizing was massively used for heating. Welding is contraindicated for galvanized steel, since the anti-corrosion coating inevitably burns out in the seam area. Therefore, all elements of the heating system were mounted only on the threads.


Heating in stalinka: all connections are threaded
In the case of top filling, the supply in the attic of the house is laid with a constant slope. An expansion tank with a relief valve is mounted at the upper filling point of the supply.
What is the difference in installation? With the order of starting heating systems.
In the first case, when the discarded circuit is started, it is distilled to a dump in order to expel the maximum amount of air from the risers; then air locks from the remaining cold risers are vented through the Mayevsky taps in each bulkhead. It is long, inconvenient and often associated with the search for the absent tenants of the upper floors.


To start heating, the air must be vented in each apartment on the top floor.
But the instructions for starting a top-filling house are much simpler than an example:
- Fill the heating circuit by slowly opening the house (heating) valves on the return and supply;
- Go up to the attic and bleed air through the expansion tank vent. Due to the slope of the filling of the supply, it will be displaced by water exactly there.
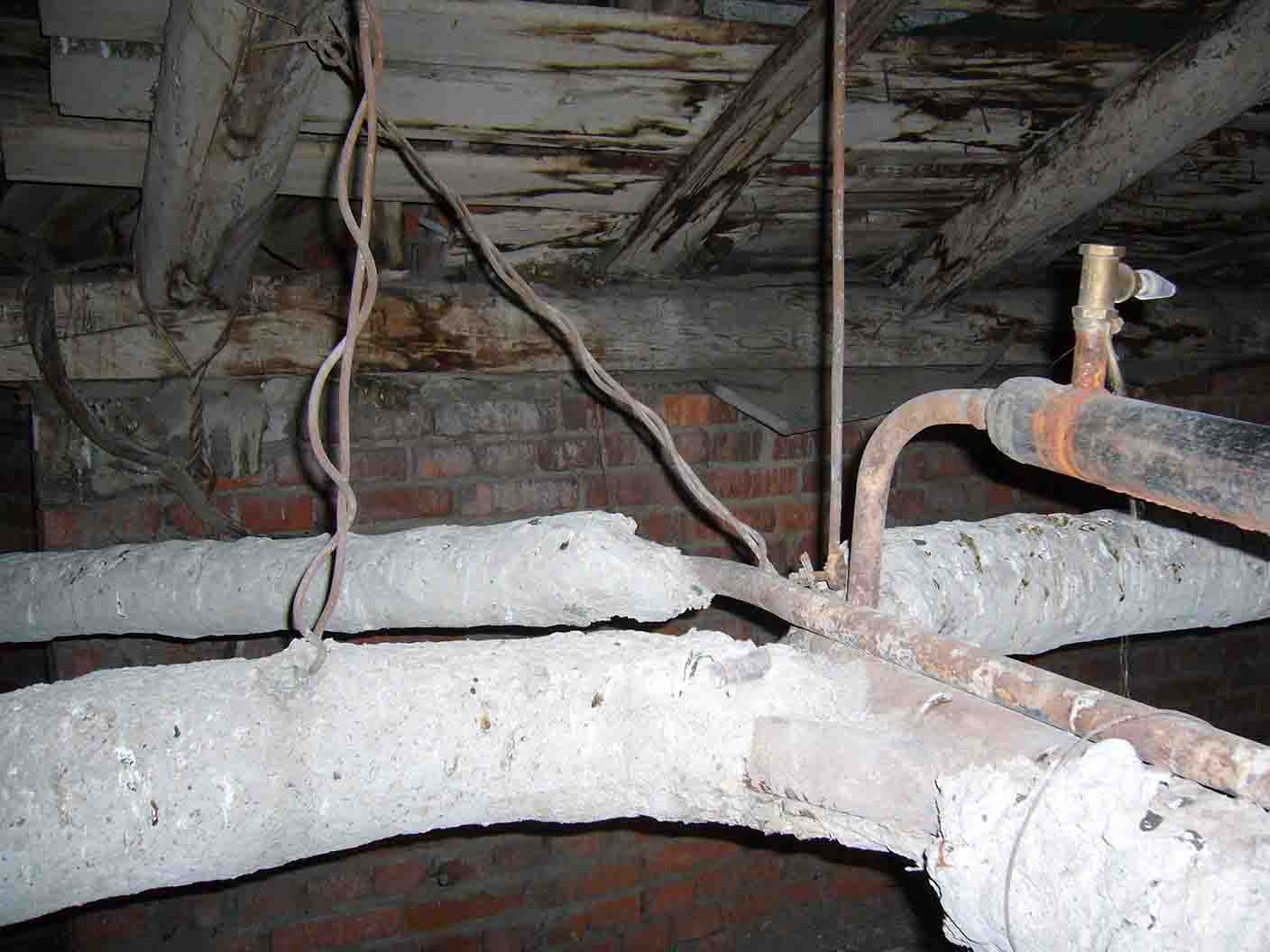


Expansion tank and air vent are located at the top filling point of the supply
Heating risers
Typical diameter of heating pipes is 20-25 mm.


Steel heating pipes. Size - DN 20
Let's clarify: steel pipes, which are used to mount heating and hot water supply of apartment buildings, are designated by a conditional passage (DU, or DN). It indicates the possibility of connecting the pipeline to a pipe thread of the corresponding size and approximately corresponds to its inner diameter.
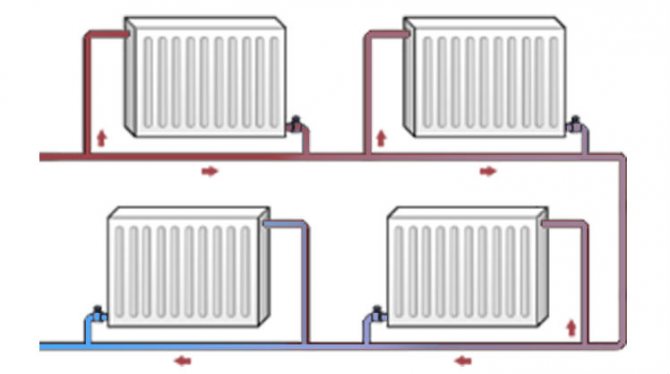
The risers go into the connections to the heating device; between the connections, a bypass jumper is usually mounted the same as the riser, or a step smaller.The bypass provides circulation in the riser with fully or partially closed shut-off and control valves on the connections (throttles, thermal heads, ball or three-way plug valves).
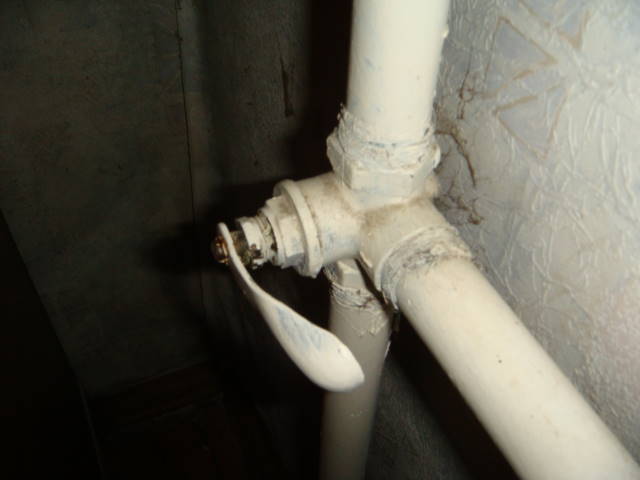


Three-way valve for adjusting the heat transfer of the cast iron battery
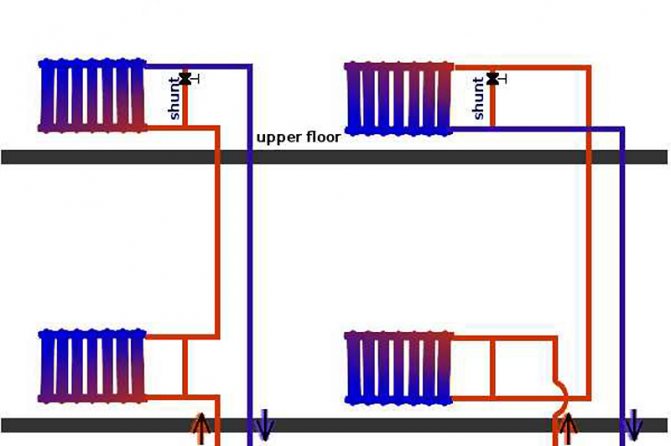
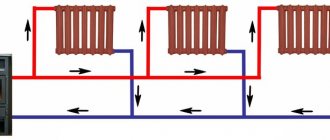
At bottom filling, a jumper is laid between the paired risers:
- At the level of the upper manifold of heating radiators;


Loopback of paired heating pipes on the upper floor
- Under the ceiling of the top floor apartment;
- In the attic.
Hot water filling
The diameter of hot water supply spouts varies from 25 to 100 mm. Fills with a cross section of 50 mm or more can be found mainly in houses built before the 80s of the last century: they were designed with an allowance for the overgrowth of steel water pipes with rust and lime deposits.
In later buildings, the diameters were selected without a reserve, taking into account the estimated service life of black steel on the water supply of 15 years.


Filling hot water and heated towel rails in the basement of the Khrushchev
Filling of water supply systems is laid only in the basement or subfloor.
The functionality of two hot water filling in a recirculation system can be:
- Identical (hot water risers with draw-off points and heated towel rails are attached to both bottlings);
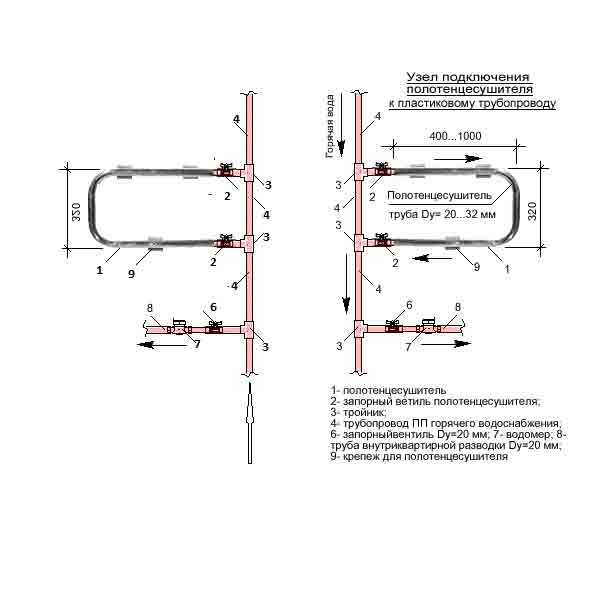

Both draw-off points and heated towel rails are connected to the paired risers
- Separate (the filing of the supply is connected to the risers on which the points of the water intake are mounted, and the risers with heated towel rails are connected to the pouring of the return). Less often, a group of risers with mixers and towel dryers is combined with a single idle (without attached devices) return riser.
Curious: up to 7 hot water risers can be combined into groups. In the author's practice, the risers were usually combined into groups common for a separate apartment or for an entrance.
DHW risers
Typical diameters (DU) of hot water risers are 20-32 mm.
They can be installed in apartments:
| Picture | Location of hot water risers |
| In the niche of the bathroom (open or closed). |
| At the entrance to the toilet or bathroom. |
| In the kitchen niche (kitchen hot water riser with apartment-based connection of risers in the circulation circuit). |
The connection of modern heated towel rails in the circulation circuits of hot water supply is carried out in the break of the riser and ensures their constant heating.
Useful: when installing a heated towel rail with your own hands, it is better to connect it not to the break in the riser, but parallel to it. Shut-off valves are installed at the inlet and outlet of the dryer. This will help you turn off heating in the summer heat.
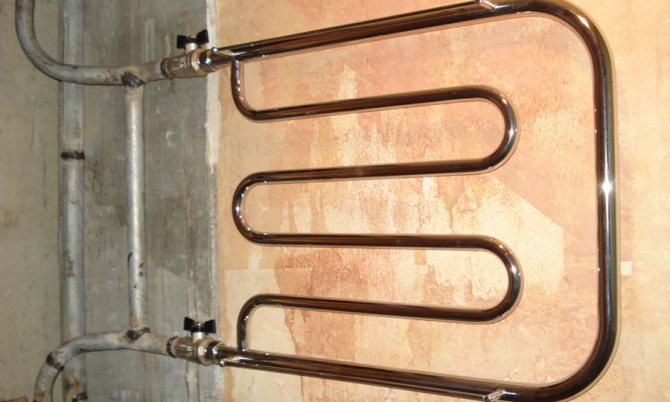


Connecting a heated towel rail with shut-off taps and bypass
Advantages and disadvantages of a central heating system
The central heating system has the following advantages:
- the possibility of using inexpensive fuels;
- reliability ensured by regular monitoring of performance and technical condition by special services;
- the use of environmentally friendly equipment;
- ease of use.
Among the disadvantages of such a heating scheme for an apartment building, it should be noted:
- the system operates according to a strict seasonal schedule;
- impossibility of individual regulation of the temperature of heating devices;
- frequent pressure drops in the system;
- significant heat loss during transportation and heating in an apartment building;
- high cost of equipment and its installation.
How is the heating of a residential building arranged? The increase in tariffs prompts the transition to autonomous heating of the apartment; but the rejection of central heating in an apartment building, in addition to the mass of bureaucratic obstacles, also means a number of technical problems.To understand the ways to solve them, you need to imagine the layout of the coolant.
Payment
Finally, we will answer a few questions, one way or another related to the growing tariffs for heat and hot water every year.
How is the payment for heating and hot water supply calculated?
The key parameter in calculating payment for heating is the amount of heat used to maintain a comfortable temperature in an apartment or to heat water. The cost of thermal energy for 2017 is 1000 - 1800 rubles per gigacalorie, depending on the region.
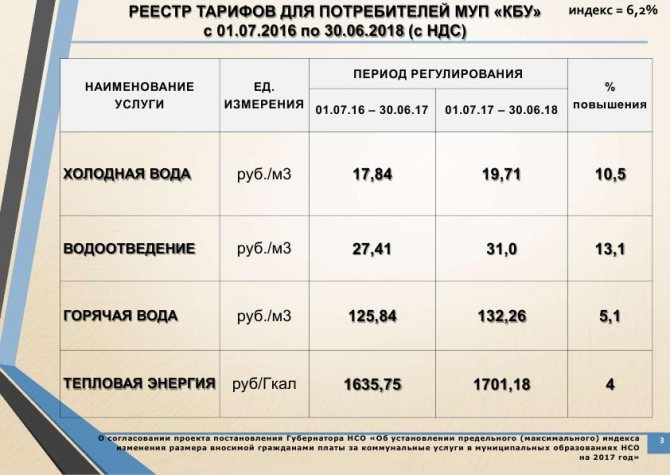

Utility rates for 2020 for the city of Berdsk
However, heat meters are far from being in all apartments, so receipts often include:
- Fixed payment for heating per square meter (it is calculated as the product of the heat consumption standard for a given region and the price of a unit of thermal energy);

Simplified scheme: the cost of heating is calculated by the footage of the heated area
- The cost of a cubic meter of hot water, taking into account the meter (90-170 rubles per cubic meter).
How can you save on heating?
To reduce costs, you must:
- Install heat metering devices on each radiator;
- Mount throttles or thermal heads on the connections to limit the flow of the coolant through the heater.
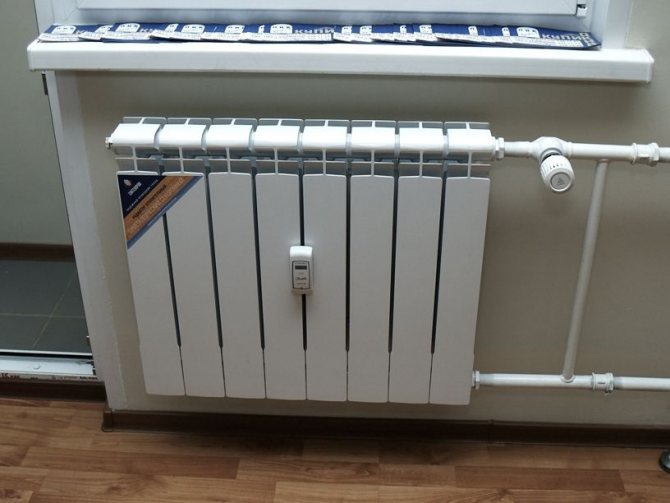


In the photo - a sectional radiator with a heat meter and a thermostatic head throttling the supply line
Can hot water be used to heat an apartment?
Technically, yes. To do this, it is enough to form a closed heating circuit (for example, the simplest one-pipe Leningrad) and connect it to the gap in the hot water riser. Since there are no metering devices on the riser, the heat obtained in this way will be absolutely free for you.

The simplest heating system - Leningrad
But:
- Any change in the configuration of public utilities requires approval from the housing organization and, in the case of hot water supply and heating, from the respective service providers. Of course, none of the organizations will give permission for such a change in the heat supply scheme;
- Uncoordinated re-planning of communications is an administrative offense and is punishable by a fine with an order to restore the original configuration at your own expense;


The Housing Code regards the uncoordinated redevelopment of communications as an administrative offense
- Finally, the main thing: you can disconnect from the DH system only by an entrance or a house, with the provision of a plan for an alternative heating scheme and agreement with suppliers of electricity or gas (alternative heat sources). Without the formal termination of the supply of heating services, you will continue to receive bills that you want to get rid of.


To stop paying for DH services, you need to cut off the heating devices from the heating pipes and draw up a shutdown certificate with the representatives of the housing dwellers
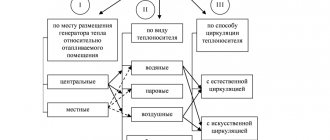
Classification of district heating systems
The variety of schemes for organizing central heating that exists today makes it possible to rank them according to some classification criteria.
According to the mode of consumption of thermal energy
- seasonal, heat supply is required only in the cold season;
- year-round, requiring constant heat supply.
By the type of heat carrier used
- water - this is the most common heating option used to heat an apartment building; such systems are easy to operate, allow transporting the coolant over long distances without deteriorating quality indicators and regulating the temperature at a centralized level, and are also characterized by good sanitary and hygienic qualities.
- air - these systems allow not only heating, but also ventilation of buildings; however, due to the high cost, such a scheme is not widely used;
Figure 2 - Air heating and ventilation scheme of buildings
- steam - are considered the most economical, because small diameter pipes are used to heat the house, and the hydrostatic pressure in the system is small, which makes it easier to operate. But such a heat supply scheme is recommended for those objects that, in addition to heat, also require water vapor (mainly industrial enterprises).
By the method of connecting the heating system to the heat supply
- independent, in which the heat carrier circulating through the heating systems (water or steam) heats the heat carrier supplied to the heating system (water) in the heat exchanger;
Figure 3 - Independent district heating system
- dependent, in which the heat carrier heated in the heat generator is supplied directly to the heat consumers through the networks (see Figure 1).
By the method of connection to the hot water supply system
- open, hot water is taken directly from the heating network;
Figure 4 - Open heating system
- closed, in such systems, water is taken from the common water supply, and its heating is carried out in the network heat exchanger of the central unit.
Figure 5 - Closed central heating system
Types of air vents and places of their installation
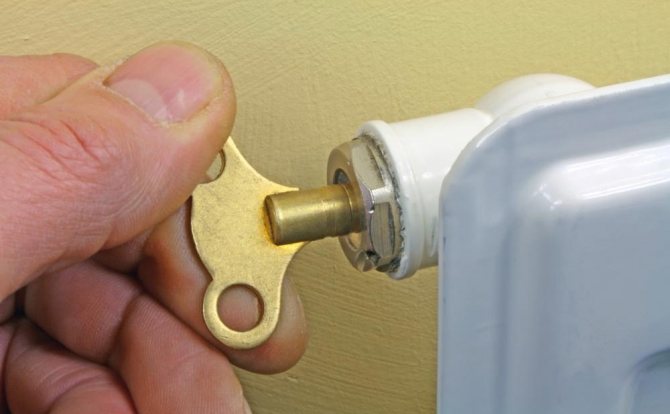
Air vents are manual and automatic. Manual air vents or Mayevsky taps are small in size. They are usually installed on the end of the heating radiator. They regulate the Mayevsky crane with a key, a screwdriver, or even manually. Since the faucet is small, its performance is low, therefore it is used only for local elimination of air locks in the heating system.
Air vents for the heating system are of two types: manual (Mayevsky's valve) and automatic (work without human intervention).
The second type of air vents - automatic - work without human intervention. They are installed both vertically and horizontally. They have high performance, but they are quite sensitive to contamination in water, so they are installed together with filters on both supply pipelines and return pipes.
Automatic air vents are installed in closed-type heating systems along the pipelines at different points. Then air discharge from each group of devices is carried out separately. The multi-stage de-airing system is considered the most effective. With proper laying and proper installation of pipes (at the desired slope), it will be easy and hassle-free to remove air through the air vents. Removing air from heating pipes is associated with an increase in the flow rate of the coolant, as well as an increase in pressure in them. A drop in water pressure indicates a violation of the tightness of the system, and temperature drops indicate the presence of air in the heating radiators.
Determination of the site of plug formation and its removal
How can you tell if there is air in the radiator? Usually, the presence of air is indicated by extraneous sounds, such as gurgling, water flow. To ensure full circulation of the coolant, it is imperative to remove this air. With a complete airing of the system, you must first determine the places of formation of plugs by tapping with a hammer on the heating devices. Where there is an airlock, the sound will be more resonant and strong. Air is collected, as a rule, in radiators installed on the upper floors.
Realizing that there is air in the heater, you should take a screwdriver or wrench and prepare a container for water. Having opened the thermostat to the maximum level, you need to open the valve of the Mayevsky tap and substitute the container. A slight hiss will indicate that air is coming out.The valve is kept open until water flows out and only then is it closed.
Elimination of the airlock in the heating battery with the help of the Mayevsky crane installed on it: the valve is opened with a special key or manually and kept open until water appears
It happens that after carrying out this procedure, the battery does not heat up for long or not well enough. Then it needs to be blown and washed, since the accumulation of debris and rust in it can also cause air to appear.
If after bleeding the air the battery still does not heat up well, try draining about 200 g of the coolant to make sure that the air lock is completely removed. If it does not help, but you need to blow out and rinse the radiator from possibly accumulated dirt
If there is still no improvement, check the filling level of the heating system. Air pockets can also form in pipe bends. Therefore, it is important during the installation process to observe the direction and magnitude of the slopes of the distribution pipelines. In places where the slope for any reason differs from the project, air vent valves are additionally installed.
In aluminum radiators, air locks are formed more intensively due to the poor quality of the material. As a result of the reaction of aluminum with the coolant, gases are formed, therefore, they must be regularly removed from the system. In such situations, it is recommended to replace aluminum radiators with devices made of better materials with an anti-corrosion coating and install air vents. In order for the heating of the rooms to be normal, before filling the heating system with water, it is necessary to timely take care of removing air from it, which prevents the normal movement of the coolant, and then in winter your house will be warm and comfortable.
- Author: Oksana
Rate the article:
(14 votes, average: 4.6 out of 5)
Even modern technologies of construction and interior arrangement of premises, laying of utilities do not guarantee uninterrupted heat supply. Problems can arise even for the simplest reasons. Then the problem arises of how to expel the airlock from the heating system, returning the network to normal operation. There are reliable, time-tested methods for solving these problems.
Reasons for airing the heating system
The main cause of the problems is water leakage. Even the smallest fluid loss results in bubbles in pipes and radiators. Before figuring out how to remove air from the heating system, you need to understand what factors caused the pre-emergency situation.
The formation of air spaces can be facilitated by:
- Overheating of the system to a state close to boiling. This usually happens when starting it after a summer idle time or when trying to get out of a defrosting situation.
- Incorrect installation. Even if high-quality elements are used, one must not forget about the slope of the pipes. Smooth geometry is not at all an assistant here.
- Excessive steam generation. This is due to the use of low-quality water and constant serious changes in internal and external temperatures.
- Errors during repair, maintenance work, when a lot of air gets inside.
- Careless attitude to filling the system with liquid. Use of fresh water.
- Serious drop in line pressure.
- Partial depressurization.
Air in the heating system. How to remove an airlock without draining the water.
Even in closed individual communications, it is unrealistic to completely avoid airing. It is initially impossible to eliminate all negative factors. But, observing the technology of network maintenance, you can minimize risks, reduce the consequences of emergency situations.
Visible signs of traffic jams
It is necessary to expel air from the heating system when radiators are not able to warm up the room, their elements and pipes remain cold, while the supply of the carrier is correct. But it would be right not to postpone the adoption of measures until obvious manifestations of a failure, but to carry out preventive maintenance of the economy on the eve of each autumn-winter season. This applies to both apartment buildings and individual buildings.
If the failure occurred during the heating period, it is possible to recognize that airing is to blame by the following signs:
- The battery warms up unevenly in parts. Most often, the top of the radiator turns out to be colder, although there are exceptions.
- The supply pipes become warm in some places and cold in others.
- The system starts to make noise, to seethe. This is a clear manifestation of the presence of air bubbles in it, which create obstacles for the passage of the heat carrier. It usually goes on silently.
- Structural elements vibrate, rattle. In this case, the problem is already overripe, measures to eliminate it must be applied immediately.
- When tapped, some elements of the network give a more sonorous response inherent in emptiness.
- Leaks appear in the metal, small holes are formed.
In addition to not providing residential, office, and retail space with heat, airing the network also leads to its rapid deterioration. The so-called dry friction occurs, in which the elements of the system are damaged. This is another argument for the fact that communications must be constantly maintained in good condition.
An airlock is a problem for the heating system
Ways to eliminate air gaps
The mixture of air and water is dangerous for the network. It promotes rusting processes and the formation of limescale. Even a gas boiler can not withstand the impact of an aggressive environment, therefore, the timely removal of air from the heating system of a private house is an important matter.
To get rid of bubbles in communications, you can bleed air. Some features should be taken into account:
- First you need to try to warm up the system well. When that doesn't work, the air will have to be vented.
- Even if Mayevsky cranes or other drain valves are installed on the network, you need to act carefully. The screw should be loosened gradually, be sure to substitute a jar or bucket under the drain.
- Bleeding is accompanied at first by hiss and splashes, then the carrier begins to flow more freely. As soon as this happens, the process must be stopped.
- If the bubble is found far from the valve, you need to open the valve that is closer to the problem area. The layer must be pushed towards the drainer, adding water to the network.
- When several places are problematic, but there are more than one or two cranes, the taps are opened strictly in turn, moving from the network entrance to the room.
- With boiler heating, you first need to release air from the elements closest to the boiler, and leave the farthest and highest in relation to it at last.
- If there are no Mayevsky diverters, there are not even valves, then the radiator caps will have to be unscrewed. This needs to be done even more carefully, because the pressure can simply knock them out. Then, instead of one problem, another will arise - the apartment may be flooded. The reset must be done before the hissing stops. Then the screw must be tightened immediately until it stops.
- If the process is successfully carried out, the pipes will warm up for a maximum of half an hour. When this does not happen, the work must be repeated and not only bleed off the air, but also drain more water.
When it is impossible to remove the plug, or its elimination did not lead to an improvement in the operation of the heating, the system must be cleaned.
How to remove air from the heating system!
Heating network arrangement rules
The best prevention is the proper installation of the network.Removing the plug in the heating system is more difficult than immediately investing in the reliability and safety of communications. If possible, it is necessary to install automatic regulators that will remove most of the problems. This is especially true in a private house.
But even without automation, you can do a lot:
- Correctly mount the pipes, observing the rules of the slope (each meter - 5 ml).
- Install radiators slightly at an angle to the walls.
- Equip each element of the network with a Mayevsky crane or a simpler drainer.
- It is best to put an open expansion tank or air receiver at the top pole of the network. The tank is about 2/3 full.
- Make the coolant inlet with a slight rise, and the return flow - with a decrease.
- The boiler must be equipped with a drain. This will protect the equipment from the occurrence of the dry friction effect, which can quickly disable the device, and also threaten to increase the accident rate.
Removing an air lock from the heating system
The taps are clogged too. Their work is affected by pressure jumps, sudden changes in temperature, water hammer. We must not forget that these devices also need attention and cleaning.
Removing the plug in the heating system
It is important to observe the heating mode itself... To simplify monitoring, the network can be equipped with a thermometer and a pressure gauge. If the system is closed, it is a good idea to provide for automatic water replenishment. Compliance with these and some other rules largely determines the quality of heating and protects against problems with air supply.
Layout of the pipeline in a multi-storey building
As a rule, in multi-storey buildings, a one-pipe wiring diagram with an upper or lower filling is used. The location of the straight and return pipe can vary depending on many factors, even including the region where the building is located. For example, a heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from heating in a three-story building.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created that allows you to bring all the parameters to the maximum. The project may involve various options for filling the coolant: from bottom to top or vice versa. In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which provide alternating movement of the coolant.

Where does the air come from
Here are the main reasons for the formation of an airlock:
- Replacement of heating devices in apartments. It is performed mainly in summer, outside the heating season. After pressure testing, the riser is simply filled with water, and the air release from it is safely left for the fall;


Replacing the convector with a bimetallic radiator.
- Revision of valves on risers. It is associated with the need to completely drain the heating circuit;
- Revision of valves in the elevator unit. Again, the heating circuit is completely reset;
- Water leaks through threaded connections with impaired tightness, intersectional connections of radiators, valve glands, fistulas in pipes, etc. With closed and serviceable valves in the elevator, they lead to a gradual drop in pressure in the circuit. It is necessary to slightly open the washer or Mayevsky tap on one of the upper floors - and the vacuum that has arisen in the upper part of the circuit will suck in the air.


Mayevsky's tap on a heating radiator.
Air Lock Removal Methods
Since one or more of these factors may be present in many homes, the question of removing air in the heating system necessarily arises. This operation can be performed in various ways. It all depends on what kind of coolant circulation we are dealing with - natural or forced.
In a natural circulation heating system (meaning the upper piping), the formed air lock can be removed through the expansion tank - it is at the highest point in relation to the entire system. The flow line should be laid up to the expansion tank. With lower piping, air is removed in the same way as in heating systems equipped with a circulation pump.
You can bleed air from the heating system with natural circulation using an expansion tank
In heating systems with forced circulation of the coolant, an air collector is installed at the highest point, specially designed for air release. In this case, the supply pipeline is laid with an ascent along the course of movement of the coolant, and air bubbles rising up the riser are removed through the air taps (they are installed at the highest points). In all cases, the return line must be laid with a slope in the direction of the water drain for faster emptying if repairs are required.